Table of Contents
Mitochondria are known as the cell’s powerhouses. They participate in various cell activities such as respiration, differentiation, cell signaling, aging, controlling the cell cycle, cell growth, and other metabolic processes. They are rod-shaped and have a double membrane, found in both plant and animal cells.
The term ‘mitochondrion’ comes from a Greek word meaning threadlike granules, first described by German pathologist Richard Altmann in 1890.
Mitochondria are double-membrane-bound cell organelles found in most eukaryotic organisms. These organelles float freely within the cytoplasm of all living cells.
The diagram of mitochondria is useful for students in classes 10 and 12. It is one of the important topics, often asked in exams, with a high weightage of marks.
Compound Microscope Diagram | Food Chain diagram
Autoclave Diagram | Iron Carbon Diagram
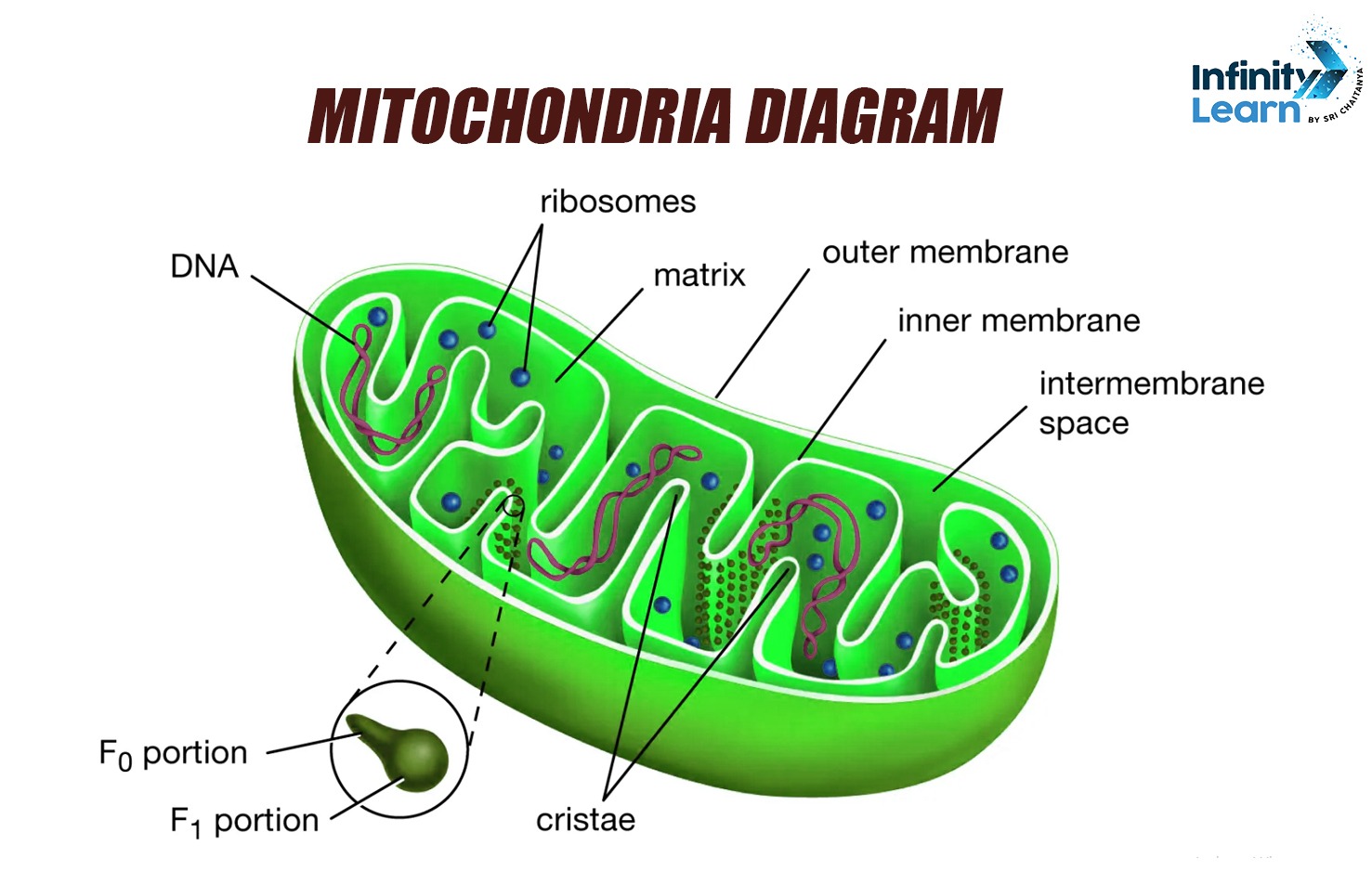
Functions and Structure Of Mitochondria
Structure of Mitochondria
- Outer Membrane:
- The outer membrane covers the mitochondrion and has a smooth texture.
- It has small pores that allow molecules to pass through easily.
- Inner Membrane:
- Inside the outer membrane, there is the inner membrane which has many folds called cristae.
- These folds increase the surface area, allowing more space for chemical reactions.
- Matrix:
- The space inside the inner membrane is filled with a fluid called the matrix.
- The matrix contains enzymes, mitochondrial DNA, and ribosomes.
- Intermembrane Space:
- The space between the outer and inner membranes is called the intermembrane space.
- It plays a role in the process of energy production.
Functions of Mitochondria
- Energy Production:
- Mitochondria are known as the “powerhouses” of the cell.
- They produce energy in the form of a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) through a process called cellular respiration.
- This energy is used by the cell to perform various functions.
- Regulation of Metabolism:
- Mitochondria help in regulating the metabolism of the cell.
- They break down nutrients and convert them into energy that the cell can use.
- Calcium Storage:
- Mitochondria store calcium ions, which are important for many cellular processes.
- Calcium helps in muscle contraction, cell division, and other functions.
- Cell Death:
- Mitochondria play a role in programmed cell death, also known as apoptosis.
- This is important for removing damaged or unwanted cells from the body.
- Heat Production:
- In some cells, mitochondria can produce heat to maintain body temperature.
- This process is called thermogenesis and is especially important in brown fat cells.
Importance of Mitochondria
- Mitochondria are essential for the survival and functioning of cells.
- They provide the energy needed for growth, repair, and maintenance of the cell.
- Without mitochondria, cells would not be able to perform their necessary functions, leading to the breakdown of tissues and organs.
Mitochondria Diagram FAQs
What is mitochondria and diagram?
Mitochondria are cell organelles that produce energy. Here’s a simple diagram:
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria create energy for the cell by converting nutrients into ATP.
What are the 3 main parts of the mitochondria?
The three main parts are the outer membrane, inner membrane, and matrix.
What are the parts and function of the mitochondria?
Parts include the outer membrane, inner membrane, and matrix; they produce energy for the cell.
What do mitochondria look like?
Mitochondria look like tiny, bean-shaped structures inside cells.






