Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Uses of Concave Mirror
- Solar Heater
- Astronomical Telescope
- Other Applications
- Summary
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we learned about the properties of the image formed by a convex mirror. In this segment, we will learn about the uses of concave mirrors.
Uses of Concave mirror
We have already learnt about the properties of the image formed by a concave mirror. We will now see that by utilizing these properties how concave mirrors are used in different devices.
Solar Heater:
A device that uses the energy from the sun to heat objects. It is the most common device which uses a concave mirror for its function.
Solar Heater
How are concave mirrors used in Solar Heaters?
We know that a concave mirror forms a point-sized image of an object kept very far away from it. Since the sun is very far away from us, its image formed by a concave mirror will be a point-
sized image. The point at which the sun’s image is formed is the point where the rays coming
from the sun are concentrated. Thus, this point is hotter than its surroundings.
Point image of the Sun
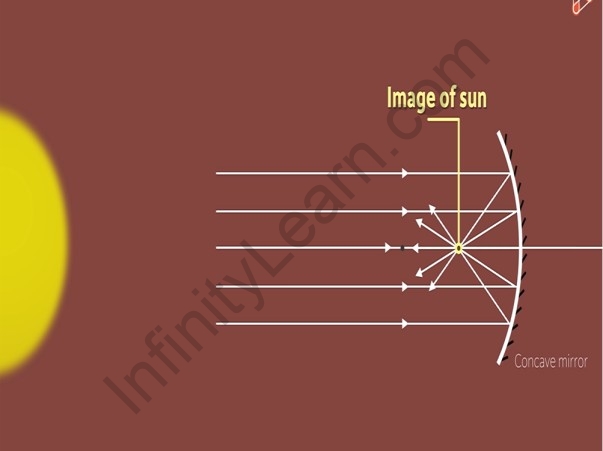
A container when placed on a stand at or near this point heats up and then can be used to cook food or boil liquids.


Astronomical Telescope:
It is an optical instrument that is used to see the magnified image of distant heavenly bodies like stars, planets, satellites, galaxies, etc.
Astronomical telescopes use concave mirrors to gather and focus light from distant celestial objects. Here’s how they work:
1. Light gathering: A concave mirror is used as the primary mirror in the telescope. Its shape allows it to gather and reflect light from distant objects, which is then focused onto a secondary mirror or an eyepiece.
2. Focal length: The shape of the concave mirror allows it to focus the light to a single point known as the focal point. This point is where the secondary mirror or the eyepiece is placed to create a magnified image.
3. Magnification: The magnification of the telescope is determined by the focal length of the primary mirror and the eyepiece. By changing the eyepiece, the magnification of the telescope can be adjusted to suit the needs of the observer.
4. Correcting aberration: Concave mirrors can be designed to minimize or correct for aberrations, which are distortions in the image caused by imperfections in the mirror’s shape. This allows for sharper, clearer images of celestial objects.
5. Compact design: Astronomical telescopes that use concave mirrors are often more compact than those that use lenses, making them easier to transport and set up. This is because mirrors can be shaped to have a larger aperture without increasing their weight or size.
In summary, the concave mirror in an astronomical telescope gathers and focuses light from distant objects, creates a magnified image, corrects for aberrations, and allows for a more compact design.



