Table of Contents
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Solved 2016 Set 8
Section A
1.Skin act as a major type of a physical barrier. Discuss its role.
2.Justify the process proposed by Mendel in which alleles tends to move into different gametes.
3.Define secondary productivity.
4.Vestigial organs differs from atavistic organs in human beings. Discuss with examples of each.
5. If a dicotyledonous plant tends to bear flowers but fails to produce fruits and seeds. What might be the cause behind this? Explain.
Section B
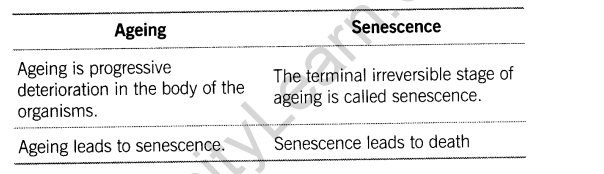
6.Differentiate between ageing and senescence.
7.State the cause behind the discontinues synthesis of DNA on one parental strand of DNA. Also explain what happens to these short stretches of DNA been synthesised.
8.On a visit of a Botanical garden, vidhu got to know about the storage of pollen grains of flowers. What do you think about this? How pollens are stored in a bank according to you? Discuss.
9.What are the disadvantages of ecological pyramids?
Or
Why the pyramid of energy is always upright?
10.Biotechnologists often believes that line of treatment of genetic disease is often different when compared to the infectious diseases. Discuss.
Section C
11.Explain the functions of
(i)restriction endonucleases (ii) DNA polymerase (iii) DNA ligase
12.Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow.
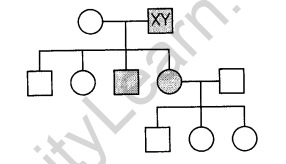
(i)Is the trait recessive or dominant?
(ii)Is the trait sex-linked or autosomal?
(iii)Give the genotypes of the parents shown in generation I and their third child shown in generation II and the first grand child shown in further generation.
13.Describe how the changing levels of FSH, LH and progesterone during menstrual cycle induce changes in the ovary and the uterus in human female.
14.Give adapting features of plants and animals, growing in an inadequate water conditions.
15.What are the benefits of transgenic animals?
16.Describes the terms
(i)Tetrasomic
(ii)Monosomic
(iii)Nullisomic
17.Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
Or
Explain the function of bone marrow and thymus in providing immunity.
18.Does fitness of a population help in evolution?
19.Biologists believes that Amniocentesis is the advantageous technique as it can easily detect the genetic disorder in a developing foetus. Describe its procedure and also state if it is useful then why is banned to use.
20.Green revolution has increased the food supply but yet it was not enough to feed the growing human population. In a country like India, where majority of farmers are poor, what could be the other option and how the food quality and quantity can be enhanced?
21.Explain the technology of tissue culture briefly.
22.As a responsible citizen of your nation does you really believes in a natural method of controlling population which states that if a big animal eats a small animal, population will be maintained. Is it really true? Put forth your opinion about this phenomenon (both advantages and disadvantages) and the fact behind it.
Section D
23.Some parents wrote a complaint letter to the local municipality to remove all the hoardings in city advertising the use of condoms and matters relating to AIDS prevention. The children of these parents came to know about the matter and raised their voice against removal of those hoardings. The parents were convinced by the awareness level of their children and withdraw the complaint. If parents considered the hoarding to be sight pollution then, why do you really disagree? Also discuss the methods by which AIDS spreads and the value promoted by the children to protest against their parents.
Section E
24.When a garden pea plant with green pods was cross-pollinated with another pea plant with yellow pods, 50% of the progeny bore green pods.
(i)Work out the cross to illustrate this.
(ii)What do you refer to this type of cross and why it is done?
(iii)Sex determination in human beings set an example of male heterogamety. Why it is so?
Or
Study the schematic representation of the genes involved in the lac operon given below and answer the questions that follow.
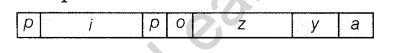
(i)Identify and name the regulatory gene in this operon. Explain its role in ‘switching off’ the operon.
(ii)Why is lac operon’s regulation referred to as negative regulation?
(iii)Name the inducer molecule and the products of the genes ‘z’ and ‘y’ of the operon. Write the function of these gene products.
