Table of Contents
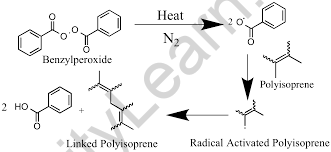
Rubber vulcanization is a process that improves the flexibility and strength of rubber by heating it in the presence of sulfur, resulting in three-dimensional cross-linking of the chain rubber molecules (polyisoprene) connected to each other by sulfur atoms.
There are two types of rubber:
- Natural
- Synthetic
Natural rubber is made from latex, which is a milky emulsion extracted from the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) or other plants. Coagulation of latex results in the formation of a soft, plastic, and sticky material (crude rubber), which is subsequently vulcanized (cured). Polyisoprene molecules make up natural rubber.
Synthetic rubbers are Elastomers, which have elastic qualities comparable to natural rubber. The chemical makeup of synthetic rubber may be comparable to that of natural rubber (synthetic polyisoprene).
Polybutadiene, poly(styrene-butadiene-styrene), polychloroprene (Neoprene), polyisobutylene (Butyl rubber), and silicone are examples of synthetic rubbers.
The vulcanization procedure consists of the following major stages:
- Mixing crude rubber with 5-30% sulphur (cross-linking agent) and other additives such as activator (commonly zinc oxide or stearic acid), accelerator (guanidines, thiazoles, dithiocarbamates, xanthates, thiurams), coagulants (acetic acid, calcium chloride), anti-oxidants (amines, phenolics, phosphites), colour pigments, surfactants, softeners ( (Rosin derivates, coumarone-indene resins, aliphatic petroleum resins, alkyl-modified phenol-formaldehyde resins).
- At this point, slow cross-linking begins. It is critical to avoid aggressive vulcanization during mixing, which might result in crack development during the moulding step.
- The rubber mixture is moulded (shaped). Because cross-linking makes shaping difficult, the rubber must be formed prior to heating.
- Heat the mixture to a temperature of 250-400°F (120-200°C). Temperature increases hasten the vulcanization process, resulting in rapid and full cross-linking. C-S bonds are used to connect chain polyisoprene molecules instead of C-H bonds. One to seven sulfur atoms form each connection.
- To avoid the production of brittle rubber, the density of cross-links must be regulated.
Tensile strength, elasticity, hardness, tear strength, abrasion resistance, and solvent resistance are all increased by vulcanization.
Rubber Applications
Rubber may be used for a variety of purposes and on a variety of platforms, a few of which are listed below.
- It is commonly used to line chutes, bins, and industrial mixers. It may be converted into an excellent insulator due to its water-proof and robust properties.
- Rubbers are also utilized for flooring because they provide cushioning, minimize fatigue, and are waterproof and slip-resistant.
- Its employment in the vehicle sector may be seen in tires, brake padding, airbags, seats, and roofs, among other places.
- It may be utilized in the apparel sector as wetsuits and expanded clothing such as gym and cycling shorts, among other things.
FAQs
What exactly is the distinction between natural and synthetic rubber?
Natural rubber is polyisoprene with isoprene monomer units, i.e. 2-methyl-1,3 butadiene. Natural rubber is derived from the bark of some tropical and subtropical plants as solid particles floating in a milky white liquid (called latex). Neoprene is a kind of synthetic rubber. Neoprene's monomer is 2-chloro-1,3-butadiene, often known as chloroprene.
What are some of the drawbacks of natural rubber?
The drawbacks of natural rubbers include their low resistance to organic acid assault. It has a short lifespan. It experiences irreversible distortion when stretched to a higher amount.



