Table of Contents
Introduction
Carbs are macronutrients and one of the three fundamental wellsprings of energy for our bodies. Carbs are named for the substance components carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that they contain. Carbs, which contain sugars, filaments, and starches, are essential supplements. They can be found in oats, vegetables, natural products, and dairy items like milk and cheddar. They are the fundamental dietary sorts that are fundamental for carrying on with a solid way of life.
Proteins are huge, muddled particles comprised of at least one wound and collapsed amino corrosive strands. Proteins are very convoluted particles that assume a vital part in the most principal and fundamental pieces of life. Digestion, versatility, protection, cell correspondence, and atomic acknowledgement are among them.
A brief outline
The phrases “fats” and “cholesterol” are frequently used by the general public and health enthusiasts. There’s a good explanation behind this. Fat is the most main source of energy in the diet, with approximately 8 to 9 calories per gram compared to only four calories per gram for carbohydrates and proteins. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are the three elements that makeup fat. However, it has more carbon and hydrogen than oxygen, resulting in nine calories per gram. Fats, which are a collection of components known as lipids, are a mixture of saturated or unsaturated fats that provide energy to meals.
Important concepts
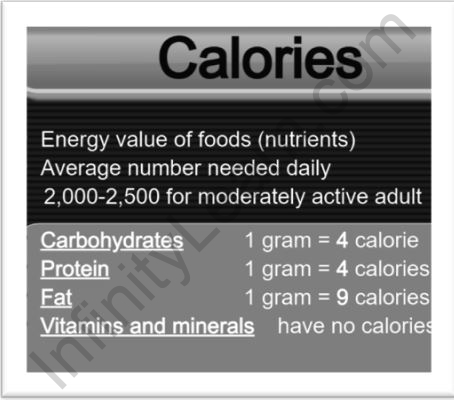
The caloric value of fat, protein, and carbohydrate
Calorific value is the amount of energy in food or fuel that is measured by measuring the heat produced by full combustion with a given amount of oxygen. It’s expressed as kcal/g. It’s also known as the energy value of food and fuel, which indicates how much energy is gained by the human body’s metabolism.
Carbohydrates
Sugar, fibre, and starch are all naturally occurring sugars, fibres, and starches in the diet. When glucose is digested, it transforms to pyruvate in glycolysis and, in the absence of oxygen, to lactate. Vegetables, pasta, rice, grain, and each gram of carbs, for example, contain 4 kacl/g.
Protein
Protein is a macromolecule that is made up of amino acids, which are the fundamental building blocks of life. Proteins are essential macromolecules whose absence in the body can cause a variety of problems. Egg, pork, and poultry products are all good sources of protein. Proteins have the same calorific value as carbs.
Fats
Fats are the slowest and most recently digested kind of energy. Some foods, such as sausages and potatoes, have more calories and fewer vitamins and minerals than the above two fats, hence they have a greater calorific value.
- To determine the calorific value of any macromolecule, use the following formula:
- The heat kilogram formula will be utilized.
- The heat estimated using the formula above will be evaluated in kilojoules per kilogram, which is the same as total combustion in kilograms.
How much hotness energy is present in food or fuel is determined by full burning of a characterized amount at consistent strain and under ordinary circumstances. Calorific power is one more name for it. The kilojoule per kilogram, or KJ/Kg, is the unit of calorific worth. Starches have four calories for each gram, protein contains four calories for every gram, and fat contains nine calories for every gram. On food bundles, this data can be found at the lower part of the Nutrition Facts Panel. Carbs and proteins have over two times as numerous calories per gram as fat. A gram of fat has around 9 calories, though a gram of starch or protein contains roughly 4 calories. At the end of the day, for a similar number of calories, you could eat two times as many carbs or proteins as fat.
Significance of caloric value of carbohydrates in NEET exam
Due to population expansion, there is a greater need to improve food production techniques. The importance of this topic varies depending on the topic. There are both short and long questions. They don’t, however, get you a lot of points. The majority of the questions are taken directly from the NCERT textbook. It can, however, be beneficial. As a result, thorough planning is recommended.
FAQ’s
Carbohydrates give the body energy. It decomposes into glucose and enters our circulation. Glucose is used by body cells to make ATP.
The sugar molecules in complex carbohydrates are connected together in long, complicated chains. Carbohydrates can be found in a variety of foods such as peas, beans, vegetables, and grains.
Proteins are big, complex molecules that play a number of significant tasks in the human body. They conduct the majority of the work in cells and are vital for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs. These proteins provide shape and support to cells. On a broader scale, they also cause the body to move.
In basic terms, fats are the most important component of the diet because they aid in the maintenance of a healthy lifestyle.
Apart from the three essential fatty acids Linoleic, Linolenic, and Arachidonic acids, our bodies are capable of producing a wide range of fatty acids. These important fatty acids must be obtained through dietary sources. What role do carbs play in our bodies?
What distinguishes complex carbs from simple carbohydrates?
What is protein and what does it do?
What Exactly Are Fats?
What are necessary fatty acids, and what do they do?









