Table of Contents
Introduction
The heart is a muscular organ made up of specialized muscles called the heart muscle. The primary function of the human heart is to pump blood to various parts of the body. There are several internal factors that enable the human heart to regulate its activities on its own, but there are also external influences that regulate heart activity. These factors include the autonomic nervous system, chemicals such as hormones, ions etc. Let’s start our conversation with the heart cycle.
Autonomic regulation-Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Sensors
Differences in heart rate and rhythm control can also be achieved by the autonomic nervous system (ANS) impulse generation. The medulla oblongata in the brain is responsible for this ANS function. The ANS contains two emotions – sensitive and parasympathetic, antagonistic. Stimulation of sensitive nerves leads to strong ventricular and atrial contractions that increase cardiac output. It also increases heart rate. In contrast to the act of empathy, parasympathetic stimulation reduces the narrowing of the atria and ventricles. This causes a slight heartbeat and heartbeat.
Chemical Regulation-Hormones and Ions
In addition to self-regulation, there are certain chemicals that can affect the regulation of cardiac function. These chemicals include hormones such as epinephrine, nor-epinephrine, thyroxine etc. It can increase heart rate and heart rate. Ions are other chemicals that affect the heart.
Heart control is not only affected by these factors. Even a person’s sex can have an effect on him.
Your heart is beating fast. She breathes quickly and deeply. And she is sweating. Well, that is probably because you have been moving large muscles in your legs, arms, and hips for a long time. When these large muscles are involved in the exercise, there is an increased rate of respiration for energy production. Next, the need for more oxygen leads to increased respiration and heart rate. And that type of activity is called cardiovascular exercise — or cardio for short.
What is cardiovascular exercise?
Also called aerobic exercise or endurance, cardiovascular exercise is any type of activity that utilizes aerobic metabolism. That is, during work, oxygen is actively involved in the cellular reaction to produce the energy needed to maintain function. Your heart rate rises and you breathe deeply to increase the amount of oxygen in your bloodstream and to help you use more oxygen properly. Therefore, you feel energized and do not tire easily.
Cardiovascular exercise is any dynamic activity that increases heart rate and respiration and increases oxygen and blood flow throughout the body while using large groups of body muscles repeatedly and rhythmically. Such activity gradually challenges your vital organs and improves the functioning and functioning of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system. Cardio improves many aspects of health, including heart health, mental health, mood, sleep, weight control and metabolism.
In fact, the heart is much stronger with all the beats as it pumps oxygen-carrying blood, the lungs effectively absorb oxygen, and the muscles are more equipped to use more oxygen. However, like breathing and heart rate increase, surgery should not make you feel like you need to stop and relax. During cardio such as walking, cycling, swimming, running or climbing, if you feel a strong desire to stand and rest, unusual pain or terrible symptoms, then you should stop immediately and seek medical help.
But for exercise to be considered cardio, it should increase your heart rate and respiratory rate to moderate to high intensity (at least 50 per cent of normal) for at least 10 minutes. This is why activities that are performed to improve strength, such as exercise, weight training, weight lifting, and basic exercise are NOT considered cardio because they do not increase heart rate during exercise.
Why should you engage in cardiovascular exercise?
Cardio exercises use your major muscles in the long run, keeping your heart rate at least 50 per cent high. With regular aerobic exercise, you will have a stronger, more capillary cardiovascular system that brings more oxygen to your muscle cells. You will also enjoy extra strength and endurance in each passing moment.
Some benefits of cardio exercise include:
Improved heart health
When you participate in 30-60 minutes of daily cardiovascular exercise, you can build stronger muscles, including those of the heart, which control your blood pressure, improve HDL (good cholesterol), reduce anxiety and stress, lower blood proteins and fats. they contribute to the increase in blood pressure, prevent heart disease, and lower blood sugar and control diabetes.
Improved brain health
By engaging in regular cardio, the brain regions that control memory and thinking skills grow in volume or size. The regular cardiovascular function also reduces the rate of brain damage in older people, improving their mental performance. But cardio can help you achieve a good night’s sleep, which is essential for your mental health.
