Table of Contents
Introduction
Genetics contains information about the various characters and characteristics of living creatures. Genetic information is passed on from generation to generation by code. It determines the characteristics of an organism, for example, whether it is a bacterium or a person. The genetic code that a person has controls the entire process of life.
We will learn about the definition of genetic code and its structures in this section.
What is the meaning of genetic code?
We can define genetic code as a set of rules for living cells to translate information entered into genes (DNA or mRNA sequences). Ribosomes are responsible for completing the translation process. They use tRNA molecules (transfer RNA) to transport amino acids and read mRNA, three nucleotides at a time, to link amino acids to a specified system (messenger RNA).
Genetic code features
It is interesting to look at the intricate process of genetic engineering and to copy it into offspring to create a new set of genes. Millions of chemical reactions occur in the cell and require a well-regulated environment to perform all the biochemical processes.
Let us now continue to better understand the key features of the genetic code.
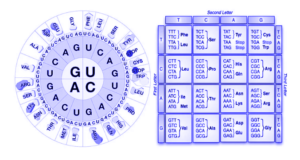
- Each codon has three bases, resulting in a total of 64 codons. Only 61 out of 64 codons can produce amino acids. The remaining three are used as stopping codons during the translation process.
- One codon is responsible for directing the reaction leading to the production of amino acids. As a result, the process is special.
- The synthesis of other amino acids may require many codons. This is called genetic code degeneracy. For example, Valine (Val) integration requires four consecutive codons – GUA, GUC, GUU, and GUG.
- Codons play a role in the production of mRNA; on the other hand, mRNA is responsible for protein production.
- Genetic code is also unique because it is found all over the world. It means that a single codon results in the production of single amino acid. Phenylalanine (Phe), for example, has the genetic code UUU. All living things are shared.
- This indicates that the Phe of the bacterium will be compared to that of a human.
- Codons can have multiple functions sometimes. AUG, for example, is the genetic code of Methionine (Met). It also acts as the first codon or launcher.
- The basic genetic code is most commonly found in all living things.
Genetic Code Properties
- Three-letter code: Codon is represented by 3 consecutive nucleotides in mRNA by 5 ’→ 3’
Mysterious and Universal: All living things have the same set of 64 codons.
Corrupted code: One amino acid may be coded with more than one codon.
Non-stick code; The same nucleotide cannot function as part of the next consecutive cone.
Commaless: The genetic code is continuously studied and every nucleotide participates in the formation of the genetic code.
Start and configure codons: AUG is the first codon for each protein synthesis. Includes methionine codes. # Codons #, UAA, UAG, and UGA are not disconnected codons and do not contain any amino acids.
Polarity: Each triplet is read from 5 ′ to 3 ′, with the first base 5.
These aspects of the genetic code are discussed below.
- Triple code
The codon, commonly known as the code name, is a sequence of nucleotides that express amino acids. There is ample evidence that the sequence codes of the three nucleotides of the amino acid in a protein indicate that the code is a triplet.
Three-core codons are composed of four nucleotide bases (A, G, C, and U). Sense codons are included in 64 codons (specifying amino acids). As a result, there are 64 codons of 20 amino acids. This means that in one amino acid there is more than one cone.
- Unlimited code
There is no space between the punctuation marks, which indicates that each codon is adjacent to its predecessor except for nucleotides between them.
Non-passable code
The code is read by three nucleotide groups, and the nucleotide that is part of one triplet is never the next.
For example,
Serine has a 5′-UCU-3 ′ code.
Code 5′-AUG-3 stands for methionine ’.
- Polarity
Each triplet is read from 5 ′ to 3 ′, the first base is 5 ′, the middle base is 3 ′ and the last base is 3 ′. This means that codons have a concentrated polarity, which means that when the codon is read backward, the base sequence will slow down, leading to the identification of two different proteins.
What are the genetic principles?
The following is the genetic code postulates:
AUG – a codon that initiates a strand of DNA.
In most cases, a single amino acid is associated with multiple mRNA codons in the genetic code. The first two nucleotides in one codon of one amino acid are identical, and the third is different.
The genetic code is made up of three parts. Codon refers to an mRNA triplet.
Codon stops are UAG, UAA, and UGA.
The nucleotide sequence is visible only one way, three times per triplet.
All living things have the same genetic code.
Modification of genetic codes
Not all people are the same. In fact, some parts have been found to disappear. Genetic codes are altered and erased during recording and duplication, leading to this condition. Different parts of the DNA are changed and released during the process, leading to mutations.
At that point, genes are discovered and lost, leading to new physiological features in living organisms. Consider the following scenario. Sickle cell anemia is a blood disorder that occurs when the amino acid valine (Val) is replaced by the amino acid glutamine (Gln) gene sequence.
Also read: NEET Exam Pattern 2022
FAQs
Explain Genetic Modification.
Translation is the process of converting macromolecule information into amino acids. This genetic information is encrypted within a type of code called order or codon. Order can be a set of coded data within the nucleic acid sequence that generates the code for the proteins to be synthesized. Any changes in the genetic code may cause mutations.
What is Genetic Modification?
Genetics are the functional units of living organisms. It is very concerned with structure and functional changes as well as biodiversity that can be good or bad. Even momentary changes in DNA sequence can alter the amino acids that will be produced and the proteins that are involved in them. The sequence may be a dictionary containing nucleotide sequences and Amino Acid sequences.





