Table of Contents
Definition:
Reproduction can be defined as the biological process of producing a new person or offspring. This process ensures an increase in the number of people of a particular type if conditions permit. It is one of the fundamental elements of living things and the essential process of life.
Types of Production
There are mainly two types of production –
- Sexual Reproduction – This reproductive process is very complex and involves the formation and transfer of gametes, followed by fertilization, zygote formation, and embryogenesis.
- Asexual Reproduction – This reproductive process involves only one parent and the new offspring produced are genetically similar to the parent.
Human Reproduction
Every human being has a sexual reproductive system there, with both parents involved in producing a new offspring. Fertility is produced by the combination of gametes (sex cells) in each parent. Thus, the newly formed person will be different from the parents, genetically and physically. In humans, both men and women have different reproductive systems; therefore, they are known for displaying sexual dimorphism. Males have testicles – also called testicles, and females have two ovaries
Human Reproductive System
Human reproduction involves combining male and female gametes produced in their reproductive system. The male reproductive system is different from the female reproductive system, both in structure and function.
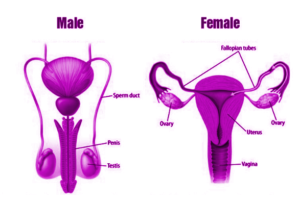
Male Reproductive System
Male gametes, that is, sperm are produced within the male reproductive system. Sperm are small unicellular structures with a head, a piece in the middle, and the tail.
The male reproductive system consists of:
- Testicles (testicles): A pair of oval-shaped organs wrapped in a scrotum that regulates the production of sperm and the male hormone testosterone.
- Scrotum: It is a sack-like organ hanging under the penis and behind it. It is the testicles that maintain the proper temperature needed to produce sperm.
- Epididymis: It is a spiral tube adjacent to the inner side of each testicle. In particular, it is responsible for storing and feeding sperm.
- Ejaculatory ducts: They are formed at the junction of the vas deferens and the duct from the seminal vesicle. These cells are responsible for carrying sperm and secreting seminal vesicles.
- Vas deferens: The sperm produced in the testicles are stored in a tube called the epididymis. Here the sperm mature and pass into the urethra through a muscle tube called the vas deferens.
Accessory glands
These include the three glands, namely the sperm gland, the prostate gland, and the Cowper or bulbourethral gland.
- Seminal Vesicle – These are sack-like pieces found near the base of another. The fluid in this gland is alkaline and makes up about 60% of the sperm volume. The pH of the semen is 7.4 and plays an important role in reducing the acidic environment of the urine.
- Prostate Gland – This gland surrounds the urethra and the removal of this gland serves the purpose of nourishment and makes the sperm swim.
- Cowper’s Gland – These glands are located on both sides of the urethra and the removal of these glands is alkaline. This alkaline release makes the urine acids less effective.
Penis: The penis is a cylindrical tube-like structure that acts as a reproductive organ and a drainage organ. It helps to insert semen into the vagina during sex.
Functions of the male reproductive system
The functions of the male reproductive system are summarized below:
- The emergence of spermatogenesis by which sperm are produced.
- The male sex hormones are released by Leydig cells.
- During fertilization, the reproductive organs (penis) transmit sperm into the female reproductive system.
Female Reproductive System
A woman’s reproductive system is active before, during, and after fertilization.
It contains the following sections:
- Eggs: The ovaries are a complex structure and are the main sex organs for women. Ovum is produced and stored in the Ovaries. The ovaries are also responsible for producing female sex hormones.
Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts)
They are a place of fertility. They attach the ovaries and uterus. Each Fallopian tube has the following components-
- The infundibulum
- An ampoule
- The world
- Part of the uterus
The uterus: The uterus is the site of fetal development.
Female genital: It is the part that connects the cervix to the external parts of a woman’s body. It also forms the lining of the penis during coitus and the foetus during childbirth.
Female Reproduction Program Activities
The functions of the female reproductive system are given below:
- The production of female gametes is called ovum/egg.
- Provide nutritious food and protect the developing fetus.
- During puberty, eggs in the ovaries begin to mature. One of the ovaries produces a mature egg every 28 to 30 days and the process is called ovulation.
Reproduction Process
A fertilized egg is called a zygote. The zygote begins to divide into many cells and grow into an embryo. The embryo travels to the uterus and attaches itself to its walls. This process is called implantation, and the implanted embryos eventually develop into embryos.
FAQs
What Is Reproduction?
Reproduction is the basic biological process of producing offspring or offspring, such as their parents.
What Is Fertilization?
Fertilization of the union of male gametes with the female haploid (egg and sperm) leads to the formation of the diploid zygote.
What Is Cell Splitting?
Cell Differentiation is a process in which a small, immature cell grows into a special, mature cell.
Describe the process of human reproduction?
The process of human reproduction usually begins with a combination, followed by Pre-fertilization, Fertilization, and Post-fertilization. During this basic process, both the male and the female reproductive organs play a vital role.