25.(i) Draw a labelled longitudinal view of an albuminous seed.
(ii)How are seeds advantageous to flowering plants?
Or
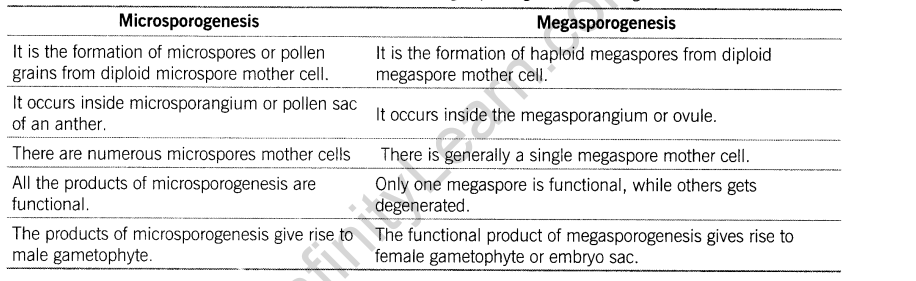
Differentiate between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis. Name the structure formed at the end of the two events.
26.Enumerate some major effects of air pollution on plants and animals.
Or
Explain any two ways of ‘improper resource utilisation’ that can cause degradation of natural resources.
Answers
Section A
1.Skin act as a major type of a physical barrier. Discuss its role.
Ans.Skin is the first line of mucus coating of defence because it prevents the entry of the pathogens into the body.
2.Justify the process proposed by Mendel in which alleles tends to move into different gametes. Ans.Mendel proposed a law of Segregation which acts as the phenomenon in which alleles tends to move into different gametes.
3.Define secondary productivity.
Ans.Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by the consumers.
4.Vestigial organs differs from atavistic organs in human beings. Discuss with examples of each.
Ans.Vestigial organs are supposed to be non-functional in an organisms but were functional in their ancestors, e.g. vermiform appendix of a men. While, atavistic organs are those which have the tendency to revert to their ancestral type. e.g. baby formed with a tail.
5. If a dicotyledonous plant tends to bear flowers but fails to produce fruits and seeds. What might be the cause behind this? Explain.
Ans.It a flower shows such condition, this ensures that plant is dioecious in nature and bears only staminate flowers.
Section B
6.Differentiate between ageing and senescence.
Ans.Differences between ageing and senescence are given below
7.State the cause behind the discontinues synthesis of DNA on one parental strand of DNA. Also explain what happens to these short stretches of DNA been synthesised.
Ans.Discontinuous synthesis of DNA occurs on the lagging strand of the replication fork which indicates that base pairs runs in the opposite direction to the leading strand. The polymerase attaches to the DNA and replicates away from the fork. The short stretches thus formed also known as Okazaki fragments are joined by the enzyme called DNA ligase to form a complete single strand of DNA.
8.On a visit of a Botanical garden, vidhu got to know about the storage of pollen grains of flowers. What do you think about this? How pollens are stored in a bank according to you? Discuss. Ans.Pollen grains from flowers can be stored in pollen banks just like the seeds in the seed banks. These can be easily stored for years altogether in a liquid nitrogen at -196°C, and can be used in different plant breeding programmes whenever needed.
9.What are the disadvantages of ecological pyramids?
Or
Why the pyramid of energy is always upright?
Ans.Disadvantages of ecological pyramids are
(i)It does not accommodate a food web and never takes into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
(ii)Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though, they play an important role in ecosystem.
Or
Pyramid of energy is always upright because when energy flows from a particulartrophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step. Each bar in the energy pyramid indicates the amount of energy present at each trophic level in a given time or annually per unit area.
10.Biotechnologists often believes that line of treatment of genetic disease is often different when compared to the infectious diseases. Discuss.
Ans.Believing such thing is really true because line of treatments of both types of diseases is very different because genetic diseases are actually not treated with any medication i.e. their signs and symptoms can betaken most care of. Hence, they can be only treated by the manipulation of defective gene and replacing it with the correct one. While, the condition not same with the infectious diseases as they are usually caused by pathogens thus, can be easily treated with medication by hampering the growth of the microbes.
