NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets is a beneficial study component required for the students studying CBSE board Class 6 Science. This solution has detailed answers and explanations to the exercise questions provided in the NCERT Class 6 Science textbook.
These NCERT Solutions will boost your confidence by helping you in building your problem-solving abilities on a given topic. It is essential for students to get well versed with this study material to score good marks in the examinations.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 provided here will help you to understand the discovery of magnets along with magnetic and non-magnetic materials, poles of the magnet, finding directions using magnets, construction of magnets, attraction, and repulsion forces.
Important topics covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with magnets
- How Magnets were Discovered
- Magnetic and non-magnetic materials
- Poles of magnet
- Finding directions
- Make your own magnet
- Attraction and repulsion between magnets
-
Do you need help with your Homework? Are you preparing for Exams? Study without Internet (Offline)Fun with Magnets×
CHAPTER 13_ Fun with Magnets ncert textual questions
1. Fill in the Blanks :
i) Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as _________, _________ and ________.
ii) The materials that are attracted towards magnets are called _____________.
iii) Paper is not a ___________ material.
iv) In olden days, sailors used to find direction by suspending a piece of ____________.
v) A magnet always has _________ poles.
Answers:
i) Bar magnets, horseshoe magnets, cylindrical magnets
ii) Magnetic materials
iii) Magnetic
iv) Bar magnet
v) Two
2. State whether the following statements are ‘True’ or ‘False’.
i) A cylindrical magnet has only one pole.
ii) Artificial magnets were discovered in Greece.
iii) Similar poles of a magnet repel each other.
iv) Maximum iron fillings stick in the middle of a bar magnet when it is brought near them.
v) Bar magnets always point towards the North-South direction.
vi) A compass can be used to find the East-West direction at any place.
vii) Rubber is a magnetic material.
Answers:
i) False ii) False iii) True iv) False v) True vi) True vii) False
3. It was observed that a pencil sharpener gets attracted by both the poles of a magnet although its body is made of plastic. Name a material that might have been used to make some part of it.
A. The blade of a pencil sharpener is made of iron. Iron is a magnetic material. Since magnets can attract objects made of magnetic materials, a pencil sharpener gets attracted towards both the poles of a magnet.
4. Column – I shows different positions in which one pole of a magnet is placed near that of the other. Column – II indicates the resulting action between them for each situation. Fill in the blanks.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| N – N | ––––––––– |
| N – ____ | Attraction |
| S – N | ________ |
| ___ – S | Repulsion |
A.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| N – N | Repulsion |
| N – S | Attraction |
| S – N | Attraction |
| S – S | Repulsion |
5. Write any two properties of a magnet.
A. The two properties of a magnet are given as follows:
- Directive property: When a bar magnet is suspended freely, a magnet always aligns itself in
North-South direction. - Attractive property: A magnet attracts magnetic materials like iron, cobalt, nickel, etc.
6. Where are the poles of a bar magnet located?
A. The poles of a bar magnet are located near its two endpoints.
![]()
7. A bar magnet has no markings to indicate its poles. How would you find out near which end is its north pole located?
A. A freely suspended bar magnet always comes to rest in the North-South direction. The north-facing end of the magnet is its north pole, the south-facing end is its south pole. Hence, the unknown poles of a bar magnet can be marked by suspending it freely by a string.
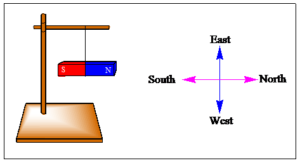
8. You are given an iron strip. How will you make it into a magnet?
A. The ‘Touch and stroke’ method can be used to make an iron strip into a magnet. For this, a bar magnet is required. The bar magnet is moved along the length of the iron strip starting from one end to the other end. Then the bar magnet is lifted from the other end and brought to the starting point again with the same pole of the bar magnet. On repeating the process at least 40 to 50 times, the iron strip will become a bar magnet with two poles.
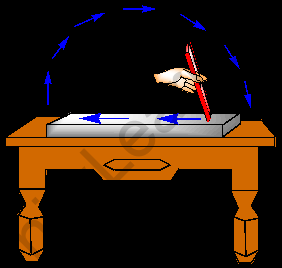
9. How is a compass used to find directions?
A. Compass is based on the directive property of a magnet. In a compass, a magnetized needle is pivoted at its centre, which can rotate freely. The compass is kept at the place where we wish to know the directions. The magnetized needle due to its directive property shows the geographic North-South directions.

10. A magnet was brought from different directions towards a toy boat that has been floating in water in a tub. The effect observed in each case is stated in Column- I and possible reasons for the observed effects are mentioned in Column – II. Match the statements given in Column – I with those in Column – II.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| 1) Boat gets attracted towards the magnet
2) Boat is not affected by the magnet 3) Boat moves towards the magnet if north pole of the magnet is brought near its head 4) Boat moves away from the magnet when the north pole is brought near its head 5) Boat floats without changing its direction |
The boat is fitted with a magnet with a north pole towards its head
The boat is fitted with a magnet with a south pole towards its head The boat has a small magnet fixed along its length The boat is made of magnetic material The boat is made of a non-magnetic material |
A.
| S. No. | Column – I | Column – II |
| 1)
2) 3)
4)
5)
|
The boat gets attracted to the magnet
The boat is not affected by the magnet The boat moves towards the magnet if the north pole of the magnet is brought near its head The boat moves away from the magnet the north pole is brought near its head when Boat floats without changing its direction |
The boat is made of a magnetic material
The boat is made of a non-magnetic material The boat is fitted with a magnet with the south pole towards its head The boat is fitted with a magnet with the north pole towards its head The boat has a small magnet fixed along its length |
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13
- List out any two properties of a magnet from Chapter 13 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science.
- What concepts can I learn from Chapter 13 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science?
- Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 PDF absolutely free of cost?
Q. List out any two properties of a magnet from Chapter 13 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science.
Ans. The properties of a magnet from the Chapter 13 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science are –
1. Objects that are made of cobalt, nickel, and iron are attracted by the magnet.
2. Like poles of two magnets repel each other and opposite poles attract each other.
To understand this Chapter clearly, students can access the NCERT Solutions designed by the faculty at INFINITY LEARN. The concepts are explained in a comprehensive way to improve the students with their analytical thinking abilities.
Q. What concepts can I learn from Chapter 13 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science?
Ans. From Chapter 13 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science, you can learn about concepts like –
- How Magnets were Discovered
- Magnetic and non-magnetic materials
- Poles of magnet
- Finding directions
- Make your own magnet
- Attraction and repulsion between magnets
Q. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 PDF absolutely free of cost?
Ans. Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 PDF is absolutely free of cost. Students who have doubts regarding this Chapter can access the solutions PDF from INFINITY LEARN. The solutions are designed in a clear and accurate manner to help students score well in the annual exams. The PDF format of solutions can be downloaded from the links available at INFINITY LEARN and can be used by the students without any time constraints. The questions present in the NCERT textbook are answered in an interactive manner as per the syllabus and marks weightage designed by the CBSE board.