Increased metabolic rate
All forms of cardio increase metabolism by producing the hormone Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21), which increases body metabolism, suppresses appetite and causes the burning of extra calories.
Weight control
By increasing the heart rate in the target area of the heart, which is the area where the body burns many calories, cardio helps to burn excess calories and control weight. Exercises such as walking, swimming, jogging and jogging burn excess calories over time while moderate to extreme cardio burns quite a few calories per exercise session. Examples of cardio exercises that are very effective in weight loss include jumping rope, running stairs, walking, rowing, cycling and temporary high-intensity training (HIIT).
Emotions and strengths developed
Exercise and cardiovascular activity trigger the production of endorphins — chemical substances that cause pleasure. Cardio also causes an increase in the production of mood-stimulating hormones such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. When the weather improves, you feel energized and ready to complete your normal activities. But the increased release of hormones also reduces stress, intensifies energy, increases energy, and improves memory and concentration.
The immune system is strong
Regular exercise increases the release of antibodies and white blood cells, which improve your body’s ability to fight infections. The release of FGF21 also speeds up metabolism and strengthens the immune system. In fact, cardio protects the body against a number of diseases, including high blood pressure, stroke, osteoporosis, diabetes, and heart disease.
Treatment of arthritis
Cardiovascular exercise helps to reduce the pain associated with arthritis and reduces joint stiffness.
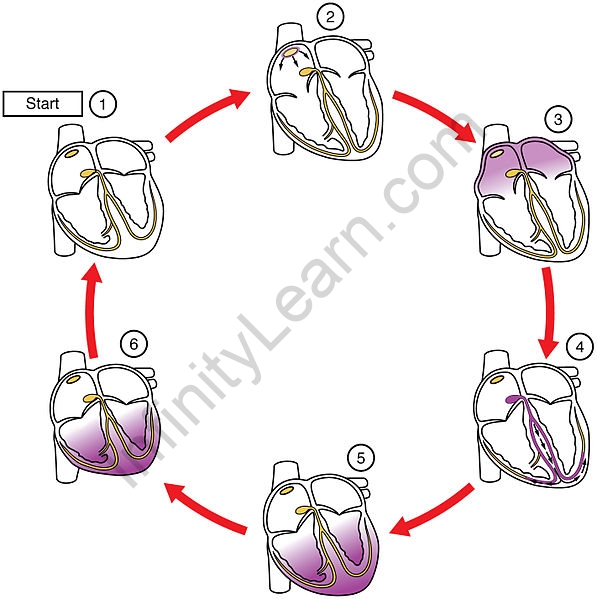
The main purpose of the heart is to pump blood to the body; it acts in a repetitive sequence called the heart cycle. The cardiovascular system is associated with the filling and pouring of blood vessels through electrical signals that cause the heart muscle to reach and relax. The human heart beats more than 100,000 times a day. In each cardiovascular system, the heart contracts (systole), pump blood and pumps it to the body; this is followed by a resting phase (diastole), in which the heart is filled with blood, as shown in Figure 1. Atrial contraction at the same time, forcing blood through the atrioventricular valves in the ventricles. Closing the atrioventricular valves produces a monosyllabic “lup” sound. After a short delay, the ventricles contract at the same time forcing the blood through the semilunar valves into the aorta and the arteries (through the pulmonary artery). Closing the semilunar valves produces a monosyllabic “dup” sound.
FAQ’s
How is cardiac function control done?
Photo effect of 38 faqs cardiac activity The cardiovascular system is a normal function of the human heart and is automatically controlled by the nodal tissues- sinoatrial node (SA node) and the atrioventricular node (AV node). Heart fluctuations cause an increase or decrease in cardiac output.
How is heart rate controlled?
The body's need for oxygen changes, such as when exercising, and heart rate is adjusted by adjusting both the heartbeat (HR) and the stroke volume (SV). As a result, cardiac output control is subjected to a complex mechanism involving the autonomic nervous system, endocrine system, and paracrine signalling mechanisms.







