Table of Contents
Fission & Fusion Reactions
Nuclear chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies changes in the nucleus of elemental atoms. These nuclear alterations are a source of nuclear power and radioactivity, and the energy supplied by nuclear reactions has several applications.
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion are the two types of nuclear processes. Nuclear fission and fusion are caused by the breakdown and fusing of the elemental nucleus. An atom divides into two or smaller or lighter atoms in the case of nuclear fission. Nuclear fusion happens when two or more atoms combine or fuse to generate a larger or heavier atom.
Nuclear fission is a nuclear process that occurs when the nucleus of an atom is attacked by low-energy neutrons, causing the nucleus to divide into smaller nuclei. This procedure generates a large quantity of energy. Nuclear fission processes are employed in nuclear power reactors because they are simple to manage and provide a huge quantity of energy.
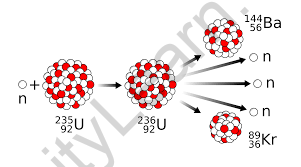
When uranium-235 atoms are bombarded with neutrons, the uranium’s heavy nucleus breaks, producing krypton-94 and barium-139 with the release of three neutrons.
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two atoms join to generate one or more distinct atomic nuclei and subatomic particles such as protons and neutrons. This process generates a tremendous quantity of energy, far more than the energy generated during the nuclear fission reaction.
Fusion happens in the sun when atoms of (hydrogen isotopes, Hydrogen-3, and Hydrogen-2) Deuterium and Tritium mix in a high-pressure environment at extremely high temperatures to generate a neutron and an isotope of Helium. Furthermore, the quantity of energy released in fusion is far larger than the amount of energy created in fission.
Difference Between Fission & Fusion Reactions
Nuclear Fission |
Nuclear Fusion |
| Nuclear fission occurs when the nucleus of an atom breaks into lighter nuclei as a result of a nuclear reaction. | Nuclear fusion is a process that occurs when two or more light nuclei collide to generate a heavier nucleus. |
| A great quantity of energy is produced when each atom splits. | The energy released during nuclear fusion is many orders of magnitude more than the energy released during nuclear fusion.
|
| Fission reactions do not occur spontaneously in nature. | Stars and the sun undergo fusion processes. |
| In a fission process, little energy is required to divide an atom. The nuclear fission concept underpins the operation of an atomic weapon. | A high amount of energy is required to fuse two or more atoms together in a fusion process. The hydrogen bomb operates on the same principles as a nuclear fusion weapon. |
Also read: Electron and Electron Charge
FAQs
What are the Differences Between Fission and Fusion Reactions?
Fission, as we describe it, is the splitting of an atom when it is struck by a highly active proton or neutron. Nuclear fusion, on the other hand, is the joining of two atoms into a single atom.
What is nuclear chemistry?
Nuclear chemistry, often known as radiochemistry, is the study of the elements that make up the cosmos, as well as the creation and production of radioactive pharmaceuticals for therapeutic purposes and a variety of other scientific applications.
For more enhanced information on the subject, download the Infinity Learn app – the ultimate learning app for classes 3 to 13.







