Class 9 Physics Motion: Equation for Position Time Relation
Table of Contents
- Derivation of the Second Equation of Motion
- Summary
- Did You Know?
In the previous segment, we derived the first equation of motion. In this segment, we will derive the second equation of motion.
Derivation of second equation of motion: Position–time relation
With the help of a velocity–time graph, let us obtain the equation for the position–time relation.
We will use the velocity-time graph with the same labellings that we used to derive the first equation of motion.
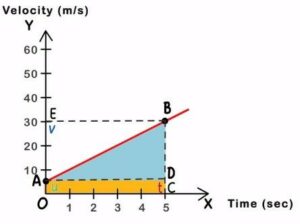
Velocity-time graph
We know that the distance travelled by a vehicle can be calculated by finding the area of the velocity-time graph. Hence, the distance travelled in time ‘t’ equals the area of trapezium OABC.
Let’s call the distance travelled as ‘s’. To calculate ‘s’, we divide the trapezium OABC into a
rectangle OADC and a triangle ABD, find the areas of the figures individually, and sum them up.
Also Read: Equation for Position Velocity Relation




