Table of Contents
Everything in our surroundings is composed of fundamental particles known as elements. Only 31 chemical elements were found in the beginning, in 1800. Following technological improvements in 1865, around 63 additional elements were found. This necessitated periodic elemental classification. Presently, there are 118 elements now that we are aware of. As there were only 31 elements, it was quite straightforward to analyze the properties of these chemical elements individually.
With 118 elements currently in existence, examining the properties of each element individually would take an inordinate amount of time. Scientists began to consider ways to simplify the study of elements to make their jobs easier. Based on the information available about the elements and the many properties they display, they chose to arrange them in a periodic table. Periodicity has been noticed in the characteristics of elements. Many tables were built to organize the elements in an ordered manner depending on their features to investigate the attributes of elements in a defined pattern.
The information about modern periodic law from various physics-related articles is available here. Modern periodic law and the modern periodic table are important topics in physics. Students who want to flourish in chemistry need to be well known about periodic tables to gain deep knowledge about doing well on their exams. The definition, brief explanations, and features are provided here to assist students in effectively understanding the respective topic. Continue to visit our website for additional physics help.
Overview
The grouping of elements provides us with a stable pattern in which the attributes of the elements are very regular. The periodic table sped up and organized the study of elements’ physical and chemical properties. We can now easily go to the group and view the periodic table elements’ properties or forecast the properties of an element if we know the properties of other elements in the same group.
Even though so many elements have been discovered, there is still a possibility that additional elements will be discovered. Scientists can use a periodic table to learn about the trending features of elements and so differentiate new elements from existing ones. Furthermore, scientists are always working to discover new elements and study their properties.
Modern Periodic Law Definition
We can state the modern periodic law as: “The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.”
Modern Periodic Law or Law of Modern Periodic Table
Mendeleev’s periodic law and the periodic table are the foundations of the contemporary periodic table. Mendeleev devised his periodic table during the late 18th century. The scientists were not aware of the interior structure of the atom at the time. The development of many atomic models and the growth of quantum theory revealed that the atomic number is the most fundamental attribute of a chemical element. As a result, Mendeleev’s periodic law, now known as modern periodic law, was modified.
According to this law, an elements’ physical and chemical properties are periodic functions of its atomic numbers.
The atomic number in this context refers to the number of electrons or protons in a neutral atom. Once knowing about the fundamental unit of elements, scientists now had a firm grasp on quantum numbers and the electronic configuration of elements in the periodic table. Once chemists learned about the periodic law, chemists noticed an analogy between the 94 naturally occurring chemical elements. People became interested in the chemistry of these elements due to this similarity. Scientists invented a wide range of artificial components. Finally, one new periodic chart based on modern periodic law was constructed by altering Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Modern Periodic Table
The present form of the periodic table frequently used worldwide is the long form. In this type of periodic table, the horizontal rows are known as periods, while the vertical columns are known as groups. Elements in a group contain atoms with comparable outer shell electronic structures.
The groups are labeled with numbers such as 1, 2, 3, and so on. Periods are the modern periodic table’s seven horizontal rows. The quantum number n determines the element’s period. The principal quantum number (n) is one of the four quantum numbers (n, l, m, and s). It provides information on the fundamental electron shell.
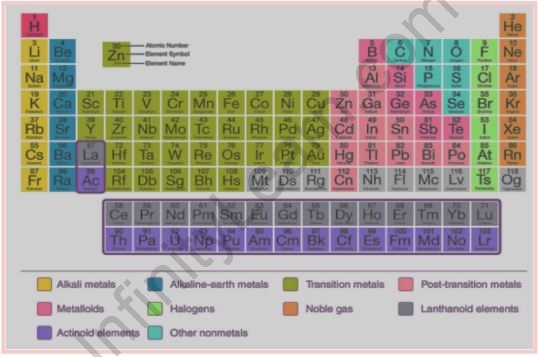
It would have been difficult to study all of the required elements now without the contemporary periodic table. The properties of these elements can be deduced from their classification. As a result, the table is quite useful to us today.
The elements are categorized into:
- Noble gas elements are elements from the modern periodic table’s group 18. These elements are particularly stable since their octet is full.
- Representative elements: These elements include S-block and P-block elements. Groups 1 and 2 elements are referred to as s – block elements. Groups 13-17 are the p-block elements.
- Transition elements: These elements are elements from groups 3 through 12. This type of element is also known as a d-block element.
- Inner transition elements are found near the bottom of the periodic table in the lanthanides and actinides series. Because some orbitals in these elements are partially filled, they have distinct properties.
Modern Periodic Table – Features and Significance:
- The contents of the table are organized in increasing atomic number order.
- The table has seven horizontal rows, referred to as the rows. Similarly, 18 vertical columns are referred to as groups.
- Physical and chemical properties are similar for all of the elements in the table. They have the same number in the outer electrons but gradually alter from the top to the bottom of the group of elements.
- When we proceed from left to right, the items in the period gradually alter. The atomic size decreases from left to right as well.
- This periodic chart has more elements than the preceding version, such as Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Also read: NEET Exam Pattern 2022
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: How do periodic trends relate to periodic law?
Answer 1: Periodic trends are normal patterns in the periodic table that show us different features of an element, such as electronegativity, atomic radius, and ionizing power. The periodic law states that certain properties of elements occur regularly when they are grouped by atomic number.
Question 2: How were the positions of cobalt and nickel resolved in the modern periodic table?
Answer 2: Mendeleev’s Periodic Table was founded on the principle that element characteristics are a periodic function of their atomic masses. As a result, cobalt with an atomic mass of 58.93 should come after nickel with 58.71. But due to similar properties, it has to be put before nickel in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. The classification of elements in the modern Periodic Table is based on the law that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. As a result, the problem was overcome because cobalt had a lower atomic number (27) than nickel (28). As a result, nickel (atomic number 28) comes after cobalt (atomic number 27).
Question 3: Why are elements arranged in the form of a periodic table?
Answer 3: It aids in the study of elements in an organized manner and aids in the correlation of elemental properties. It will be easy to determine the relationship among the elements.









