Table of Contents
Radiation is energy. It travels in the form of energy swells or high-speed patches. Radiation can be natural or man-made. There are two types of Non-ionizing radiation, and they are radio swells, cell phones, broilers, infrared radiation. The visible light Ionising radiation includes ultraviolet radiation, radon, x-rays, and gamma shafts. Let us learn what are the sources of radiation exposure.
Background radiation is around us all the time. Most of it forms naturally from minerals. These radioactive minerals are in the ground, soil, water, and indeed our bodies. Background radiation can also come from external space and the sun. Other sources are man-made, similar x-rays, radiation remedies to treat cancer, and electrical power lines.
What are the health goods of radiation exposure?
Radiation has been around us throughout our elaboration. So our bodies are designed to deal with the low situations we are exposed to every day. However, radiation can damage tissue by changing cell structure and dangerous DNA. This can beget serious health problems, including cancer.
Numerous units of radiation of physics-related articles are available here. There are many materials and quantities in physics. Distinct units can be used to express different quantities in physics. Students who want to flourish in physics can get complete knowledge of radiation and can learn about different types of radiation present and get complete knowledge from this article. The comprehensive unit of radiation is provided here to assist students in effectively comprehending the respective topic. Continue to visit our website for additional physics help.
Overview
Awareness radiation is present on Earth at all times. The majority of background radiation occurs naturally from minerals, and a small bit comes from man-made rudiments. Naturally, radioactive minerals in the ground, soil, and water produce background radiation. The mortal body indeed contains some of these naturally – being radioactive minerals. Cosmic radiation from space also participates in the background radiation around us. There can be large dissonances in natural background radiation situations from place to place, as well as changes in the same position over time.
Cosmic radiation comes from extremely energetic patches from the sun and stars that enter Earth’s atmosphere. Some patches make it to the ground, while others interact with the atmosphere to produce different types of radiation. Radiation situations increase as you get near to the source, so the quantum of cosmic radiation generally increases with elevation. The higher the altitude, the more advanced the cure.
Radiation
Radiation is energy that arrives from a source and travels through space at the speed of light. This energy has an electric field and a glamorous field associated with it and has surge-like parcels. You could also name radiation “ electromagnetic swells”.
Types of radiation
There are four major types of radiation – nascence, beta, neutrons, and electromagnetic swells similar to gamma shafts. They differ in mass, energy, and how deeply they access people and objects.
- The first is a nascence flyspeck. These patches correspond to two protons and two neutrons and are the heaviest type of radiation flyspeck. Numerous of the natural being radioactive accoutrements in the earth, like uranium and thorium, emit nascence patches. An utmost illustration people are familiar with is the radon in our homes.
- The alternate kind of radiation is a beta flyspeck. It’s an electron that isn’t attached to a snippet. It has a minor mass and a negative charge. Tritium, which is produced by cosmic radiation in the atmosphere and exists each around us, emits beta radiation. Carbon-14, used in carbon- courting of funds and other vestiges, also emits beta patches. Carbon-dating barely makes use of the fact that carbon-14 is radioactive. However, it tells you how important carbon-14 is left in the reactionary, which allows you to calculate how long ago the organism was alive If you measure the beta patches.
- The third is a neutron. This is a flyspeck that does not have any charge and is present in the nexus of a snippet. Neutrons are generally seen when uranium titles resolve or fission, in a nuclear reactor. However, you wouldn’t be suitable to sustain the nuclear response used to induce power, If it was not for the neutrons.
- The last kind of radiation is electromagnetic radiation, like X-rays and gamma shafts. They’re presumably the most familiar type of radiation because they’re used extensively in medical treatments. These shafts are like the sun, except they’ve further energy. Unlike the other kinds of radiation, there’s no mass or charge. The quantum of energy can range from veritably low, like in dental X-rays, to the veritably high situations seen in irradiators used to emasculate medical outfits.
X-ray Radiation
X-rays are significant imaging used around the globe. Since first being used to image bones over 100 times agone, the-ray has saved numerous lives and helped in a range of important discoveries.
X-rays are a naturally occurring form of electromagnetic radiation. They’re produced when charged patches of sufficient energy hit a material. To develop a radiograph, a case is deposited so that the part of the body being imaged is located between an x-ray source and an x-ray sensor. When the machine is activated, x-rays travel through the body and are consumed in different quantities by different tissues, depending on the radiological viscosity of the napkins they pass through. Radiological viscosity is determined by both the viscosity and the infinitesimal number (the number of protons in a snippet’s nexus) of the accoutrements being imaged.
When are medical x-rays used?
