Table of Contents
Introduction
All living things need the energy to perform various vital functions. This force is derived from the respiratory system. Breathing may or may not occur when there is oxygen. If breathing occurs when there is oxygen, it is called aerobic breathing and in the absence of oxygen, it is called anaerobic breathing. Most organisms find energy in aerobic breathing, but few organisms such as bacteria, yeast, etc. breathe in an ineffective way. These organisms gain energy when there is no oxygen by converting starch or sugar into alcohol or acid. This process of enzyme-catalyzed metabolism is called fermentation. Fermentation is a biochemical process that occurs in other organisms. The onset of this process is similar to cellular respiration. That is the formation of pyruvic acid by the process of glycolysis in which net 2 ATP molecules are synthesized. In addition, pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid, ethanol, or other products. The NAD + formed in this process is also used in the glycolysis system.
Fermentation occurs in yeast cells and viruses and in animal tissues. It is an anaerobic method in which glucose is broken down.
Breathing that occurs at the minute in our body, that is, in a cell is called cellular respiration. It happens when you are with or without oxygen. Any type of cellular respiration begins with glycolysis where a 3-C molecule, pyruvic acid is formed as the final product.
Different cells treat this pyruvate in two main ways, fermentation is one of them. Let’s take a closer look at fermentation, your types, and anaerobic respiration.
Types of Fermentation
There are three different types of fermentation:
- Lactic Acid Fermentation
In this, starch or sugar is converted into lactic acid by yeast strains and bacteria. During exercise, energy expenditure is faster than the oxygen supplied to the muscle cells. This results in the formation of lactic acid and painful muscles.
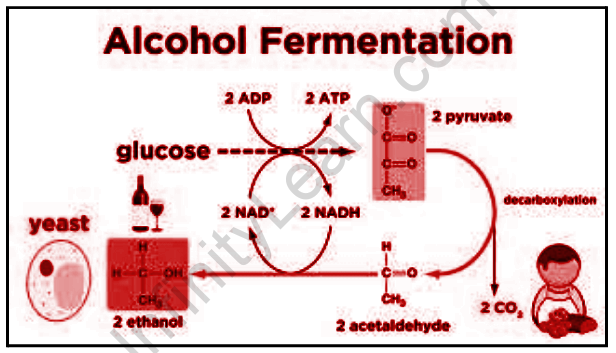
- Alcohol Fermentation
Pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, is broken down into alcohol and carbon dioxide. Wine and beer are produced by alcoholic fermentation.
- Acetic Acid Fermentation
Starch and sugar present in grains and fruits ferment into vinegar and condiments. E.g. apple cider vinegar.
Fermentation – Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration where respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation is an anaerobic pathway- a common pathway in the majority of prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes. In this process, glucose is partially oxidized to form acids and alcohol.
In organisms like yeast, the pyruvic acid formed by partial oxidation of glucose is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide (CO2). This anaerobic condition is called alcoholic or ethanol fermentation. The whole reaction is catalyzed by the enzymes, pyruvic acid decarboxylase, and alcohol dehydrogenase. In certain bacteria and animal muscle cells, under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid by lactate dehydrogenase. This is called lactic acid fermentation. The end products of these anaerobic pathways make them hazardous processes. For example, a concentration of alcohol above 13 percent produced by yeast cells could kill themselves.
Fermentation is a chemical process that breaks down compounds such as glucose anaerobically. The fermentation, in a broad sense, of fermentation that occurs during the production of wine and beer, is a process that has existed for at least 10,000 years. Foaming is the result of the production of carbon dioxide, which was not discovered until the 17th century. In the nineteenth century, French chemist and microbiologist Louis Pasteur used a little fermentation to describe the changes caused by yeast and other organisms that grow in the air (anaerobically); he also realized that ethyl and carbon dioxide are not the only fermentation products.
During the 1920s, the revelation was that in the absence of air, lactate binding was accelerated by muscle fibers from glucose, and that muscle produced the same intermediate chemicals as grain fermentation. As a result, an important generalization arose: fermentation processes not only performed the function of yeast but also occurred in many other cases of glucose use.
In alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation, NADH+H+ is the reducing agent which is oxidized to NAD+. The energy released in both the processes is not much and the total sum of ATP molecules produced during fermentation is two, which is very less as compared to aerobic respiration. However, this is commercially employed in the food and beverage industries, and pharmaceutical industries.
Fermentation Utilisation
Fermentation is one of the oldest metabolic processes commonly used by prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is also a process used in industries to produce various products. Different types of fermentation are used to produce the final product you wish to use. Common products we use in our daily lives produced by fermentation include:
- Wine
- Beer
- Biofuels
- Yogurt
- Cucumbers
- Bread
- Lactic Acid containing sour foods
- Certain vitamins and antibiotics
- VinegarThings like apple cider vinegar, kombucha, etc.
Benefits of Fermentation
Ripe food tastes better, is easier to digest, and is more nutritious. The benefits of using processed foods are as follows:
- Ripe food helps to keep germs in the stomach, thus helping digestion.
- It has an anti-carcinogenic effect.
- It is good for the immune system.
- It is also helpful for lactose-intolerant people.
There are more applications for fermentation than industrial and domestic. Example – Used to produce methane in sewage treatment plants.
Also read: Important Topic of Biology: Renal Failure
FAQs
Q. What Types of Fermentation?
Ans: Depending on the type of final product produced, fermentation is classified as:
- Lactic Acid Fermentation
- Alcohol fermentation
- Butyric acid fermentation
- Acetic acid fermentation
Q. What Are the Benefits of Eating Solid Foods?
Ans: Ripe food tastes better, is easier to digest, and is more nutritious. The benefits of using processed foods are as follows:
- Ripe food helps to keep germs in the stomach, thus helping digestion
- It has an anti-carcinogenic effect.
- It is good for the immune system
- It is also helpful for lactose-intolerant people
Why Is Butyric Acid Fermentation Called Combined Acid Fermentation?
Butyric acid fermentation is also known as hybrid acid fermentation because together with butyric acid, n-butanol, acetic acid, ethanol, isopropanol, and acetone are also formed according to the process.








