Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil Updated for 2024-25
NCERT Solutions for class 7 Science chapter 9 Soil is one of the important topics for the students of 7th standard. The NCERT solutions for soil are provided here to help students in not only clearing their doubts but also to understand the chapter in an easy and more effective way.
The soil has massive applications; knowing more details about soil will help the students to face the exam confidently and to score good marks in the CBSE Class 7 examination. We present various true and false, MCQ type questions regarding the classification of changes. Here, the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions are also available in PDF format updated for 2024-25 CBSE syllabus which students can access and download easily.
Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil Questions and Answers PDF
Here are all the NCERT textbook class 7 chapter 9 questions and answers pdf:
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Questions and Answers
1. In addition to the rock particles. The soil contains
i) Air and Water
ii) Water and Plants
iii) Minerals and Organic matter, Air and Water
iv) Water, Air and Plants
Ans : iii) Minerals and Organic matter, Air and Water
2. The water holding capacity is the highest in
i) Sandy soil
ii) Clayey soil
iii) Loamy soil
iv) Mixture of sand and loam
Ans : ii) Clayey soil
3. Match the items in Column – I with those in Column – II
Column – I Column – II
i) A home for living organisms a) Large particles
ii) Upper layer of the soil b) All kinds of soil
iii) Sandy soil c) Dark in colour
iv) Middle layer of the soil d) Small particles and packed tight
v) Clayey soil e) Lesser amount of humus
Ans : i) b ii) c iii) a iv) e v) d
4. Explain how soil is formed?
Ans : Soil has been formed by weathering of parent rock material over millions of years. It is a very slow & gradual process forming fine particles of soil.
5. How is Clayey soil useful for crops?
Ans : Clayey soils are very useful for crops because, these soils :
a) Contain humus, providing fertility to the soil.
b) Hold sufficient water due to the presence of smaller particles.
6. List the differences between clayey soil & sandy soil
Ans :
Sandy soil Clayey soil
1) It contains greater proportion of big 1) It contains greater proportion of fine particles particles
2) Particles are loosely packed 2) Particles are tightly packed
3) Large space is present between particles 3) Very less space is present between particles
4) Water holding capacity is very less 4) Water holding capacity is maximum
5) Sandy soil is well aerated 5) Clay is not well aerated
6) Water can drain quickly through particles 6) Water cannot drain quickly through particles
7. Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers
Ans :
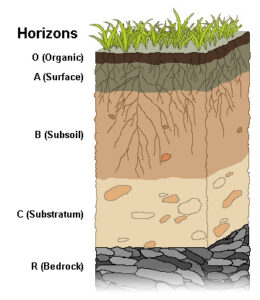
8. Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation she observed that it took 40 mins for 200 ml of water to percolate through the soil sample. Calculate the rate of percolation.
Ans : Formula of percolation rate
9. Explain how soil pollution & soil erosion could be prevented
Ans : Polyethene bags are made up of plastics that pollute the soil other substances which pollute the soil are a number of waste products, like chemicals & pesticides. So to prevent the soil pollution.
Prevention of soil pollution :
1) There should be a ban on polyethene bags & plastics
2) Waste products & chemicals should be treated before they are released into the soil
3) The use of pesticides should be minimized
Prevention of soil erosion : It can be done by
a) Planting of trees
b) Protecting of forests
c) Holding suitable material (or) organic matter in proper amounts.
d) Maintaining porous structure of soil
e) Control & reclamation of streaks & shifting of cultivation
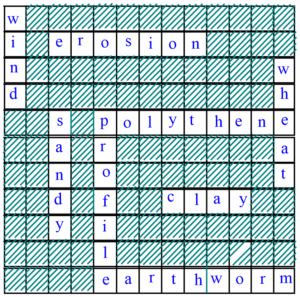
10. Solve the following cross word puzzle with the clues given:

Ans :
cross Down
2) Plantation prevents it 1) In desert, soil erosion occurs through
5) Use of these should be banned to avoid
soil pollution 3) Clay and loam are suitable for cereals like
6) Type of soil used for making pottery 4) This type of soil can hold very less water
7) Living organism in the soil 5) Collective name for layers of soil
Important Topics covered in Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil
The key topics covered in CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil include:
What is Soil?
- Soil is the uppermost layer of the earth’s crust that supports life and is the foundation for agriculture.
- It is composed of minerals, organic matter (humus), air, water, and living organisms.
- The composition of soil varies based on geological factors, climate, and human activities.
Soil Profile and Horizons
- The soil profile consists of different layers called horizons, each with distinct characteristics.
- The main horizons are:
- A horizon (topsoil): soft, porous layer that can absorb and hold water
- B horizon (middle layer): more compact and harder layer
- C horizon: layer made up of small rocks
- Bedrock: the hardest bottom layer
Types of Soil
- Sandy soil: contains large solid particles, lacks water and nutrients
- Clayey soil: contains over 30% fine particles, swells and shrinks when wet and dry
- Loamy soil: ideal topsoil, contains an equal proportion of sand, silt and clay
Soil Properties
- Water holding capacity: highest in clayey soil, lowest in sandy soil
- Percolation rate: speed at which water moves through soil
- Soil erosion: removal of soil by wind, water or ice
Importance of Soil
- Provides anchorage and nutrients for plants
- Habitat for many living organisms
- Essential for agriculture and food production
These NCERT solutions for Chapter 9 are created by subject experts according to the latest CBSE syllabus (2020-2021). Students must practise the solutions regularly to prepare effectively for their examination.
These NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science will help students in revising all the chapters so that they can increase their knowledge of Science.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil
What is the best soil definition?
Soil is the thin layer of material covering the Earth's surface that plants can grow in. It is made up of tiny pieces of rock, decayed plants and animals, air, and water.
What soil is red?
Soil that has a reddish color is called laterite soil. This type of soil is found in areas with a hot, wet climate, like parts of India, Africa, and South America. The red color comes from iron and aluminum that have been exposed to a lot of rain over many years.
What is soil particles Class 7?
Soil is made up of different-sized pieces of rock and minerals, called soil particles. These particles are classified into three main types: Sand: Large, gritty particles Silt: Medium-sized, smooth particles Clay: Small, sticky particles The amount of each type of particle in the soil determines its texture and how well plants can grow in it.
Why is the soil important?
Soil is important for many reasons: It provides nutrients for plants to grow It acts like a sponge to hold water for plants to use It is home to many small animals and insects that help keep the soil healthy It is used to grow the food we eat and the plants we use for other purposes
How is soil formed?
Soil is formed over a long period of time from the weathering of rocks and the decomposition of dead plants and animals. This process happens in several steps: Rocks break down into smaller pieces due to wind, water, ice, and changes in temperature. Dead plants and animals decay and mix with the broken-down rock pieces. Tiny living organisms in the soil help break down the organic matter and release nutrients. Over many years, layers of soil build up on the Earth's surface. The type of soil that forms depends on the climate, the type of rocks and plants in the area, and how long the soil has been developing.



