Table of Contents
Atmospheric pollutants are compounds that build up in the air to the point that they affect living beings or objects exposed to the air. Smoke, smog, and gases such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen and sulfur oxides, and hydrocarbon fumes are all common air pollutants. Solid or liquid impurities in smoke and haze are plainly observable, whereas gaseous contaminants are often invisible. When sulfur and nitrogen oxides interact with atmospheric moisture to form sulfuric and nitric acid, it is a particularly harmful form of air pollution. Acid rain causes harm to lakes, rivers, flora, buildings, and other items when the acids are delivered to Earth in the form of rain.
A brief outline
Control of air pollution has become a top concern in many countries due to the considerable harm it causes. Several methods have been shown to be effective. A system of air alarms, which are sent when air pollution monitors reveal dangerously high levels of contamination, is one urgent management tool. Pollution-producing industries are being obliged to scale back their operations until conditions improve. Atmospheric inversions, which prevent the upward mixing of contaminants, are frequently the source of these emergency situations.
Pollutants can be dispersed more widely via taller smokestacks, reducing local pollution. Dispersion, on the other hand, does not reduce overall levels; rather, it might cause issues for populations downstream of the source. Vehicles, houses, electric power plants, and industrial plants with higher energy efficiency emit fewer pollutants. This reduction in fuel use minimizes pollution caused by the production of fuels, and it also saves money because more energy-efficient operations are more cost-effective. By reducing the need for personal vehicles, efficient and convenient mass transit also helps to reduce urban air pollution.
Important concepts
Causes of Atmospheric pollution
Air pollution can be caused by a variety of natural or artificial sources (man-made). Some leave visible residues in the air, while others can go undiscovered unless specific tests are performed – or until you become ill as a result of their impacts.
Natural Factors
- Volcanic eruptions release a variety of hazardous gases (such as sulfur and chlorine) as well as particulate debris (ash particles), however, they are usually limited to a small area.
- Winds and air currents – have the ability to mobilize pollutants from the ground and carry them over huge distances.
- Wildfires – release carbon monoxide and particulate matter into the atmosphere (which can contain organic contaminants like PAHs); they can damage large areas, although they are usually limited and can be contained.
- Microbial decaying processes – microorganisms found in all environments play an important role in the natural decaying of living creatures and environmental toxins, resulting in the natural release of gases, particularly methane gas.
- Radioactive decay activities — for example, natural decay processes of the Earth’s crust release radon gas, which has the potential to collect in enclosed locations such as basements;
- Increasing temperatures cause a rise in the number of toxins that are released into the air from dirty soil and water.
Anthropogenic (Man-made) factors
- Mining and smelting – release a variety of metals trapped on particulate matter dispersed in the air as a result of the crushing and processing of mineral deposits;
- Mine tailings – due to their small particle nature (coming from the crushing and processing of mineral ores), mine tailings are a source of metals in the ambient air that can be transported by the wind over broad distances;
- Foundry activities – release a variety of metals into the air, which is absorbed by particulate matter dispersed in the air as a result of the processing of metallic raw materials (such as the use of furnaces);
- Accidental spills and leaks of stored chemicals, as well as the handling and storage of chemicals – particularly volatile inorganic chemicals –, can all emit both organic and inorganic pollutants.
International and national laws and regulations have indeed been implemented to limit the effects of air pollution. Local rules, when properly executed, have resulted in significant advances in public health. Some of these efforts have been successful at the international level, such as the Montreal Protocol, which reduced the release of harmful ozone-depleting chemicals, and the 1985 Helsinki Protocol, which reduced sulfur emissions, while others, such as international action on climate change, have been less successful.
Atmospheric Ozone
Ozone in the atmosphere we breathe can be harmful to our health, particularly on hot, bright days when ozone levels can reach dangerously high levels. Even modest levels of ozone can be harmful to one’s health. Anyone with asthma, youngsters, older persons, and people who are active outside, particularly outdoor laborers, are all at risk from breathing ozone-containing air. People with particular hereditary features, as well as those who consume less of certain nutrients, such as vitamins C and E, are more vulnerable to ozone exposure.
