Table of Contents
Paramecium, also known as Paramoecium, is a type of single-celled protozoa that moves with thousands of tiny hair-like structures called cilia. These organisms live in freshwater, as well as in saltwater and brackish water environments. They can be found attached to surfaces. Paramecia mainly reproduce by splitting into two (binary fission), and they have a distinctive slipper-like shape. They also engage in a reproductive process called conjugation. Paramecia are easy to grow in labs and are widely used in studying various biological processes
Compound Microscope Diagram | Food Chain diagram
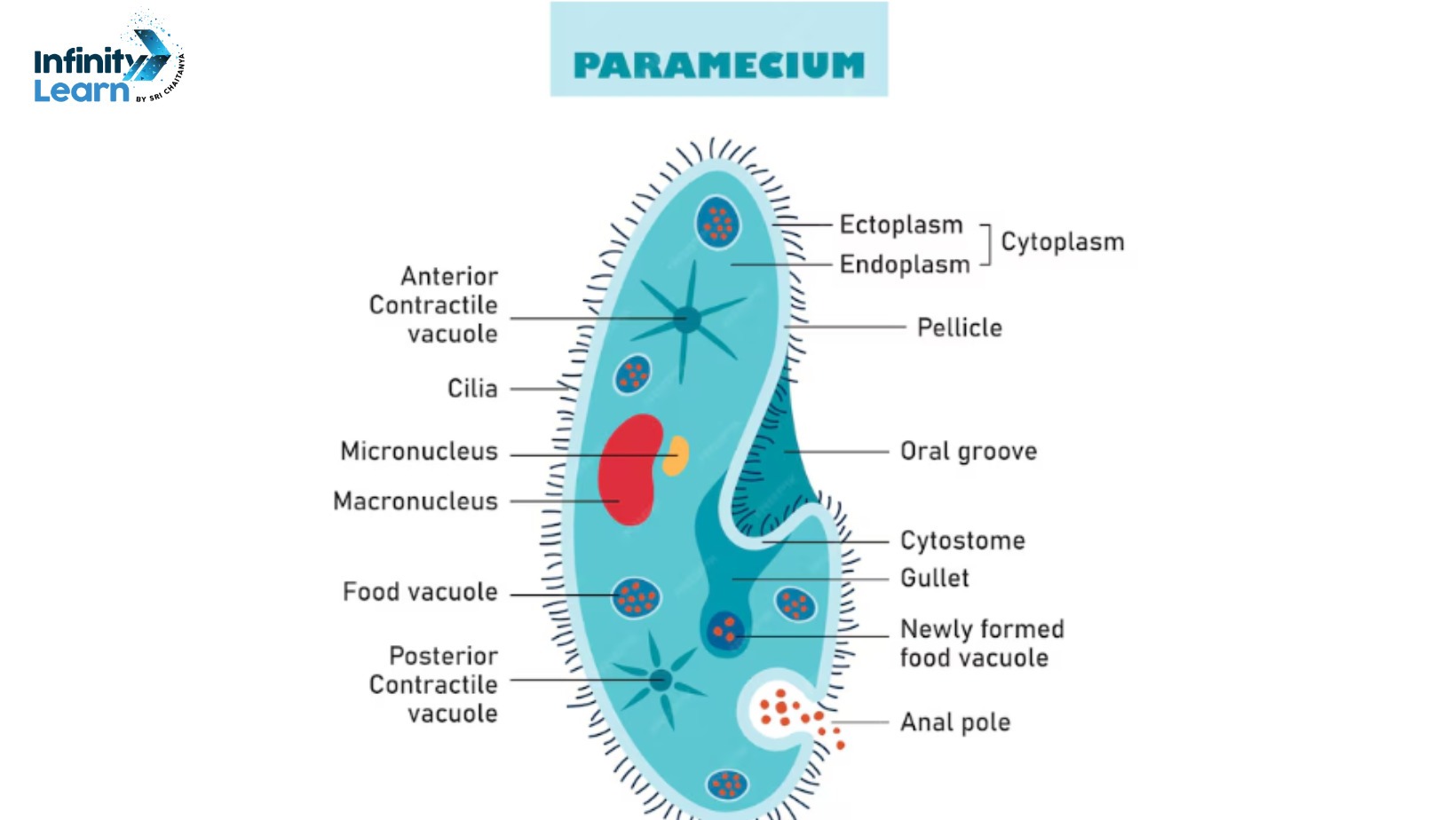
Functions and Features of Paramecium
Paramecium is a single-celled organism belonging to the group of protists called ciliates. It is found in freshwater environments and is known for its unique shape and movement. Here are the functions and features of Paramecium explained in simple terms:
- Shape and Structure: Paramecium has an elongated slipper-like shape with a slightly pointed anterior end and a rounded posterior end. It is covered with tiny hair-like structures called cilia, which help in movement and feeding.
