Table of Contents
Boltzmann Constant
The Boltzmann regular which is normally represented by means of both k or kB is a proportionality factor that allows examining the common relative kinetic strength of particles in fuel with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. The Boltzmann constant is measured by way of the usage of power per diploma of temperature devices. The cost after calculation of the Boltzmann constant rounds up to at least 1.380 X 10-23 joule according to kelvin. This Boltzmann steady can be expressed in numerous methods with an alternative in the gadgets as well.
Dimensions of Boltzmann Constant – Explanation
We know that derived units may be acquired from the essential gadgets of mass, duration, and time. Let’s represent mass with M, period with L, and time with T. Then we will say that the dimensional formula for a physical amount is an expression that tells us the following:
1. The essential (simple) units on which the amount depends, and
2. The nature of dependence.
For example,
[M^0 L^1 L^-1], is the dimensional system for velocity. It shows that velocity relies upon L and T. Furthermore, the unit varies immediately as a unit of length and inversely because of the unit of time.so, [M^0 L^1 L^-1] is the dimensional equation for velocity
Dimensional Constants
We understood the concept of finding the dimensional formula of a bodily amount. So there are different quantities that we are going to use, this is a dimensional constant. So, dimensional constants are those quantities whose values are regular, and they own dimensions.
For instance, Gravitational constant, Boltzmann constant, Planck’s steady, etc. Here, we are able to find out the measurement of a Boltzmann regular.
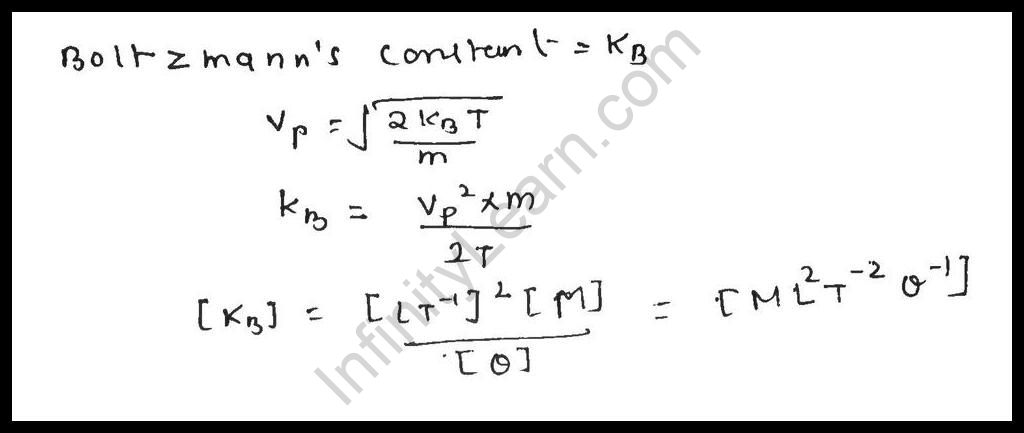
The Dimension of Boltzmann Constant
We recognise that the dimensional system for Boltzmann consistent
The dimensional formula for energy(E) / Dimension of temperature in Kelvin
What is Boltzmann’s Constant?
Let’s say, you hold a water-crammed container on the fireplace, and cover it with a lid. After some time, whilst you eliminate the lid, you could see that there are several vibrations in the container.
So, Why is There a Vibration within the Container?
Well, the molecules inside the water benefit three kinetic energies, i.E., translational kinetic electricity, rotational kinetic power, and vibrational kinetic energy.
So, when the temperature will increase, their kinetic power additionally increases. As the extent increases, the molecules reach the brink of the box and start growing stress on the walls.
Since the molecules are at high temperatures, whilst you put your hand inside the box, the molecules in your hand take in the energy transferred with the aid of these gasoline molecules, spread around your hand, and damage your pores and skin.
On increasing the temperature, the kinetic strength of a molecule will increase. In this method that the kinetic energy of each molecule is immediately proportional to the temperature.
T ∝ KE
We know that PV = n * RT is the best gas regulation, where
P is the pressure, measured in Pascals
V is the volume, estimated in a cubic meter
n is the number of moles,
R = universal Gas Constant, and
T = the temperature in Kelvin
We know that n = N/NA = total number of molecules in the gas/Avagadro’s number
Let’s rewrite the ideal gas law:
PV = N__T
Here, we are thinking about the number of atoms (since n is a little worth it), so we will utilize an alternate steady and that consistency is the Boltzmann steady.
So, the new equation becomes, PV = NKbT
Here, Kb = Boltzmann’s constant
nR = NKb
Also read: Ionic Equilibrium lonization and Dissociation
FAQs
What is Kb in Boltzmann's Formula?
Kb in Boltzmann's components describes the relationship among entropy (randomness of the gasoline molecules) and the way the range of ways the atoms or molecules of a thermodynamic machine may be arranged.
How is Boltzmann Constant Calculated?
In thermodynamics, Boltzmann steady is the physical steady that relates the average kinetic electricity of the gasoline molecules with the temperature of the molecules. It is represented with the aid of okay or Kb. The price of the Boltzmann consistent is measured by the use of J/K.









