Table of Contents
Introduction
Genetic flow and genetic erosion are two of the three most important processes involved in the evolution of species. Both of these names are different, however, they are also connected. Genetic flow focuses on the transfer of genes from one gene to another, whereas genetic variation relies on allelic frequencies, another genetic variant.
Definition of gene flow and genetic predisposition
The flow of genes can be defined as the transfer of genes or genes from one gene to another into a group of genes that reproduce and lead to genetic mutations in the recipient. Genetic flow is also known as genetic migration.
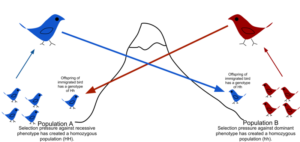
Genetic drift can be described as a powerful consequence of instability given the allelic frequencies of young people. It is usually caused by random events, errors in allele selection, or samples. Genetic mutations occur mainly in a small number of people because, for the most important people, allelic frequencies usually remain stable, releasing environmental factors such as natural selection.
Possible causes of gene flow and genetic erosion
Genetic flow and genetic predisposition are linked but vary in size, size, variability, gene expression, etc. Possible causes of genetic and emotional flow are a few factors listed below:
Reason for occurrence
Genetic flow occurs through continuous reproduction or breeding between two adjacent individuals while genetic abstinence occurs with continuous sample errors, termination, or imbalance in allelic frequencies of a small group of genes.
Population size
Genetic engineering is highly dependent on people of a particular type or group. Genetic groups with a limited population usually have a genetic drift. In contrast, an infinite number of people or large groups make a genetic flow, which changes the genetic group of the recipient group.
Evolution
The emergence of new genotype species and traits occurs through genetic flow and erosion, and the only difference is how growth occurs. In the process of genetic engineering, mutations occur through genetic mutations, the combination of their genetic makeup, and the opposite of evolution. In genetic drift, the formation of adjacent human beings is done with several effects: the bottle and the originator.
Genetic mutations
The variability occurs in genetic flow mainly due to the size of their group. The most genetic transfer is attributed to the flow of genes because they occur due to the pure natural migration of gametes, encounters with a number of young people, and the development of allelic diversity occurs. This is the process by which an allele is made. While genetic drift, due to its sudden and short-lived occurrence and small size, the emergence of diversity may not occur.
Factors affecting genetic flow and genetic erosion
- Geographical obstructions
Local factors prevent gene flow and genetic erosion in some cases. On the other hand, some natural conditions do not allow them to actually migrate and lead to genetic variation or alleles, which in turn hinders processes. For example, some environmental factors lead to a genetic variation where they are unable to reproduce with another population due to unavailability. Otherwise, human activities such as deforestation or forest fires also lead to genetic predisposition and genetic erosion.
- Productivity barriers
Reproductive barriers prevent genetic flow due to very low reproduction, or if a certain number of genes do not allow reproduction, then it can cause genetic flow inhibition. In addition, in genetic predisposition, due to the suspension of alleles reproduction can increase instability and prevent genetic erosion.
Examples of gene flow and genetic predisposition
- Genetic flow
Let’s take a real example of Indian citizens in America to understand the genetic flow. America may have had very few Indians living in their region at first. However, over time, the Indians began migrating to the United States and settling in, increasing the number of Indians in the Americas. Over time, several Indian colonies were formed in the United States, which could be referred to as a genetic mutation.
- Genetic drift
Let’s take the example of children with leopards and brown eyes. The brown eye is more common compared to children with leopard eyes; this makes brown eyes a prominent allele. However, because of the instability of children with leopard eyes, they may be at risk as their next-generation may not always have leopard eyes.
Also read: Darwin’s Contribution
FAQs
What factors contribute to the genetic flow and genetic erosion?
There are two major factors that influence gene flow and genetic predisposition 1.) Genetic interaction 2.) Positive location.
What are the three main processes of diversity?
Genetic flow, Genetic drift, Natural selection.
What are the different types of genetic drift?
Genetic drift has two known types, namely the bottleneck effect and the originator effect.
What is the allele that is acceptable for the next generation?
Alleys are a variety of genes that can also be described as one of their own as they are found in the same genetic makeup.





