Table of Contents
Properties Of Ammonia and Nitric Acid
Ammonia is one of the most widely produced compounds. It is one of the most prevalent hydrides in the environment. Small amounts of ammonia are found in soil and air owing to the decomposition of nitrogenous organic materials. The primary application of nitric acid is in the production of fertilizers. It is utilized in the production of a variety of polymers, including polyamides and polyurethane.
| S.NO | CONTENT |
| 1 | INTRODUCTION |
| 2 | AMMONIA |
| 3 | STRUCTURE OF AMMONIA |
| 4 | PREPARATION OF AMMONIA |
| 5 | PROPERTIES OF AMMONIA |
| 6 | NITRIC ACID |
| 7 | STRUCTURE OF NITRIC ACID |
Ammonia
Ammonia is one of the most widely produced compounds. It is one of the most prevalent hydrides in the environment. The ammonia in the atmosphere is mostly created by the breakdown of bacteria, which is released from the nitrogenous components of animals and plants. Azane is the IUPAC term for ammonia. Ammonia’s chemical formula is NH3. Ammonia has a variety of properties.
Structure of Ammonia:
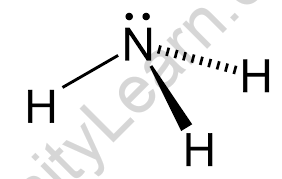
Ammonia is an atom with a covalent bond. It is seen as a dot structure. The particle is formed by the overlap of three hydrogen atom orbitals and three nitrogen sp3 hybrid orbitals in the structure as the center atom. A single pair is engaged in the fourth sp3 hybrid orbital.
This gives the compound a trigonal pyramidal form. The H-N-H bond edge is 107.3°, which is somewhat less than the 109°28 tetrahedral edge. This is due to the bond pair-lone pair repulsions pushing the N-H bonds inwards. Ammonia is linked in solid and liquid phases by hydrogen bonds.
Preparation of Ammonia:
- Small amounts of ammonia are found in soil and air owing to the decomposition of nitrogenous organic materials.
- Ammonium salts are prepared for small-scale manufacture and react with caustic soda to produce ammonia:
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → 2NH3 + 2H2O + CaCl2
- Haber’s technique is employed on a huge scale. The steps in Haber’s procedure are as follows:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ↔ 2NH3 (g)
The basic ingredients for the reaction are nitrogen and hydrogen. Scrubbing is a procedure that removes contaminants from gases. Following the cleaning procedure, the gases are amalgamated and pushed via a compressor. After that, the mixture is crushed at a pressure of 200 atm. The compressed gases are then transferred via a converter, where they are heated to 450°C and compressed to 200 atm. Nitrogen interacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia, however, only about 15% of the gas is produced. The ammonia, hydrogen, and nitrogen mixture is extracted from the converter. It is cooled to the point that it liquefies in the tank and is thus collected.
Properties of Ammonia:
The Properties Of Ammonia are mentioned as follows-
- Azane is a gas that is colourless in nature and has a strong odour.
- It has a boiling point between 198.4K and 239.7K.
- This gas dissolves easily in water. Because OH- ions are produced, the aqueous solution of NH3 is a weak base.
NH3+H20 → NH4++OH–
- When ammonia combines with an acid, it produces ammonium salts.
ZnSO4+2NH4OH (g) → Zn(OH)2+(NH4)2SO4
Uses of ammonia:
- In its aqueous state, it is used as a refrigerant.
- It is used in the manufacturing of Urea. Urea is an excellent fertilizer of nitrogen.
Nitric acid
Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald invented a method for producing nitric acid from ammonia at the turn of the twentieth century. Because of the creation of nitric acid, the Germans were able to create explosives without having to import them from other nations such as Chile during World War II. HNO3 is the chemical formula for nitric acid.
Structure of Nitric Acid:
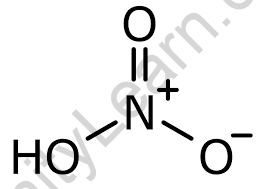
Three oxygen atoms, one nitrogen atom, and one hydrogen atom make up a nitric acid molecule. In HNO3 molecules, one of the oxygen atoms is doubly connected to the central nitrogen atom. Another oxygen atom is coupled to the central nitrogen atom as well as a hydrogen atom in a single bond. The final oxygen atom in the nitric acid molecule has a charge of -1 and is connected to the central nitrogen atom singly. The nitrogen atom in the molecule’s centre has a charge of +1 because it is engaged in four covalent bonds (with three oxygen atoms).
As a result, the nitric acid molecule has no net charge. It should be emphasised that as a result of resonance, the charges in these molecules may become delocalized.
Preparation of Nitric Acid:
- On a modest scale, this gas is produced by heating concentrated sulphuric acid with NaNO3 or KNO3.
NaNO3+H2SO4 → NaHSO4+HNO3
- The Ostwald technique is used for large-scale preparations.
- At 500 K at a pressure of 9 bars, NH3 is catalytically oxidized by oxygen present in the environment in the presence of Pt/Rh as a catalyst. 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO(g) + 6H2O
- The generated nitric oxide is then induced to combine with oxygen to create NO2.
2NO+O2 → 2NO2(g)
- HNO3 is generated when NO2 is dissolved in H2O.
3NO2 (g)+H2O (l) →2HNO3(aq)+NO (g)
Properties of Nitric Acid:
- In nature, it is colourless.
- The boiling point of the liquid is 84.1°C, and it freezes to form a white solid at -41.55°C.
- It is a powerful acid that dissociates into nitrate ions and hydronium.
HNO3 (aq) + H2O (l)→ H3O+(aq)+NO–3 (aq)
- In its concentrated form, HNO3 is a powerful oxidant.
Cu+4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2+ 2NO2+2H2O
Uses of Nitric Acid:
- The primary application of nitric acid is in the production of fertilizers.
- It is utilized in the production of a variety of polymers, including polyamides and polyurethane.
- Nitric acid is also commonly used to purify precious metals such as platinum, gold, and silver.
- In the woodworking industry, diluted nitric acid is used to age maple and pine wood.
FAQ’s
Is ammonia combustible or explosive?
Although ammonia is not very flammable, ammonia canisters may explode when exposed to intense heat.
What effects does ammonia have on the human body?
When excessive amounts of ammonia are introduced to the human body, they induce rapid burning of the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, as well as blindness, lung damage, and death. Inhaling a greater dosage of 300 ppm is instantly hazardous to one’s life and health. Lower quantities might induce coughing and nose and throat discomfort if inhaled.
Is nitric acid harmful?
Nitric acid exposure can induce eye, skin, and mucous membrane irritation, as well as delayed pulmonary edema, pneumonitis, bronchitis, and tooth erosion. Nitric acid is a very corrosive substance.
Is nitric acid capable of dissolving plastic?
The majority of polymers are resistant to dilute nitric acid.
For more visit Oxoacids of Phosphorus – Explanation, Example and Uses









