Table of Contents
Introduction
DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a group of molecules that are responsible for passing on genetic instructions or genes from the parents to the offspring. DNA is a natural compound with a unique cell structure and is found in all eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
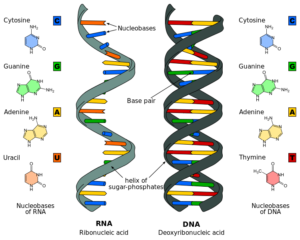
DNA is the nucleic acid in cells that serve as the primary building block of a protein. It contains phosphate, a unique sequence of nitrogenous foundations guanine (G), thymine (T), adenine (A), cytosine (C), and sugar deoxyribose.
RNA refers to ribonucleic acid, which helps to synthesize proteins in the human body. Nucleic acid is responsible for producing new cells in our bodies. It is usually found in the DNA molecule. RNA is similar to DNA, the only difference being that RNA has one fiber while DNA has two strands. RNA forms one molecule of ribose sugar in it. Therefore, it is called ribonucleic acid.
DNA and RNA structure:
DNA structure:
Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as DNA, is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions for the development and function of living organisms. It is made up of two strands of nucleotides twisted into a double helix, with each strand containing alternating sugars and phosphate groups. The nucleotides are made up of four different bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). These bases pair up to form base pairs, with A always pairing with T and G always pairing with C. This base pairing is what allows for the two strands of the double helix to bind to each other.
The structure of DNA is essential for its function. The double helix structure allows for the strands to be replicated and the information to be passed on to the next generation. The base pairing also allows for the genetic information to be accurately copied and transferred. DNA is also responsible for determining the characteristics of organisms, as it contains the instructions for the synthesis of proteins and other essential molecules.
The structure of DNA is essential for the stability of the genetic material. The two strands of the double helix provide mechanical stability, and the base pairing keeps the strands in place. This structure also allows for the strands to be replicated accurately. Replication is essential for the passing of genetic information to the next generation.
RNA structure:
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a type of nucleic acid molecule that plays a vital role in the process of protein synthesis. It is composed of a single strand of nucleotides made up of nitrogenous bases, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group. Unlike DNA, RNA does not have a double-stranded helix structure. Instead, its structure is more complex and varies depending on the type of RNA and the process for which it is used.
- There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All three types play an important role in the process of protein synthesis, but each has its own unique structure.
- mRNA is composed of a single strand of nucleotides and is responsible for carrying the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. It is composed of codons, which are nucleotide sequences that code for specific amino acids. The structure of mRNA is relatively simple and consists of a linear sequence of codons.
- tRNA is also composed of a single strand of nucleotides and is responsible for translating the genetic code into proteins. It is composed of anticodons, which are nucleotide sequences that match up with the codons of mRNA. The structure of tRNA is more complex and consists of a loop structure that contains the anticodon sequence at one end and an amino acid at the other.
- rRNA is composed of a single strand of nucleotides and is responsible for forming the ribosomal complex. It is composed of both codons and anticodons and its structure is the most complex among the three types of RNA. It consists of base pairs, loops, and bulges that form the ribosomal complex.
Separation of DNA and RNA
Structural DNA classification is as follows:
- A-DNA: A-DNA, also referred to as A-form DNA, is a double helix right helix form with a mean propeller twist of + 18 °. It has a rotation of 32.7 ° for each base (bp), and 11 means bp per turn. It has a + 19 ° bp inclination on-axis. Its diameter is 23 Ȧ. It has a 28.2 Ȧ pitch per turn of the helix.
- B-DNA: B-DNA, also referred to as B of DNA form, is a right-handed helix structure with a mean propeller twist of + 16 °. It has a rotation of 34.3 ° each (bp) and ten which means bp per turn. It has a – 1.2 ° inclination of bp on the axis. Its diameter is 20 Ȧ. It has a 33.2 Ȧ pitch per turn of the helix.
- Z-DNA: Z-DNA or Z-form DNA is a left-handed form of the helix with a proportional proportion of 0 °. It has a rotation of 30 ° each (bp), and 12 means bp per turn. Has – 9 ° bp inclination on-axis. Its diameter is 18 Ȧ. Its double helix spirals left with a zig-zag pattern. It has a pitch of 45.6 Ȧ for each helix turn.
There are several types of RNA, which are commonly studied in the human body are:
- Messenger RNA [mRNA]: Messenger RNA contains a genetic blueprint for protein synthesis. Its main function is to transfer genes to the ribosomes and provide instructions on the type of protein that the cells need. mRNA plays an important role in the writing process or during protein synthesis.
- RNA Transmission [tRNA]: TRNA translates mRNA into proteins and is responsible for carrying the amino acids the body needs. It is found at the end of each amino acid and has the structure of a cloverleaf.
- Ribosomal RNA [rRNA]: Ribosomal RNA forms ribosomes and plays a key role in binding proteins. They are found in all living organisms and are active in modifying the instructions found in mRNA.
Also read: Important Topic of Biology: Central Dogma
FAQs
Question 1: Where is DNA found?
Answer 1: DNA is mainly found in the cell nucleus and is also called nuclear DNA, but a small portion of it is also found in the mitochondria and is known as mitochondrial DNA. They are sources of energy in the human body that convert the food we eat into the way cells can use to produce energy.
Question 2: What is the most important function of DNA?
Answer 2: The most important function of DNA is to transfer genetic data from the parent to the coded offspring in the way nitrogen bases are made up of nucleotides.
Question 3: Why is the structure of RNA important?
Answer 3: The structure of 3-D RNA is important because of its function and stability, which makes ribose sugars and nitrogen bases regenerated differently by cellular enzymes that bind chemical groups (e.g., methyl groups) in a series.