Section C
11.Explain the functions of
(i)restriction endonucleases (ii) DNA polymerase (iii) DNA ligase
Ans.(i) Restriction Endonuclease cuts DNA at specific site forming DNA fragments.
(ii)DNA Polymerase uses DNA template to catalyse the reaction and also catalyses polymerisation of a large number of nucleotides in a very short time.
(iii)DNA Ligase joins discontinuously synthesised DNA fragments.
Thus, all these three enzymes find heavy uses in DNA replication, transcription and translation.
12.Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow.

(i)Is the trait recessive or dominant?
(ii)Is the trait sex-linked or autosomal?
(iii)Give the genotypes of the parents shown in generation I and their third child shown in generation II and the first grand child shown in further generation.
Ans.(i) Trait is recessive.
(ii)Trait is autosomal.
(iii)Genotype of parents in generation l-female-Hba Hbs, male-Hbs Hbs.
Genotype of third child in generation Il-Hbs Hbs
Genotype of first grandchild in generation 11 l-Hba Hba.
13.Describe how the changing levels of FSH, LH and progesterone during menstrual cycle induce changes in the ovary and the uterus in human female.
Ans.The secretion of gonadotropins, i.e. LH and FSH increase gradually during the follicular phase, which stimulates follicular development as well as secretion of estrogens by the growing follicles. The rapid secretion of LH during mid-cycle induces rupture of Graafian follicle and thereby, release of the ovum.
The corpus luteum, developed from Graafian follicle, secretes large amounts of progesterone, which is essential for the maintenance of endometrium for implantation.
14.Give adapting features of plants and animals, growing in an inadequate water conditions. Ans.Adapting features of plants and animals that growing in an adequate water condition are Plants Desert plants live in scarcity of water and show thick cuticle on leaf surface. Stomata are arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss through transpiration. Special photosynthetic pathway (CAM plants) enables their stomata to remain closed during day time. e.g. Opuntia have no leaves, they are reduced to spines and the photosynthetic function is taken over by flattened stems.
Animals
Kangaroo rat in deserts of North America is capable of meeting all of its water requirements through its internal fat oxidation (in which water is a byproduct). It also has the ability to concentrate its urine for minimal loss of water.
15.What are the benefits of transgenic animals?
Ans.Transgenic animals are beneficial in the following ways
(i)Normal Physiology and Development To study that how genes are regulated and how they affect normal function of the body. For example, the study of complex factors involved in growth such as insulin like growth factors.
(ii)Study of Disease To increase our understanding of how genes contribute to the development of diseases such as cancer, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer etc.
(iii)Biological Products Transgenic animals that produce useful biological products can be created by the introduction of the portion of DNA (or genes), which codes for a particular product. For example, Human protein (a-1 -antitrypsin) used to treat emphysema.
16.Describes the terms
(i)Tetrasomic
(ii)Monosomic
(iii)Nullisomic
Ans.(i) Tetrasomic It is aneuploid having one chromosome represented four times. Tetrasomics show more variability than trisomics.
(ii)Monosomic It is an aneuploid in which one chromosome is devoid of its homologue. Monosomic is generally weaker than the normal form.
(iii)Nullisomic The aneuploid is deficient in a complete pair of homologous chromosomes.Nullisomics do not survive except amongst polyploids.
17.Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
Or
Explain the function of bone marrow and thymus in providing immunity.
Ans.When the symptoms of the disease are not visible and the pathogen concentration is very low, then detection by conventional diagnostic tests is very difficult. However, at that time detection is possible by the amplification of their nucleic acid by the technique known as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
The principle involved here is that a single DNA molecule can be copied endlessly in a test-tube, using primers, DNA polymerase enzyme and free nucleotides under appropriate conditions.
Or
Bone marrow and thymus play important part in providing immunity in the following way
(i)Both are the main primary lymphoid organ, where all the blood cells including lymphocytes are produced.
(ii)Immature lymphocytes differentiates into antigen sensitive lymphocyte.
(iii)Provides micro environments for the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes.
(iv)After maturation, lymphocytes migrates to the secondary lymphoid organs like spleen, lymph nodes, MALT, etc.
18.Does fitness of a population help in evolution?
