Table of Contents
“The chemical characteristics of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number,” according to the rule that underpins the modern periodic table. We looked at the tendencies as a group and across time. The Diagonal Relationship of the Elements refers to the pairings of diagonally adjacent elements in the second and third periodic tables.
In S block elements, a diagonal link occurs between neighbouring elements in the second and third periods of the periodic table. The attributes of S block elements differ dramatically from those of the other elements in the sub-group to which they belong.
Certain elements in the periodic table have a diagonal connection. These elements are located diagonally adjacent in the periodic table’s second and third rows, among the first twenty elements.
The characteristics of diagonal elements are frequently similar, as shown when travelling from left to right and down the group in the periodic table. It is most noticeable among the lighter members. Thus, the couples that exhibit a diagonal connection are Lithium (Li) of group IA and Magnesium (Mg) of group IIA, Beryllium (Be) of group IIA, and Aluminium (Al) of group IIIA, Boron (B) of group IIIA and Silicon (Si) of group IVA, Carbon (C) from group IVA and Phosphorus (P) from group VA.
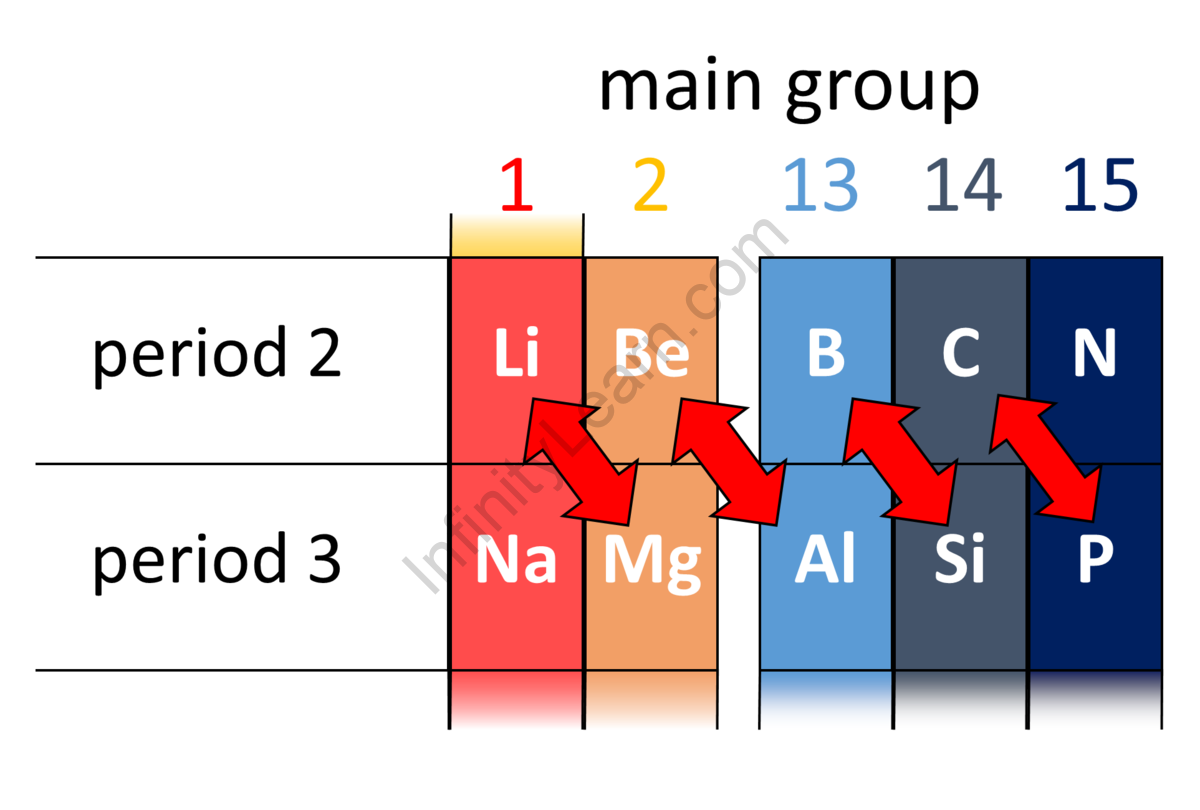
Diagonal Relationship: Reason
The diagonal connection occurs as a result of the periodic table’s distinct atomic characteristics varying between groups and eras Because of the polarizing effect of the diagonally positioned components, the polarising power rises as the charge of the ions increases, whereas the ionic size decreases. Moving down the group reduces ionic size, which reduces polarising power. These effects cancel out to some extent while travelling diagonally.
Important Points
- The diagonal neighbours have a lot in common. As you proceed from left to right and along with the periodic table, you will see such a connection; the periodic table contains opposing factors.
- Diagonal correlations arise as a result of the various ways in which numerous atomic characteristics change between groups and periods of the Periodic Table.
- In addition to group and period links, the constituents of the s and p-blocks have diagonal relationships.
- Moving diagonally across the periodic table reveals significant similarities, although they are considerably less evident than similarities within a group. The diagonal connection is most visible in the elements of the periodic table’s second and third periods.
- Because the polarising power, ionic charge/ionic radius, is equivalent for diagonally positioned components, the diagonal connection occurs.
FAQs
Is there a diagonal link between boron and silicon?
Yes, the diagonal link exists between Boron (B) of Group IIIA and Silicon (Si) of Group IIA.
What exactly is the diagonal effect?
Some components of period 2 and period 3 have a propensity to exhibit features that are similar to those of the right and down elements, rather than those of their own family. As a result, this is the diagonal effect.
What is the reason for the diagonal relationship?
The diagonal connection is generated because the ions are about the same size.



