Table of Contents
Nucleic acids are organic molecules found in all organisms that take the form of DNA or RNA. These nucleic acids are created by combining nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules, and phosphate groups that are connected together in a series of linkages. The DNA structure establishes our body’s fundamental genetic composition. In fact, it defines practically all of life on Earth’s genetic composition.
“DNA is a set of molecules that is in charge of transporting and transferring hereditary elements or genetic instructions from parents to children.” Deoxyribonucleic Acid is another name for DNA. It is an organic molecule with a distinct molecular structure.
DNA Types
There are three forms of DNA:
- A-DNA is a right-handed double helix, comparable to B-DNA. Dehydrated DNA takes on the A form, which shields the DNA against severe conditions such as desiccation. Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA, causing it to acquire an A shape.
- B-DNA is a right-handed helix and is the most prevalent DNA shape. The majority of DNA has a B-type shape.
- Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA in which the double helix coils in a zig-zag pattern to the left. Andres Wang and Alexander Rich found it. It is found before the start site of a gene and is thought to play a role in gene regulation.
The Structure of DNA (Composition)
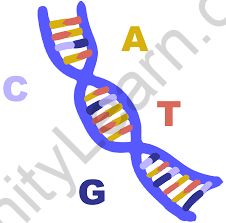
The DNA structure can be compared to a twisted ladder. This structure is known as a double-helix. It is a nucleic acid, and nucleotides are the building blocks of all nucleic acids. The DNA molecule is made up of units called nucleotides, and each nucleotide is made up of three separate components: sugar, phosphate groups, and nitrogen bases.
Nucleotides are the fundamental building blocks of DNA and are made up of a sugar group, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. The sugar and phosphate groups join the nucleotides to produce each DNA strand. Nitrogen bases are classified into four types: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
These four nitrogenous bases couple as follows: A with T, and C with G. These base pairs are required for the double helix structure of DNA, which resembles a twisted ladder. The arrangement of the nitrogenous bases determines the genetic code or DNA instructions.
Sugar is the backbone of the DNA molecule and is one of the three components of DNA structure. It is also known as deoxyribose. The DNA molecule is made up of four nitrogen bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), which combine to form the structure of a nucleotide. The letters A and G are purines, while the letters C and T are pyrimidines.
FAQs
What is the DNA structure?
DNA is a nucleotide-based double helix structure. Hydrogen bonds hold the two helices together. A sugar-phosphate backbone is also present in the DNA.
What distinguishes Z-DNA from other types of DNA?
Z-DNA is a double helix with a left-handed twist. In a zig-zag pattern, the helix winds to the left. A and B-DNA, on the other hand, are right-handed DNA.