- Movement: Paramecium moves using its cilia in a coordinated manner. The cilia beat rhythmically, allowing the organism to propel itself through water in a spiraling or zigzag pattern.
- Feeding Mechanism: Paramecium is a heterotroph, meaning it feeds on other organisms. It uses its cilia to sweep food particles, such as bacteria and algae, into its oral groove. From there, the food is enclosed in a food vacuole where digestion occurs.
- Contractile Vacuole: Paramecium possesses a contractile vacuole, which helps regulate water content within the cell. It collects excess water that enters the cell due to osmosis and then expels it periodically to maintain osmotic balance.
- Reproduction: Paramecium reproduces asexually through binary fission, where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It can also undergo conjugation, a sexual process where genetic material is exchanged between two individuals, leading to genetic diversity.
- Sensitivity and Response: Although simple, Paramecium exhibits responses to environmental stimuli. It can move towards food sources (positive chemotaxis) and away from harmful substances (negative chemotaxis) using its cilia.
- Role in Ecosystems: Paramecium plays a vital role in freshwater ecosystems by serving as prey for larger organisms and helping control bacterial populations through its feeding habits.
Autoclave Diagram | Iron Carbon Diagram
Paramecium Reproduction
Paramecium is a tiny, single-celled organism found in freshwater environments. It reproduces asexually through a process called binary fission. Here’s how it happens:
- Binary Fission: Paramecium starts by duplicating its genetic material, forming two identical nuclei inside its cell. Then, the cell divides into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell gets one nucleus and other essential cell parts. This process ensures rapid reproduction, helping Paramecium increase its population quickly in favorable conditions.
- Conditions for Reproduction: Reproduction in Paramecium happens when there’s enough food and suitable environmental conditions. They can also reproduce sexually under certain circumstances, which adds genetic diversity to their population.
- Significance: By reproducing asexually, Paramecium ensures its survival and adaptation to changing environments. This simple yet effective method allows them to thrive in various freshwater habitats worldwide.
Paramecium Nutrition
Paramecium, a tiny single-celled organism found in freshwater, gets its nutrition through a process called holozoic nutrition. This means it consumes food particles whole into its cell mouth, known as cytostome. Paramecia mainly feed on bacteria, algae, and other small organisms found in water.
Once inside, food vacuoles form around the food particles, and enzymes help digest them. The nutrients released from digestion are absorbed into the cytoplasm, providing energy and building blocks for growth and repair.
Paramecia also eliminate waste through a specialized structure called the anal pore. This process helps maintain a balanced internal environment essential for its survival and reproduction in aquatic habitats.
Paramecium Diagram FAQs
What is Paramecium class 10?
Paramecium is a single-celled organism studied in Class 10 biology.
What is Paramecium structure?
Paramecium has an oval shape with hair-like structures called cilia for movement and feeding.
What is the Paramecium diagram?
The Paramecium diagram shows its oval shape with cilia around the cell and its internal structures.
What is a Paramecium?
A Paramecium is a microscopic, single-celled organism found in freshwater environments.
What is binary fission in Paramecium?
Binary fission in Paramecium is its method of reproduction where it divides into two identical daughter cells.



