Table of Contents
Nowadays science has improved a lot. We even started learning about ourselves and also living organisms around us starting from the cell.
Cells are the basic unit of living organisms from which different types of organs start forming. So, in that tiny cell, we have different organelles which play a vital role in the functioning of our body and other living organisms too.
Today we are studying about the vacuole which is a part of the living cell.
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that is present in animals, plants, fungi, bacterial, and Protista. Vacuoles are water-containing compartments sometimes solid will also be present in vacuoles.
Vacuoles in plants are important as they take part in their plant growth and development and they also perform many functions in plants.
A vacuole is an empty cytoplasm that has a membrane mostly filled with fluids.
In the fluids, it has organic, inorganic components and some enzymes to solution-phase but some also have solid particles in them.
The shape, size, and structure of vacuoles vary which depends on the function and living organism.
Overview:
A vacuole is a plant organelle that is a membrane-bound organelle that is filled with water with inorganic, organics, and some enzymes in them but in some living organelles vacuole also has solid materials.
They are present in animals, plants, fungi cells, bacteria, and also present in protists.
Durjadin named the term vacuoles in 1842. Scheildien used this term for the first in plant cell and DeVaries in 1885 named tonoplast which is known as the membrane of the vacuole.
A vacuole is having protein, sugar, ions, and other secondary metabolites which play crucial roles in plant response for its biotic and abiotic stimulus.
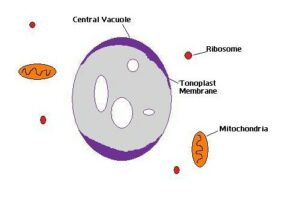
Plant vacuole:
Plant vacuoles are large in size; they cover most of the cell about 90% in total cell size. Water enters into the vacuole by creating turgor pressure which results in cell enlargement.
By following the osmotic principle where water moves from high pressure to low pressure now due to high turgor pressure the water again goes out of the cell making vacuole volume less.
Due to this turgor pressure-volume will expand and shrink due to this process many biological processes take place like cell growth and cell signaling etc.
In protozoa, the vacuole is essential cytoplasmic organelles that are taking a vital role in digestion, ingestion, and excretion.
Secondary metabolites such as tannins and various biological pigments are present in vacuoles in the plant, fungi, and algae, and also some organisms produce self toxicity to protect cells.
In animals, vacuoles play a role in intracellular digestion. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast.
Functions of the vacuole in the cell:
The function of the vacuole varies according to the organism. Vacuole has more significance in plants, fungi, and certain species of Protista and less importance in animals and bacteria. Let us see the general functions of the vacuole in living cells.
- Maintains turgidity of the cell.
- Containing waste products
- Isolating materials which are harmful to cells.
- Contains water.
- Maintain turgor pressure.
- Small molecules are present.
- Exports unwanted particles.
- Maintain pH.
- The central vacuole allows the plant to support other structures.
- It allows germinating plants or plant organs to grow fastly.
- Vacuoles are protein bodies that need germination for seeds.
Types of vacuoles:
The types of vacuoles are as follows:
- Gas vacuoles:
Gas vacuoles are known as gas vesicles. Gas vacuoles are found in prokaryotes which are air filling compartments in a cylindrical shape. They help in buoyancy.
Gas vacuoles are large protein composed and absences of lipid and carbohydrates in them. They have nano compartments that are free permeable to gas.
A small variance in amino acid changes the morphology of gas vesicles and forms various gas vesicles. They are mainly present in marine bacteria like cyanobacteria which are also known as blue-green algae and also found in some archaea.
Gas vesicles are large and parallel bundles in cyanobacteria whereas in purple sulfur bacteria they are smaller and irregularly distributed. They are protein-bound particles.
The inner membrane of gas vesicles is hydrophobic which doesn’t allow water inside them. The diameter of gas vesicles is 750 nm.
- Central vacuoles :
A large vacuole is present in plant cells which is more than 30 % in some cell types. It is even bigger in size. The vacuole cell membrane is known as tonoplast.
Filled with a vascular membrane also known as cell sap. The tonoplast function is to separate the vacuole from the cell membrane. It mainly involves regulating movements of the cell and isolating the harmful substances to the cell.
The main role of the central vacuole is to maintain turgor pressure between the cell and the vacuole. It maintains the cell pH by moving protons from there to there.