A layer of ozone on the Earth’s surface acts as a “sunscreen” for the world, sheltering it from damaging UV rays. This solar energy absorption also alters air circulation patterns, which influences weather all around the world. Furthermore, ozone is the fundamental ingredient that initiates the chemical cleaning of the atmosphere of numerous pollutants, including as carbon monoxide and methane, which could otherwise accumulate to dangerous levels or have a bigger impact on climate. As a result, ozone changes anywhere in the atmosphere can have a significant impact on the Earth.
Dust particles in the atmosphere
Fine solid matter particles make up dust. It is made composed of particles in the atmosphere that arise from a variety of sources, including wind-lifted soil (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollutants. In most homes, 20–50 percent of the dust is made up of dead skin cells. Small amounts of plant pollen, human hairs, animal fur, textile fibers, paper fibers, minerals from outdoor soil, charred meteorite particles, and other elements found in the local environment make up the rest, as well as in offices and other human locations.
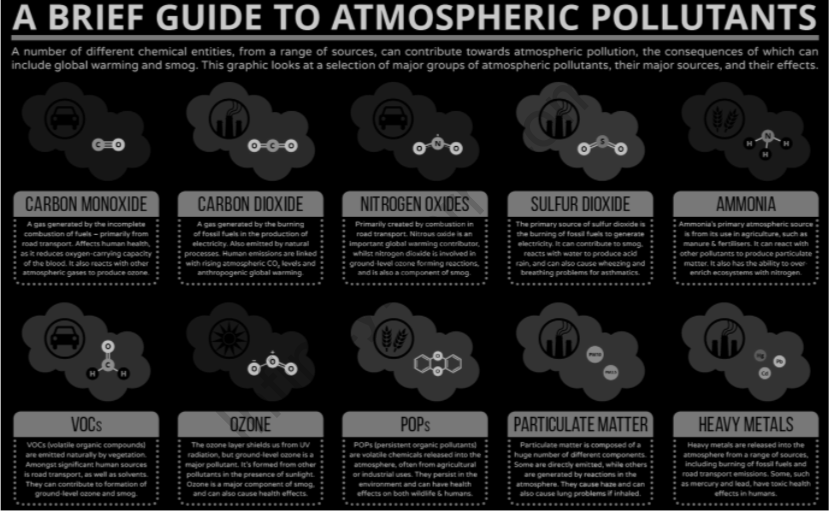
Significance of major atmospheric pollutants
Understudies should have a solid comprehension of the entire subject to pass the NEET test. While each segment is important, and you should never ignore any part of your schedule, there is one unremarkable pack that you should pay special attention to. Because passing the NEET test is such a significant achievement in a student’s life, selecting the greatest survey material is critical. The main goal of Infinity Learning is to install trust in our students. As a result, we organized the science responses to address each question that a student would ask. Because our responses are in pdf format, students can access them at any time and from any location.
Also read: NEET Exam Pattern 2022
Frequently Asked Questions
The negative consequences are that air pollution can cause heart attacks, asthma, coughing, and breathing problems, as well as irritation in the eyes, nose, and throat. Air pollution can aggravate existing heart problems, asthma, and other lung ailments.
When fossil fuels are burned, gases and chemicals are released into the atmosphere. Air pollution not only contributes to but also exacerbates the climate crisis in a particularly harmful feedback loop. Global warming is caused by pollutants in the air, such as carbon dioxide and methane. These are the main causes and their effects on the atmosphere.
Acid rain, which is precipitation with harmful amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids, is one of the severe impacts of air pollution on the environment. Acid rain has caused havoc on Massachusetts' lakes, ponds, rivers, and soils, as well as causing havoc on wildlife and woods. What are the negative consequences of pollution?
What are the causes and effects of pollution in the atmosphere?
What impact does pollution have on our environment?