Ans.Yes, according to Darwin, fitness ultimately refers to reproductive fitness. Those who best fit in an environment, can reproduce well and survive.
Hence is selected by the nature. He called this natural selection and simplified it as a mechanism of evolution.
19.Biologists believes that Amniocentesis is the advantageous technique as it can easily detect the genetic disorder in a developing foetus. Describe its procedure and also state if it is useful then why is banned to use.
Ans.Amniocentesis is a technique by which genetic disorder in a developing foetus can be detected. This is based on the chromosomal pattern in the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing embryo.
Amniotic fluid contains cells and molecules shed by the foetus. The chromosomes of foetal cells can also be used to find out the sex of the foetus and certain abnormalities. Thus, if an abnormality is found, the mother can get the foetus aborted.
Yes, the technique is banned now inspite of its usefulness as the people had started misusing it due to female foeticides. And this ban is extremely necessary to maintain or balance the ratio of males and females in our society.
20.Green revolution has increased the food supply but yet it was not enough to feed the growing human population. In a country like India, where majority of farmers are poor, what could be the other option and how the food quality and quantity can be enhanced?
Ans.The other option to enhance the quality of food that could increase the food supply by genetic modification of organisms and by using genetically modified plants is in the following ways
(i)Made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, salt and heat).
(ii)Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides (pest-resistant crops).
(iii)Helped to reduce post-harvest losses.
(iv)Increased efficiency of mineral usage by plants (this prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil).
(v)Enhanced nutritional value of food, g., vitamin-A enriched rice.
21.Explain the technology of tissue culture briefly.
Ans.Tissue culture is an advanced technique which was developed, when old traditional techniques had been failed to fulfil the growing demands of crop improvement. By this technique, whole plants can be regenerated from explants (any small plant part) under sterile condition in a special nutrient media, the nutrient media must provide a carbon source (such as sucrose), in organic salts, vitamins, amino acids and growth regulators such as auxins, cytokinins etc. The capacity to generate a whole plant from any explant is called Totipotency. The plants thus, generated are genetically similar to the original plant through which they are grown, so they are called somaclones.
22.As a responsible citizen of your nation does you really believes in a natural method of controlling population which states that if a big animal eats a small animal, population will be maintained. Is it really true? Put forth your opinion about this phenomenon (both advantages and disadvantages) and the fact behind it.
Ans.Such phenomenon of eating lower animals by the bigger ones is called predation. It is right in many ways as by doing this, the predator helps to keep the population of the prey under a control and also help in maintaining the diversity of species in a community by reducing the intensity of competition among prey species.
But, inspite of all this, it may also has an ill-effect on the population of one type of species as if bigger animals will eat lower animals continuously, the population of bigger animals may rise to the population of the lower ones which is again not satisfactory for the community. Thus, a balance should be maintained.
Section D
23.Some parents wrote a complaint letter to the local municipality to remove all the hoardings in city advertising the use of condoms and matters relating to AIDS prevention. The children of these parents came to know about the matter and raised their voice against removal of those hoardings. The parents were convinced by the awareness level of their children and withdraw the complaint. If parents considered the hoarding to be sight pollution then, why do you really disagree? Also discuss the methods by which AIDS spreads and the value promoted by the children to protest against their parents.
Ans.(i) Since, the awareness among people has not reached to that extent so, the forceful and constant reminding is always required. Our country is over-populated and number of AIDS cases are increasing rapidly.
(ii)Some methods by which AIDS spreads are
(a)Unprotected sexual contact.
(b)Use of contaminated needles and syringes.
(iii)Children are
(a)Educated
(b)Initiative takers
(c) Conscious about their society
Section E
24.When a garden pea plant with green pods was cross-pollinated with another pea plant with yellow pods, 50% of the progeny bore green pods.
(i)Work out the cross to illustrate this.
(ii)What do you refer to this type of cross and why it is done?
(iii)Sex determination in human beings set an example of male heterogamety. Why it is so?
Or
Study the schematic representation of the genes involved in the lac operon given below and answer the questions that follow.

(i)Identify and name the regulatory gene in this operon. Explain its role in ‘switching off’ the operon.
(ii)Why is lac operon’s regulation referred to as negative regulation?
