Table of Contents
Information, messages, data, and signals can now be sent from one location to another in seconds. Modulation is being used in the communication system to increase the range of the signals. The majority of signals produced in daily life have sinusoidal waveforms. A sinusoidal wave is a curve that represents smooth repetitive oscillations. Signals sent during communication contain critical information in the form of a sinusoidal wave. Modulation and its variants are critical in the rapid transmission of signals from the sender to the receiver. The superimposition of the signal wave (carrying the message) with a high-frequency carrier signal to ensure the faster signal transmission is known as modulation. Modulation is a widely used process in communication systems that uses a very high-frequency carrier wave to transmit a low-frequency message signal so that the transmitted signal retains all of the information contained in the original message signal. Because the message signals have a very low frequency, they cannot be transmitted over long distances. As a result, low-frequency message signals are modulated over high-frequency carrier signals.
Overview
The transmission of information over long distances by communication systems is a remarkable feat of human ingenuity. We can communicate with, video chat with, and text with anyone on the planet! To increase the reach of the signals, the communication system employs a very clever technique known as Modulation. This process involves two signals. Message signals, as well known as baseband signals, are the frequency band that represents the original signal. This is the signal that will be sent to the receiver. Typically, the frequency of such a signal is low. A high-frequency sinusoidal wave is also involved in this. This signal is referred to as the carrier signal. Carrier signals almost always have a higher frequency than baseband signals. The baseband signal’s amplitude is transferred to the high-frequency carrier. A higher frequency carrier can travel much further than a baseband signal.
Modulation
One of the most important branches of electronics science, modulation is widely used in communication systems. It incorporates the signal’s various fundamental properties in order to transpose it from one location to another.
Signals that are used in modulation
Modulating Signal: A message signal is a signal that contains the message to be transmitted from the sender to the receiver. Message signals are typically in the low or high-frequency range and are referred to as baseband signals. Message signals are the signals that will be sent from the sender to the receiver. In general, the frequency of the message signals to be sent is low. As a result, these signals must be modulated in order to be correctly transmitted from one location to another.
Carrier Signal: The carrier signal, which has high-frequency sinusoidal waves, is the other signal used in the modulation process. When compared to the baseband signal, the high-frequency carrier wave can travel much faster. These signals have a frequency, an amplitude, and a phase, but no information. Carrier signals are used to transmit the signal to the receiver after it has been modulated.
Modulated Signal: The resultant signal refers to the modulated signal after it has been modulated. This signal is a combination of the carrier and message signals.
Types Of Modulation
Modulation can be classified into three types:
Amplitude Modulation: When the base signal is superimposed on a carrier signal with a different amplitude but the same frequency, if the amplitude of the base signal modifies or modulates, this is referred to as amplitude modulation.
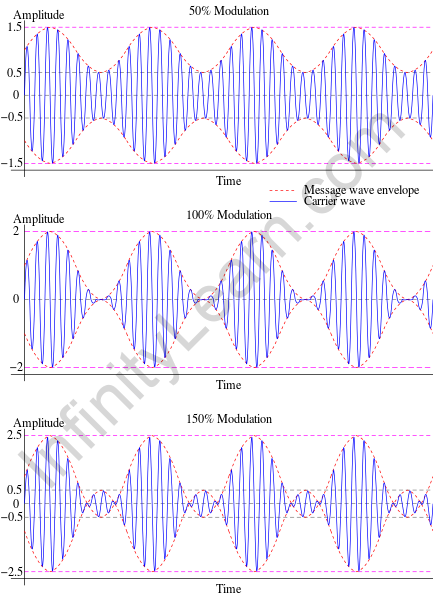
Phase modulation: This is a type of modulation in which the phase of the base signal changes while it is superimposed on a carrier signal.
