Table of Contents
Tests of Carbohydrates, Fats and Proteins in Pure Samples and Detection of Their Presence in Given Food Stuffs
Get CBSE Notes for Chemistry on Infinity Learn for free.
Food is a necessary material that must be supplied to the body for its normal and proper functioning.
The main functions of the food are:
1. to provide energy
2. to promote growth
3. to replace worn-out tissues
4. to sustain life
5. to regulate body processes like assimilation and digestion.
The essential constituents of food are:
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids (oils and fats)
3. Proteins
4. Minerals
5. Vitamins and
6. Water.
Carbohydrates
The name carbohydrate is used for the compounds having general formula, Cx(H2O)y. These are called carbohydrates because they can be treated as hydrates of carbon. For example, glucose (C6H12O6), sucrose (C12H22O11), etc. However, this definition of carbohydrates has lost significance because of the following two reasons:
(i) There are many compounds that have the general formula Cx(H2O)y but do not behave as carbohydrates. For example, oxalic acid (C2H2O2), formaldehyde (CH2O), etc.
(ii) There are many compounds that do not conform to formula Cx(H2O)y but possess characteristic properties of carbohydrates and are treated as carbohydrates. For example, rham-nose (C6H12O5).
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes, polyhydroxy ketones, their derivatives, and the compounds that give them upon hydrolysis, according to a more relevant definition.
Ketone-containing carbohydrates are referred to as ketoses, while aldehyde-containing carbohydrates are referred to as aldoses. Glycose is the broad name for all carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simple carbs. Glucose, fructose, and other sugars are examples.
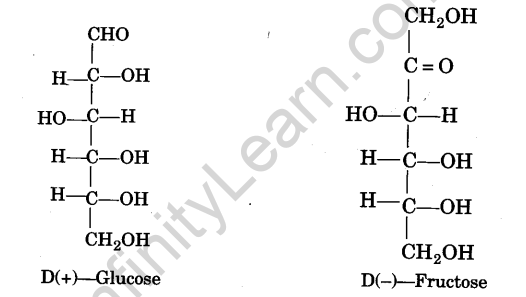
The carbohydrates which contain two to ten monosaccharide units are called oligosaccharides. For example, sucrose (C12H22O11), maltose (C12H22O11), raffinose (C18H32O16), etc.
The carbohydrates which contain more than ten monosaccharide units are called polysaccharides. For example, starch, cellulose, glycogen, etc. These may be represented by the general formula (C6H10O5)n.
Sugars and non-sugars are a more general grouping of carbs. Sugars such as glucose, fructose, and cane sugar are crystalline, water-soluble, and sweet. Non-sugars, such as starch and cellulose, are amorphous, water-insoluble, and tasteless compounds.
Reducing sugars are carbohydrates that can reduce Tollen’s reagent or Fehling solution. Reduced sugars are found in all monosaccharides. The majority of disaccharides are also sugar reducers. Sucrose is a sugar that does not reduce.
Carbohydrates are generally optically active because they contain chiral centres.
Carbohydrates perform two important functions in the body:
(a) They act as biofuels to provide energy for the functioning of living organisms.
In the human system, all carbohydrates except cellulose can serve as a source of energy. Starch and various sugars which are taken as food are first hydrolysed to glucose by the enzymes present in the digestive system.
Glucose on slow oxidation to carbon dioxide and water in the presence of enzymes liberates a large amount of energy which is used by the body for carrying out various functions.
C6H12O6+ 602 ——> 6C02 + 6H20 + 2832 kJ
In order to fulfill the emergency requirements, our body also stores some of the carbohydrates as glycogen in the liver. Glycogen on hydrolysis gives glucose.
It may be noted that cellulose cannot be hydrolysed in our body because enzymes required for its hydrolysis are not present in our body. However, grazing animals are capable of hydrolysing cellulose to glucose.
(b) They act as constituents of cell membrane.

