Table of Contents
CBSE Extra Questions
Get CBSE Extra Questions for Class 10 Science on Infinity Learn for free.
Acids, Bases and Salts
Question-1
What is an acid?
Solution:
An acid is a hydrogen-containing chemical substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) or hydrated hydrogen ions (H2O. H+) or hydronium ions (H3O+) when dissolved in water.

Question-2
What are bases and alkalies?
Solution:
Bases are metal oxides and hydroxides, as well as metal-like radicals (e.g., NH4+ ions). In aqueous solution, bases ionise to form OH– ions. In water, bases can be soluble or insoluble. Alkalies are bases that are soluble in water. As a result, all bases are alkalies, but not all alkalies are bases.
Both NaOH and Cu (OH)2 are bases, but NaOH is an alkali since it is soluble in water. Cu (OH)2 is not an alkali, though, because it is insoluble in water. KOH, Ca (OH)2, and NH4OH are examples of alkalies.
Question-3
Define pH.
Solution:
The negative logarithm to the base 10 of the hydrogen ion concentration, [H+], expressed in g ions/lit or moles/lit, is the pH of a particular solution. As a result, pH=- log1- [H+].
Question-4
What are the practical applications of neutralisation reactions?
Solution:
Cold milk, which is alkaline by nature, is used to neutralise the acidity produced by HCl in the stomach’s gastric juice.
This reaction is used by astronauts in space ships to neutralise harmful CO2 levels.
Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) is used by farmers to alleviate soil acidity.
Formic acid is found in the sting of ants and bees. Rubbing soap, which contains free sodium hydroxide, can be used to neutralise this.
Acidity is treated using antacid pills, which contain magnesium hydroxide, which neutralises excess HCl produced in the stomach. They can also drink cold milk, which will neutralise the HCl.
Question-5
Why the salts solutions of strong acid and strong alkali are neutral?
Solution:
Take potassium sulphate, for example, which is a salt of a strong acid [sulphuric acid] and a strong base [potassium hydroxide solution].
Water is always feebly ionised, as shown by the above equation, and hence potassium sulphate solution is neutral in nature.

Question-6
What is a universal indicator?
Solution:
A universal indicator is a solution that changes colour numerous times over a wide pH range. The colour is used to immediately ‘sign’ pH. In most cases, universal indicators are a combination of numerous indications.
Question-7
Why common indicators cannot determine the pH value of a solution?
Solution:
Common indicators like litmus, methyl orange, and phenolphthalein can quickly tell us whether a solution is acidic or alkaline, but they can’t tell us how much stronger one acidic solution is than another. It means they are unable to accurately determine the pH of various acidic or alkaline solutions.
We can’t discern the difference between pH levels of 5,6 and 7 using litmus. Similarly, pH readings between 3 and 8 will not be very accurate in the case of methyl orange.
Question-8
What are the general characteristics of acids?
Solution:
They have a sour flavour to them.
They change the colour of blue litmus to red and the colour of methyl orange to red.
They produce hydrogen when they react with active metals.
Carbonates are decomposed, resulting in carbon dioxide and water.
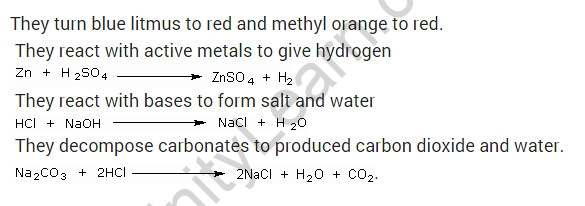
Question-9
What is called deliquescent? Give examples.
Solution:
Deliquescent compounds absorb enough water from the air to dissolve in the water they have taken up. Deliquescent substances include calcium chloride (CaCl2) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Question-10
Write the uses of chlorines.
Solution:
The chemical chlorine is used to make bleaching powder.
Chlorine is used to make dry cleaning solvents.
Chlorine is used to disinfect drinking water as well as swimming pool water.
It’s a component of hydrochloric acid manufacture.



