Table of Contents
Definition:
The human nervous system is a part of our body that coordinates both voluntary and nonvoluntary functions and transmits the signals to different parts of our body. It is a neural system of a complex network of neurons specialized to carry messages to different parts of our body. The nervous system complexity increases as we move towards higher animals. Higher organisms such as vertebrates have the most complicated structures in the animal kingdom having millions of neurons in them. Neurons play the main role in the nervous system. The nervous system coordinates with the participation of sense organs, nerves, spinal cord, and brain.
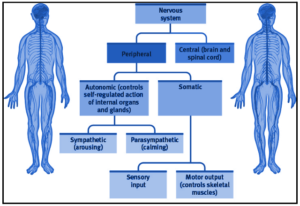
The nervous system in humans is classified into two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord whereas in PNS it’s mainly of nerves. Nerves are longer fibers that connect the CNS to every part of our body. The CNS and PNS are protected by a hard internal skeleton and vertebral column. Any injury to the brain or spinal cord leads to irreversible effects on the body like paralysis.
Central nervous system:
The CNS is also known as the central processing unit of the body which has a brain and spinal cord.
Brain:-
it is the important and central organ of the human nervous system. Brain is the control unit of this system which helps us in remembering, thinking, understanding and many other actions. It is surrounded by a skull which provides frontal, lateral, and dorsal protection to the brain. The brain is having mainly three parts:
- Forebrain- anterior part of the brain consisting of cerebrum, hypothalamus, and thalamus.
- Midbrain- the smaller and central part of the brain consisting of tectum and tegmentum.
- Hindbrain- central region of the brain which consists of cerebellum and medulla.
- Spinal cord:- it is a cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers associated with tissues that are enclosed within the spine and connect all parts of the body to the brain. It begins with the medulla and extends downwards which is enclosed with a vertebral column and surrounded by meninges membranes.
Peripheral nervous system:-
PNS develops from the central nervous system which connects different parts of the body with the central nervous system. PNS carry out both voluntary and involuntary actions with the help of nerves. PNS consists of two types of nerve fibers:
- Afferent nerve fiber- transmit a message from tissues and organs to the central nervous system.
- Efferent nerve fiber- convey messages from the central nervous system to specific peripheral organs.
The peripheral nervous system is classified into two types of nervous systems.
They are
- Somatic neural system- In this system, voluntary actions in the body are going to be controlled which transmits impulse from the central nervous system to skeletal muscle cells. In this somatic nerves are present.
- Autonomic neural system- The autonomic neural system is involved in involuntary actions like digestion, respiration etc. it transmits impulse from central nervous system to smooth muscles and involuntary organs. This neural system is further divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Neuron:-
Neurons are known as structural and functional units of the nervous system. Neurons are able to conduct electrochemical signals.
The parts of the neurons are
- Dendrite – it stretches from the cell body of a neuron and it is the shortest fiber in the cell.
- Axon – axon is the long thread and has an insulating and protective sheath of myelin around it.
Synapse – it is the microscopic gap between adjacent neurons. A neuron has a cell body consisting of cytoplasm and nucleus.
The nervous tissue has neurons and glial cells which provide nutrition, maintenance of homeostasis. Glial cells also restore the protective myelin sheath. The structural properties of nerve cells are different but have the same functional properties. The neurons are further classified based on their structure and based on function.
Importance of this chapter in NEET:
This chapter is very important as it deals with the nervous system which is the main part of our body and there is more scope of asking questions from this area. By understanding this area you can easily score high marks as it is easy to memorize and the context is simple. You have to memorize the parts, their classification, and their functions. By the quick study of this, you will be able to achieve high marks. So, don’t neglect this area.
Also read: Composition Of Blood
FAQs
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is a part of our body that coordinates both voluntary and nonvoluntary functions and transmits the signals to different parts of our body. It is a neural system of a complex network of neurons that carry messages to different body parts. The nervous system coordinates with the participation of sense organs, nerves, the spinal cord, and the brain.
What is the other name of the central nervous system?
The CNS is also the central processing unit of the body which has a brain and spinal cord.
Q. Write about the peripheral nervous system?
Ans: PNS develops from the central nervous system, which connects different parts of the body with the central nervous system. PNS carry out both voluntary and involuntary actions with the help of nerves.
PNS consists of two types of nerve fibers:
- Afferent nerve fiber- transmit a message from tissues and organs to the central nervous system.
- Efferent nerve fiber- convey messages from the central nervous system to specific peripheral organs.
The peripheral nervous system is classified into two types of nervous systems. They are
- Somatic neural system- In this system, voluntary actions in the body are going to be controlled, which transmits an impulse from the central nervous system to skeletal muscle cells. In this, somatic nerves are present.
- Autonomic neural system- Autonomic neural system is involved in involuntary actions like digestion, respiration, etc. it transmits impulses from the central nervous system to smooth muscles and involuntary organs. This neural system is further divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Q. What is a neuron?
Ans: Neurons are known as structural and functional units of the nervous system. Neurons are able to conduct electrochemical signals.
The parts of the neurons are
- Dendrite stretches from the cell body of a neuron and is the shortest fiber in the cell.
- Axon is a long thread with an insulating and protective sheath of myelin around it.
- Synapse – it is the microscopic gap between adjacent neurons. A neuron has a cell body consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus.