Control of water movement is done by the proteins which are present in the central vacuole. Due to osmosis water moves in and out because of turgor pressure.
These are the functions of the central vacuole, same as we discussed in general functions of vacuoles.
- Contractile vacuoles:
It is a specialized osmoregulatory vacuole present in protists. It includes radial arms and spongione.
It periodically contracts to remove excess water and ions from the cell to balance water flow.
- Food vacuoles:
These are also known as digestive vacuoles found in ciliates and in plasmodium falciparum.
Importance of this chapter in NEET:
As in this chapter, we will learn about the cell organelles which is basic and we should know about all the cell organelles as it is a basic unit of the living body. From this chapter, you can expect ten to fifteen based on the function and membrane, and morphology also. As it has full information regarding organelles we just need to memorize and then get good marks. Don’t neglect this chapter as it is important for scoring high marks.
Also read: Mitochondria
Frequently Asked Question FAQs:
Question: What is a vacuole?
Answer: Plant vacuoles are large in size; they cover most of the cell about 90% in total cell size. Water enters into the vacuole by creating turgor pressure which results in cell enlargement.
By following the osmotic principle where water moves from high pressure to low pressure now due to high turgor pressure the water again goes out of the cell making vacuole volume less.
Due to this turgor pressure volume will expand and shrink due to this process many biological processes take place like cell growth and cell signaling etc.
In protozoa, the vacuole is essential cytoplasmic organelles that are taking a vital role in digestion, ingestion and excretion.
Secondary metabolites such as tannins and various biological pigments are present in vacuoles in the plant, fungi, and algae and also some organisms produce self toxicity to protect cells. In animals, vacuoles play a role in intracellular digestion. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast.
Question: Write functions of vacuole?
Answer: The functions of the vacuole in cell are as follows:
Function of the vacuole varies according to the organism. Vacuole has more significance in plants,fungi and in certain species of protista and less importance in animals and bacteria. Lets see the general functions of vacuole in living cells.
- Maintains turgidity of the cell.
- Containing waste products
- Isolating materials which are harmful to cells.
- Contains water.
- Maintain turgor pressure.
- Small molecules are present.
- Exports unwanted particles.
- Maintain pH.
- The central vacuole allows the plant to support other structures.
- It allows germinating plants or plant organs to grow fastly.
- Vacuoles are protein bodies that need germination for seeds.
Question: What are the types of vacuole?
Answer: The types of vacuoles are as follows:
- Gas vacuoles:
Gas vacuoles are known as gas vesicles. Gas vacuoles are found in prokaryotes which are air filling compartments in a cylindrical shape. They help in buoyancy.
Gas vacuoles are large protein composed and absences of lipid and carbohydrates in them. They have nano compartments which are free permeable to gas.
Small variance in amino acid changes the morphology of gas vesicles and forms various gas vesicles. They mainly present in marine bacteria like cyanobacteria which is also known as blue green algae and also found in some archaea.
Gas vesicles are large and parallel bundles in cyanobacteria whereas in purple sulfur bacteria they are smaller and irregularly distributed. They are protein bound particles.
The inner membrane of gas vesicles is hydrophobic which doesn’t allow water inside them. The diameter of gas vesicles are 750 nm.
- Central vacuoles :
A large vacuole is present in plant cells which is more than 30 % in some cell types. It is even bigger in size. The vacuole cell membrane is known as tonoplast.
Filled with a vascular membrane also known as cell sap. The tonoplast function is to separate the vacuole from the cell membrane. It mainly involves regulating movements of the cell and isolating the harmful substances to the cell.
The main role of the central vacuole is to maintain turgor pressure between the cell and the vacuole. It maintains the cell pH by moving protons from there to there.
Control of water movement is done by the proteins which are present in the central vacuole. Due to osmosis water moves in and out because of turgor pressure.
These are the functions of the central vacuole, same as we discussed in general functions of vacuoles.
- Contractile vacuoles:
It is a specialized osmoregulatory vacuole present in protists. It includes radial arms and spongione.
It periodically contracts to remove excess water and ions from the cell to balance water flow.
- Food vacuoles:
These are also known as digestive vacuoles found in ciliates and in plasmodium falciparum.








