Table of Contents
Borax is a hydrated salt of boric acid known as sodium borate, sodium borate decahydrate, or sodium tetraborate decahydrate. It dissolves in water to form a basic, aqueous solution and is commonly available in powder or granular form. It is soluble and has a wide range of industrial and household applications as a component in a variety of products. Pesticide; metal soldering; glaze and enamel manufacturing; tanning of skins and hides; artificial ageing of wood; as a preservative against wood fungus; analytical chemistry as a buffering agent; and pharmaceutical aid as an alkalizer are some of the applications. In this article, we shall discuss some of the properties of borax.
Borax was discovered in dry lake beds in Tibet and was imported to the Arabian Peninsula via the Silk Road in the eighth century AD. When Francis Marion Smith’s Pacific Coast Borax Company began to market and popularise a wide range of applications under the 20 Mule Team Borax trademark, named after the method by which borax was originally hauled out of the California and Nevada deserts, borax first became widely used in the late nineteenth century.
Heating crystalline solid borax causes it to swell at first due to the loss of hydrated water, but further heating produces meta-borate and boron trioxide. Borax’s physical properties and chemistry are very similar to those of boric acid. It is made by heating a solution of boric acid and sodium carbonate. Borax is a naturally occurring mineral that is a salt of boric acid. Sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, and disodium tetraborate are all other names for it. It is a significant boron compound. Borax refers to a group of minerals that are closely related but differ in their crystal water content, such as decahydrate, pentahydrate, and octahydrate salts. It is also known as borax in its anhydrous form.
Overview
Many of borax’s properties are derived from its composition as a boron compound. Borax is a mineral and a salt of boric acid that occurs naturally as a crystalline mineral. According to the University of California, Berkeley, boron is a metalloid chemical element with properties “in between those of carbon and aluminium.” Boron is a rare element that can be found in borax and kenite. According to Science Lab, the chemical formula for borax, sodium borate, is Na2-B4-O7. Borax is a solid that has no odour and weighs 201.22 g/mole. It melts at 741 degrees Celsius. In the presence of glass, borax is stable and non-corrosive. It is incompatible with alkaloidal salts, mercuric chloride, zinc sulphate, and other metallic salts, according to Science Lab. It’s also incompatible with water. Boric acid, disodium salt, disodium tetraborate decahydrate, sodium borate, sodium borate decahydrate, sodium tetraborate, and sodium tetraborate decahydrate are all names for borax. The mineral is white, grey, bluish, or greenish-white streaked crystals with a water solubility of 6g to 100g. The density of sodium borate is 1.73, and its boiling point is 320 degrees Celsius. The pH level is alkaline.
Borax has a wide range of applications. It is found in a variety of detergents, cosmetics, and enamel glazes. It is also used in biochemistry to make buffer solutions, as a fire retardant, an antifungal compound for fibreglass insulation, an insecticide, a flux in metallurgy, and as a precursor for other boron compounds.
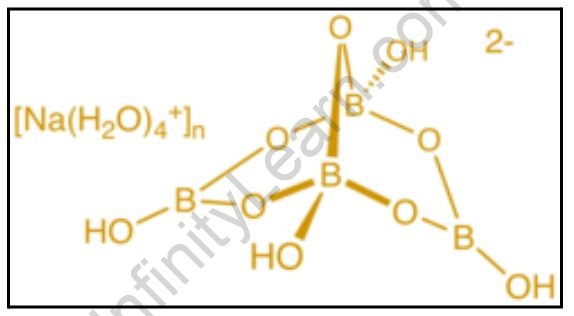
Anomalous properties of borax
Boron compounds have very similar chemistry, properties, and structures. The chemical properties of crystalline borax powder and boric acid are very similar. These chemicals are dissolved in liquid, primarily hot water. At room temperature, the molecular formula of crystalline borax powder contains ten molecules of hydrated water. It has five molecules of hydrating water in its molecular structure at 62°C. Because of hydrolysis, an aqueous solution has alkaline properties. It combines with water to form substitute boric acid H3BO3. It is a weak acid that has been tritiated against strong acids using methyl orange as an indicator on a pH scale ranging from 3.1 to 4.4).
According to the University of California, borax combines with cobalt, copper, chromium, manganese, and nickel to form colourful compounds. The mineral has been used as a pottery glaze since the Middle Ages due to this property. Borax is a weak base that is also used in photographic developers and buffer solutions. It’s also in everything from laundry detergent and household cleaners to houseplant food and dog toothpaste. Borax has a low chemical conductivity that increases significantly when heated due to its boron content. At certain temperatures, boron behaves as a semiconductor. According to the University of California, it is also added to germanium and silicon to increase conductivity.
Physical Properties of Borax –
- It has a molar mass of 202.22 (anhydrous) and a molecular weight of 381.38. (decahydrate).
- It is a solid substance that is white in colour.
- It has a density of 2.4g/cm3 (anhydrous) and 1.73g/cm3 (aqueous) (decahydrate).
- It has a melting point of 743 °C (anhydrous) and 75 °C (aqueous) (decahydrate).
- It dissolves in water.
- It has a boiling point of 1,575°C (anhydrous).
Chemical Properties of Borax –
- Borax reacts with acids and is easily converted into boric acids, a very useful compound. The reaction is as follows –
Na2B4O7·1OH2O+2HCl4B(OH)3+2NaCl+5H2O
- It’s flammable and emits a yellow-green flame.
- It has a high solubility in ethylene glycol and a low solubility in acetone.
- Sodium hydroxide reaction – Na2B4O7+7H2O+2NaOH4NaB(OH)4
Chemical composition of borax
Borax is mostly found in laundry detergent and other cleaning products. It is also used to make boric acid by reacting with hydrochloric acid, also known as HCl. Wilhelm Homberg pioneered this method. Borax is also used in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Boric acid is formed when borax reacts with hydrochloric acid. The following is the reaction:
Na2B4O7·1OH2O+2HCl4B(OH)3+2NaCl+5H2O
Borax Reaction – Each sugar residue in the polymer contains two hydroxyl groups that are positioned in the cis-form. This results in an intriguing and valuable reaction with dissociated borate ions, which is typical of such polymers.
One of the most important boron compounds is borax. The most common form of borax is sodium tetraborate decahydrate. It is a crystalline white solid. Borax occurs naturally in the form of tincal. It is one of the raw materials used in the manufacturing of borax. We learned more about borax in this article. The formula, structure, methods of preparation, and physical and chemical properties. Borax has a higher commercial value. As a result, it is used in a variety of fields. We’ve also gone over the various applications for borax.
Also read: Anomalous Properties of Boron Hydrides
Crack NEET with Result-Oriented Learning Program from Infinity Learn
FAQs
What is the purpose of borax?
The goal of Lewis structures is to provide chemists with a simple way to view molecules that allows them to make accurate predictions about the actual molecules, structure, and properties.
What is the danger of borax?
Borax can be irritating when it is absorbed through the skin or eyes, inhaled, or swallowed. Poison studies show that the misuse of borax-based pesticides can result in acute toxicity with symptoms such as vomiting, eye irritation, nausea, skin rash, oral irritation, and respiratory effects.
Infinity Learn App
Now you can find answers to all your subject queries & prepare for your Exams on our Ultimate Learning App for CBSE and K-12 – Infinity Learn.





