Table of Contents
Markownikoffs and Peroxide Effect: When a protic acid (HX) is introduced to an asymmetrical alkene, its acidic hydrogen attaches to the carbon atom with more hydrogen substituents, whereas the halide group binds to the carbon chain with one of the most alkyl substituents.
Overview
“Hydrogen is added to a carbon with the most hydrogens, and the halide is placed to the carbon with the least hydrogens,” to simplify the rule. The introduction of hydrobromic acid (HBr) to propene is an example of a reaction that follows Markovnikov’s rule.
Important concepts
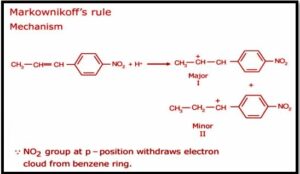
Markownikoff effect: Consider the same example as before, namely the addition reaction of hydrobromic acid with propene, to understand the mechanism behind Markovnikov’s Rule. Markovnikov’s rule mechanism can be split down into the two steps below.
Step 1: The protonation of the alkene produces a more stable carbocation. The protonation of the alkene can result in the formation of two types of carbocations: a primary carbocation and a secondary carbocation. The production of a secondary carbocation is significantly more stable than the synthesis of a primary carbocation.
Step 2 The carbocation is now attacked by the halide ion nucleophile. The alkyl halide is formed on the basis of this reaction. Because the production of the secondary carbocation is favoured, 2-bromopropane would be the main result of this reaction.
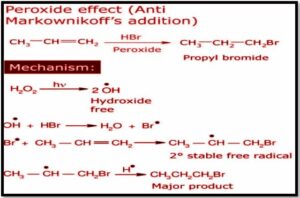
Peroxide effect: Alkanes are unsaturated hydrocarbons, meaning that each molecule of an alkane has at least one double bond. Alkenes exhibit anti-addiction Markovnikov’s reactions, in which the electrophile strikes the carbon-carbon double bond to produce extra products, due to the presence of ‘pi’ electrons. When any polar molecule is introduced to an unsymmetrical alkene in the form of organic peroxide, the negative half of the molecule is attached to the carbon atom that has more Hydrogen atoms bonded to that than the other unsaturated carbon. The peroxide effect is what causes this.
Significance of Markownikoffs and Peroxide Effect in IIT JEE exam
Markownikoff’s rule is part of organic chemistry, which is the study of organic substances. The information on Markownikoff’s rule and the Peroxide Effect is based on electrophilic addition reactions and is discussed. The weightage of Markownikoff’s rule plus the Peroxide effect is 6.33 per cent.
FAQs
What does Markovnikov's rule say about the future
When a protic acid is introduced to an unsymmetrically substituted alkene, Markovnikov's rule predicts the regiochemistry of the reaction
Which of the reactions defies Markovnikov's rule
Because the regioselectivity of the mechanism of free radical addition reactions is not predicted by Markovnikov's rule, these reactions do not obey Markovnikov's rule
What is the anti-Markovnikov rule or peroxide effect
In the presence of organic peroxides, the peroxide effect, also called anti addition, occurs when HBr puts on the wrong way around.

