Table of Contents
Dielectrics: A dielectric can generally be described as a material that conducts electricity very poorly. They are insulators and contain no free electrons. Dielectrics can be polarized easily when an electric field is applied. Dielectrics are non-conductive materials. It is an insulating material and does not conduct current well. Dielectric materials can retain an electrostatic charge while dissipating minimal energy as heat. Examples of dielectrics include mica, plastics, glass, ceramics, and metal oxides. It should be remembered that dry air is also an example of a dielectric.
The information about free Dielectrics from various physics-related articles is available here. Dielectrics and their general concepts are important topics in physics. Students who want to flourish in physics need to know the terms free charges and bound charges to get deep knowledge about it to do well on their exams, which is very useful in real life. The definition of dielectric material, its categories, and dielectric polarization are provided here to assist students in effectively understanding the respective topic. Continue to visit our website for additional physics help.
Overview
An electric charge reacts when it comes into contact with an electrical conductor and does not pass through the material. However, deviating from position and value results in dielectric polarization. Because matter is polarized, positive charges move towards the electric field, and negative charges move away. For example, if the field moves along the x-axis, the negative charge will be directed along the negative x-axis. This, in turn, creates an internal electric field that minimizes the total area inside the dielectric. If there are weakly binding molecules in the dielectric, they will not only polarize but also change direction, aligning the axis of symmetry with respect to the field.
From an atomic point of view, dielectric materials fall into two categories.
Polar molecules
Non-polar molecules
- Permanent electric dipole
- Its polarization is
- Induced electric dipole
- Its independent polarisation temperature-dependent on the temperature
Polar Molecules
Generally, a polar molecule is one in which the ‘centres of gravity of the positive and negative charges do not intersect. These molecules are called permanent electric dipoles as they have permanent dipole moments. The common polar molecules are HCl, H2O, N2O, NH3, H2 S, C2H5OH, and SO2.
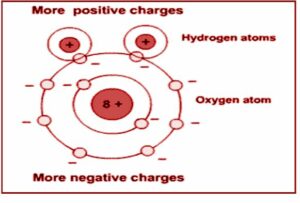
In one molecule of HCl, there is an additional positive charge on the H-ion and an equal negative charge on the Cl–ion. Thus, the molecule has a dipole moment at every instant and is a polar molecule. Some other interesting example of polar molecules is H2O.
Similarly, in the water molecule, two O-H bonds are not placed opposite (unlike the CO2 molecule) but are inclined at an angle of about 105. Here, the hydrogen ion forms a dipole moment with each oxygen ion, and there is a net dipole moment p=p1+p2.
(i) The electric dipole moments of these polar molecules point in random directions and cancel each other in the absence of an electric field. Thus, even though each molecule has a dipole moment, the average moment per unit volume is zero.
(ii) The dipole moments of these molecules align themselves parallel to the direction of the electric field on the application of an electric field. However, this alignment is incomplete due to the thermal vibrations of the molecules. Obviously, the molecules’ alignment with the applied field increases if the electric intensity of the field is increased and the temperature is reduced.
The increased electric intensity might increase the dipole moment. This is because with increased electric intensity, the distance between the centres of gravity of the positive and negative charges increases, which increases in the dipole moment.
Non-polar Molecules
In general, a non-polar molecule is one in which positive and negative charges’ centres of gravity intersect. Such molecules will not have any permanent dipole moment.
The commonly known examples of non-polar molecules are CO2, CCl4, oxygen O2, nitrogen N2, hydrogen H2, methane CH4, and ethane C2H6.
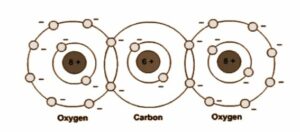
If we consider a molecule of CO2, the oxygen ions are symmetrically placed with respect to the carbon ion hence the dipole moment is zero. When the molecule is placed in an electric field E along the line joining the ions, the oxygen ions get displaced with respect to the carbon ion, and the net dipole moment induced is along the direction of E. When the electric field E is applied perpendicular to the line joining the ions, the induced dipole moment directions are again along with the field E.
Therefore, it is generally said that when a non-polar molecule is placed in an electric field, the centers of positive and negative charges shift, and the molecule becomes polarized. These molecules are then called induced electric dipoles, and their electric dipole moments are called induced electric dipole moments. When the electric field is removed, the induced electric dipole moment disappears. The induced electric dipole moment is proportional to the applied electric field but almost independent of temperature. Also, an induced dipole is parallel to the electric field at its creation. The main difference between polar and non-polar molecules is that for polar molecules, the temperature depends on the dipole moment. For non-polar molecules, there is no such dependence.
Electric Polarization
The molecule acquires a dipole moment when a dielectric plate is placed in an electric field. In these cases, the dielectric is said to be polarized. Electrical polarization is the dipole moment per unit volume of dielectric material. The letter P denotes polarization.
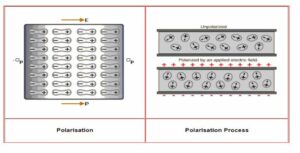
Dielectric Constant
When a dielectric plate is placed between parallel plates, the ratio of the strength of the applied electric field to the strength of the reduced value of the electric field of the capacitor is the dielectric constant.
It is given as k=E0/E.
E should always be less than or equal to E, where E0 is dielectric, and E is the net field. It is known that the larger the dielectric constant, the more charge can be stored. When filling the space between capacitor plates with a dielectric will enhance the capacitance by a factor of the dielectric constant.
Now, C=Co
Here, Co is the capacitance with no dielectric between the plates.
Dielectric properties of an insulation
The dielectric properties of an insulator include dielectric parameters such as breakdown voltage or dielectric strength, permittivity, conductivity, loss angle, and power factor. Other properties include electrical, thermal, mechanical, and chemical parameters.
Dielectric Strength
The dielectric strength is the maximum electric field strength it can inherently withstand without degrading its insulating properties.
Dielectric Polarization
Dielectric polarization occurs when an external electric field is applied to a dielectric material—a charge’s displacement (positive and negative) when an electric field is applied. The main task of dielectric polarization is to correlate macroscopic properties with microscopic properties. Polarization occurs under electric fields or other external factors, such as mechanical stress, as with piezoelectric crystals. A piezoelectric crystal is a solid material that stores an electric charge. Dielectric polarization can also appear spontaneously in pyroelectric crystals, especially ferroelectrics. Ferroelectricity is the property of some materials to exhibit spontaneous electrical polarization and can be reversed by applying an external electric field.
Also read: Important Topic of Chemistry: Strong Electrolyte
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a dielectric substance?
A dielectric material is a material that creates an additional induced electric field when exposed to an external magnetic field.
What is Polarisation density?
The vector field, which describes the density of permanent or induced electric dipole moments in a dielectric material, is called polarisation density. In an external electric field, molecules acquire an electric dipole moment, and dielectrics are said to be polarized. The electric dipole moment induced by a dielectric material per unit volume is called electric polarization.
Question: What are the important uses of dielectric material?
Answer:
- It is a capacitive material that stores electric charge between metal plates.
- Receives microwave signals from a dielectric resonator antenna.
- They are used for insulating coatings of conductors and wires.









