Table of Contents
Diagram of Spirogyra illustrates the essential features and characteristics of Spirogyra, a filamentous green algae. Each component, from the cell wall to the spiral chloroplasts, is clearly labeled, making it easier for students to grasp. By studying the “Diagram of Spirogyra,” students can comprehend how this organism reproduces through fragmentation. Whether for classroom learning or self-study, this diagram serves as a valuable resource to explore the intricate structure of Spirogyra and its reproduction process. Dive into the world of Spirogyra with the help of this informative diagram.
What is Spirogyra?
Spirogyra, a type of green algae, belongs to the charophyte group. It forms long chains of cylindrical cells with a distinctive spiral arrangement. These cells have chloroplasts that give Spirogyra its green color, featuring a unique ribbon-like structure.
Often found in freshwater, especially in slow-moving or still waters, Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation. This means parts of the filament break off to start new independent filaments. Spirogyra plays a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems and is important for the environment.
Taxonomy of Spirogyra
| Domain | Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
| Eukaryota | Plantae | Chlorophyta | Charophyceae | Zygnematales | Zygnemataceae | Spirogyra | [Various species] |
This taxonomy categorizes Spirogyra within the domain Eukaryota, the kingdom Plantae, the phylum Chlorophyta, the class Charophyceae, the order Zygnematales, the family Zygnemataceae, and the genus Spirogyra. There are various species within the genus Spirogyra, each with its unique characteristics and habitats.
Don’t Miss:
- Animal Cell Diagram
- Plant Cell Diagram
- Nephron Diagram Class 10
- Neuron Diagram
- Nucleus Diagram
- Human Brain Diagram Class 10
- Autoclave diagram
- Block Diagram of Computer
- Human Excretory System Diagram
- 8085 Pin Diagram of Microprocessor
Spirogyra Diagram
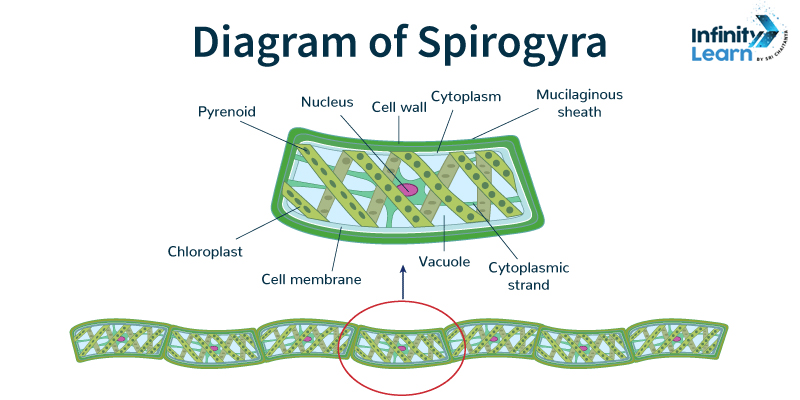
Understanding the Spirogyra Diagram
Spirogyra is commonly represented through a diagram that elucidates its unique structure. This diagram showcases the filamentous nature of Spirogyra, consisting of long, slender cells joined end to end to form chains. Each cell contains a prominent spiral chloroplast, which gives Spirogyra its name, derived from the Greek words “speira” meaning spiral, and “gyros” meaning round.
Structure of Spirogyra
The structure of Spirogyra is characterized by its unique cellular organization and reproductive structures:
- Pyrenoid: It’s like a tiny factory inside the cell that helps in storing and organizing materials. Think of it as a storage unit where the cell keeps its important stuff.
- Nucleus: Nucleus is the control center of the cell. It’s like the brain, telling the cell what to do and when to do it. It contains all the genetic information needed for the cell to function properly.
- Cell Wall: Think of the cell wall as the sturdy outer layer of the cell, like a protective wall around a castle. It gives the cell its shape and helps protect it from harm.
- Cytoplasm: Imagine the cytoplasm as a jelly-like substance filling the cell. It’s where all the action happens – like a bustling city where different processes take place, such as metabolism and protein synthesis.
- Chloroplast: These are like tiny solar panels inside the cell. They contain chlorophyll, which captures sunlight and turns it into energy through photosynthesis. This energy is crucial for the cell’s survival.
- Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is like a gatekeeper. It surrounds the cell, controlling what goes in and out. It’s selective, allowing only certain substances to pass through while keeping others out.
- Vacuole: Think of vacuoles as storage containers within the cell. Vacuoles are small storage compartments within the cell, holding water, nutrients, and waste. They help maintain the cell’s shape and regulate internal pressure.
- Cytoplasmic Strand: Cytoplasmic strands are like highways within the cell, allowing materials to move around and be transported to different parts of the cell. They’re made up of cytoplasm, the jelly-like substance that fills the cell.
- Mucilaginous Sheath: Imagine the mucilaginous sheath as a protective coat surrounding the cell, like a slimy armor. It’s made up of a sticky substance called mucilage, which helps anchor the cell and protect it from drying out.
Functions of Spirogyra
Spirogyra serves several important functions within aquatic ecosystems:
- Photosynthesis: Like other green algae, Spirogyra is capable of photosynthesis. The chloroplasts within its cells contain chlorophyll, allowing Spirogyra to harness sunlight and convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, producing oxygen as a byproduct. This process plays a vital role in maintaining oxygen levels in aquatic environments and supporting life forms such as fish and other aquatic organisms.
- Oxygen Production: As a result of photosynthesis, Spirogyra contributes to the oxygenation of its habitat. The oxygen released during photosynthesis enriches the water with dissolved oxygen, essential for the survival of aerobic organisms.
- Food Source: Spirogyra serves as a food source for various organisms in aquatic ecosystems. Microscopic animals, such as protozoa and small aquatic invertebrates, feed on Spirogyra, utilizing its rich nutritional content for energy and growth.
- Habitat and Ecosystem Support: The presence of Spirogyra in aquatic habitats provides structural support and shelter for a diverse array of microorganisms. Its filamentous structure creates a habitat for bacteria, fungi, and other algae, contributing to the overall biodiversity of aquatic ecosystems.
FAQ’s on Spirogyra Diagram
What is Spirogyra class 7?
Spirogyra is a type of long, thin green algae that often gets attention in seventh-grade biology classes. It's a helpful example for learning about plant biology basics like photosynthesis and reproduction.
What is the structure of a Spirogyra?
Spirogyra has a structure composed of lengthy, unbranched threads consisting of cylindrical cells. Each cell contains a large central vacuole surrounded by cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and a cell wall. The chloroplasts are spiral-shaped, giving Spirogyra its characteristic appearance.
What is Spirogyra called?
Spirogyra is commonly referred to as a green algae or pond scum due to its presence in freshwater habitats like ponds, ditches, and slow-moving streams.
What is the reproduction part of Spirogyra?
Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation and sexually through conjugation. In conjugation, two filaments of Spirogyra come into contact, and specialized structures called conjugation tubes form between them. These tubes allow the transfer of genetic material between cells, resulting in the formation of zygospores.
What is Spirogyra 9th Class?
In ninth-grade biology classes, Spirogyra is often introduced as a topic for studying plant diversity, cellular structure, and reproduction. Students learn about its unique characteristics, including its filamentous form, spiral chloroplasts, and methods of reproduction.
Where can I Find the Diagram of Spirogyra?
Diagrams of Spirogyra can be found in various biology textbooks, online educational resources like Infinity Learn app, and scientific websites. Additionally, many educational institutions provide visual aids and resources for studying Spirogyra, including diagrams illustrating its structure, life cycle, and reproductive processes.