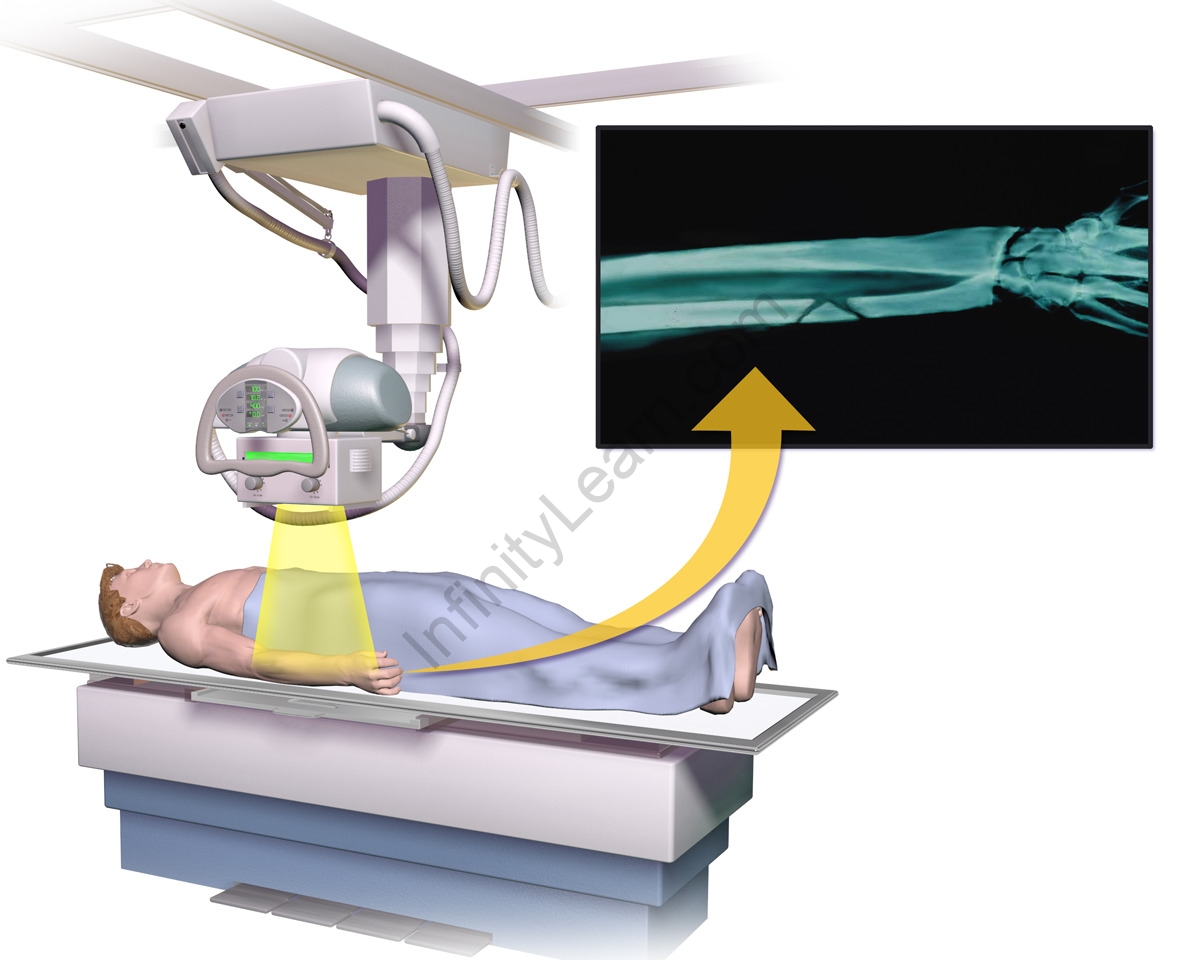
- X-ray radiography detects bone fractures, certain excrescences, pneumonia, some types of injuries, calcifications, foreign objects, dental problems, etc.
- Mammography A radiograph of the bone that’s used for cancer discovery and opinion. Excretions tend to appear as regular or irregular-structured millions that are kindly brighter than the background on the radiograph ( i.e., whiter on a black background or murk on a white background). Mammograms can also describe bitsy bits of calcium, called microcalcifications, which show up as veritably bright specks on a mammogram. While generally benign, microcalcifications may sometimes indicate the presence of a specific type of cancer.
- CT (reckoned tomography) combines traditional x-ray technology with computer processing to induce a series of cross-sectional images of the body that can later be combined to form a three-dimensional x-ray image. CT images are more detailed than plain radiographs and give croakers the capability to view structures within the body from numerous different angles.
- Fluoroscopy uses X-rays and a fluorescent screen to gain real-time images of movement within the body or to view individual processes, similar to following the path of a fitted or swallowed discrepancy agent. For illustration, fluoroscopy is used to view the movement of the beating heart and, with the aid of radiographic discrepancy agents, to view blood inflow to the heart muscle as well as through blood vessels and organs. This technology is also used with a radiographic discrepancy agent to guide an internally threaded catheter during cardiac angioplasty, which is a minimally invasive procedure for opening congested highways that supply blood to the heart.
- Radiation remedies in cancer treatments-rays and other types of high-energy radiation can be used to destroy cancerous excrescences and cells by damaging their DNA. The radiation cure used for treating cancer is much more advanced than the radiation cure used for individual imaging. Remedial radiation can come from a machine outside of the body or from a radioactive material that’s placed in the body, inside or near excellency cells, or fitted into the blood sluice.
Value of chapter for JEE Main, NEET, and Board Exams
Radiobiology (also known as radiation biology and uncommonly as actinobiology) is a field of clinical and introductory medical studies that involve the study of the action of ionizing radiation on living effects, especially health goods of radiation. Ionizing radiation is generally dangerous and potentially murderous to living effects but can have health benefits in radiation remedies for the treatment of cancer and thyrotoxicosis. Its most common impact is the induction of cancer with an idle period or decades after the exposure. High boluses can beget visually dramatic radiation becks and/or rapid-fire casualty through acute radiation patterns. Controlled boluses are used for medical imaging and radiotherapy.
Also read: De Broglie’s Relationship
FAQs
What is radiation?
Radiation is energy that arrives from a source and travels through space at the speed of light.
Who discovered x-ray?
X-ray was discovered by W.C Roentgen.
What is an X-ray?
X-rays are a naturally occurring form of electromagnetic radiation. They're produced when charged patches of sufficient energy hit a material.
How many types of radiation are there?
There are four major types of radiation nascence, beta, neutrons, and electromagnetic swells similar to gamma shafts.