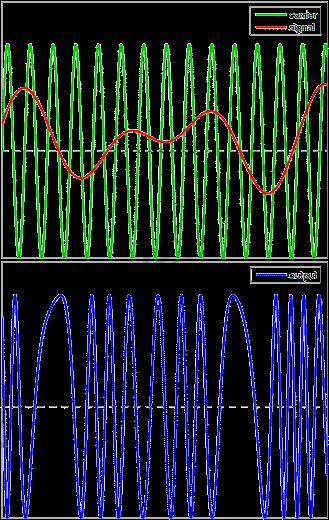
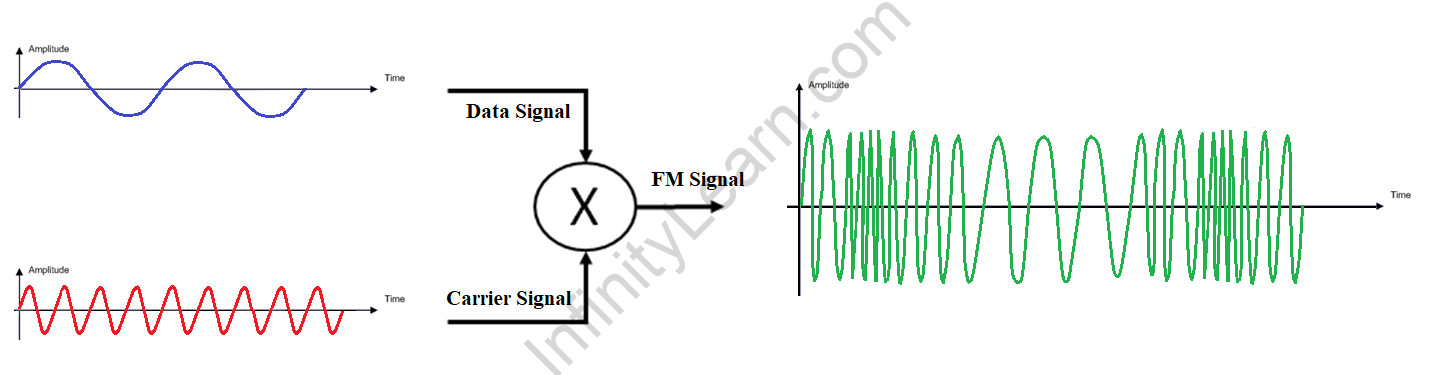
Frequency Modulation: If the frequency of the base signal modifies or modulates as a result of superimposing it with a carrier signal of a different frequency but the same amplitude, it is said to be frequency modulation.
Need for Modulation
(1) Increase Signal Strength: The sender’s baseband signals are not capable of direct transmission. The message signal’s strength should be increased so that it can travel longer distances. This is where modulation comes into play. The most critical requirement of modulation is to increase signal strength without affecting carrier signal parameters.
(2) Wireless Communication System: Modulation had already eliminated the need for wires in communication systems. This is due to the fact that modulation is widely used in transmitting signals from one location to another at a faster rate. As a result, the modulation technique has aided in the advancement of wireless communication systems.
(3) Preventing Message Signal Mixing: Modulation, as well as its variants, prevent the message signal from being interfered with by other signals. It’s because a person sending a message signal over the phone can’t tell them apart. As a result, they will cause each other problems. The mixing of the signals, on the other hand, can be avoided by using carrier signals with a high frequency. As a result, modulation ensures that the signals received by the receiver are flawless.
(4) Size of the Antenna: Signals in the 20 Hz to 20 kHz frequency range can only travel a short distance and the length of the antenna used to send the message signal should be one-quarter of the frequency used. As a result, modulation is required to raise the frequency of the message signal and increase its strength so that it can reach the receiver.
The antenna’s length can be easily calculated using the following formula:
L = λ = u/ν = (3 x 108) / ν
Where, L = length of antenna
λ = wavelength of the transmitted signal
ν = carrier wave frequency
Uses of Modulation
- The inter-conversion of signals from one form to another is one of the most common applications of various types of modulation.
- Digital modulation is a method of transmitting digital signals over analogue baseband.
- Analog Modulation is a technique for transferring low bandwidth signals, such as TV or radio signals, over a larger bandwidth.
- Modern modulation techniques have been widely used in FDM, or Frequency Division Multiplexing.
Also read: Kirchhoff’s Laws and their Applications
FAQs
What is the use of phase of modulation?
When radio waves are transmitted, the phase of modulation is critical. As a result, it has become an essential component of the transmission of coding schemes. Furthermore, it is ideal for communication signal transmission. The term phase modulation refers to the combination of two modulations, namely angle modulation and frequency modulation. Wi-Fi, satellite television, and GSM are the most common uses for radio waves.
What is the significant difference between PM and FM?
The modulating voltage determines the frequency deviation in FM. In the case of PM, however, frequency deviation is proportional to two quantities: modulating voltage and modulating frequency. When compared to PM, FM has a higher signal-to-noise ratio. In addition, FM has superior noise immunity when compared to PM.
Why modulation and demodulation are required?
Modulation could be used at the broadcasting station to send the audio signal over longer distances to a receiver. Once the modulated wave is picked up by the radio receiver, the audio signal must be recovered. It is done in the radio receiver and is known as demodulation.