(iii)Name the inducer molecule and the products of the genes ‘z’ and ‘y’ of the operon. Write the function of these gene products.
Ans.(i) To test that 50% progeny is green ‘test cross’ can be done.
(ii)This type of cross is called test cross because this is done between the organism of unknown dominant genotype with recessive parent in order to evaluate whether the dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous. (iii)Sex determination is human beings is an example of male heterogamety because males produces two different types of gametes i.e., X and Y.
Or
(i)Regulatory gene in this operon is ‘/’ gene.
Role of regulatory gene in switching off operon is as follows
- It codes for the repressor protein of the operon, which is synthesised constitutively.
- The repressor has the affinity for the operator gene. It binds to operator and prevents the RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes.
(ii)When repressor binds to the operator, the operon is switched off and transcription is stopped. So, it is called a negative regulation.
(iii)Lactose is an inducer molecule.
Gene ‘z’ codes for galactosidase, which is responsible for the hydrolysis of lactose into galactose and glucose.
Y gene codes for permease. It increases the permeability of the cell to P-galactosidase.
25.(i) Draw a labelled longitudinal view of an albuminous seed.
(ii)How are seeds advantageous to flowering plants?
Or
Differentiate between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis. Name the structure formed at the end of the two events.
Ans.(i) Longitudinal View of an Albuminous Seed
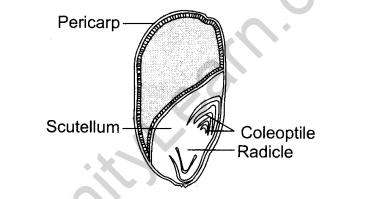
(ii) Seeds are advantageous to flowering plants in following ways
- These are the final product of sexual reproduction.
- Since, reproductive process such as pollination and fertilisation are independent of water, seed formation is more dependable.
- Seeds have better adaptive strategies for dispersal to new habitat.
- Hard seed coat provides protection to young embryo.
- Basis for agriculture.
Structures formed at the end of two events
(i)Microsporogenesis — Microspores (pollen grain)
(ii)Megasporogenesis — Megaspores (embryo sac).
26.Enumerate some major effects of air pollution on plants and animals.
Or
Explain any two ways of ‘improper resource utilisation’ that can cause degradation of natural resources.
Ans.Effects of air pollutants on plants are
(i)Causes fruit damage, leaf damage, chlorosis and necrosis, mottled spots on leaves.
(ii)Slow the growth yield of crops and cause premature death of plants.
(iii)Weakens plants and increases the infestation by pests.
(iv)Acid rain damages the aerial parts and also acidifies the soils. It leads to the production of free radicals and decrease in photosynthesis and productivity.
On Animals and Humans are
(i)About 40% of human deaths occur due to air pollution.
(ii)Increased susceptibility to diseases.
(iii)Causes cancer and genetic mutations.
(iv)Causes respiratory ailments and asthma, hay fever and allergic diseases.
(v)Causes cardiovascular diseases and damage to CNS.
(vi)Immediate effects like nausea, headache, irritation to the eyes and nose.
Or
(i)Soil Erosion and Desertification
Improper human activities can remove top soil, resulting in arid patches of land.Natural resources get degraded not only by pollutants, but also by improper practices of their utilisation and maintenance. Soil erosion is caused by human activities like over-cultivation, unrestricted grazing, deforestation and poor irrigation. All these practices lead to the removal of top soil. Desertification is also a major problem these days, that occurs mainly due to urbanisation.
(ii)Water-Lodging and Soil Salinity
Irrigation without proper drainage of water leads to water-lodging in the soil. It draws salt to the surface of the soil. Deposited salt starts collecting at the roots of the plants and affect the plant growth and productivity. It is extremely damaging to the agriculture. Water-lodging and soil salinity are some of the problems that have come in the wake of the Green Revolution.
(Download Questions PDF)
[gview file=”https://resultscareer.files.wordpress.com/2015/12/cbse-sample-papers-for-class-12-sa2-biology-solved-2016-set-8-questions.pdf”]
(Download Solutions PDF)
[gview file=”https://resultscareer.files.wordpress.com/2015/12/cbse-sample-papers-for-class-12-sa2-biology-solved-2016-set-8-solutions.pdf”]







