Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Types of Simple Permanent Tissues
- Parenchyma Tissues
- Collenchyma Tissues
- Sclerenchyma Tissues
- Summary
- Did You Know?
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we were introduced to the three types of simple permanent tissues. In this segment, we will learn about each of these tissue types in detail.
What are the types of simple permanent tissues?
Based on the structure and function, there are three types of simple permanent tissues:
Parenchyma tissues
Parenchyma (Para = beside, chyma = filling) tissue acts as a filler. Hence, it is usually present at many locations in the plant body.
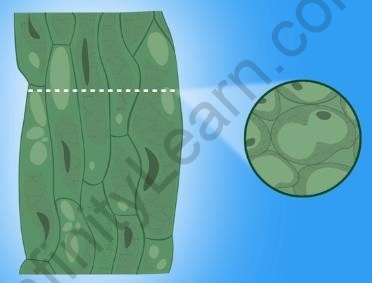
Parenchyma
Characteristics of parenchyma:
-
- Loosely-packed cells
- Thin-walled living cells
- Intercellular spaces
- Used to store food
- Can be modified depending upon the need of the plant. For example
- Aquatic plants have Aerenchyma tissue, which are modified parenchyma cells with large air cavities within, to help the plants float.
- Parenchyma cells containing chlorophyll are called Chlorenchyma. They are capable of photosynthesis.
- Parenchyma cells found in roots and stem store water and certain nutrients.
Collenchyma tissues
The main function of collenchyma tissue is to provide flexibility to the plants to deal with physical exertion. This allows the bends and movements in plants without breaks in various parts, such as twigs, stems, and leaves. This tissue is also found in leaf stalks below the epidermis.
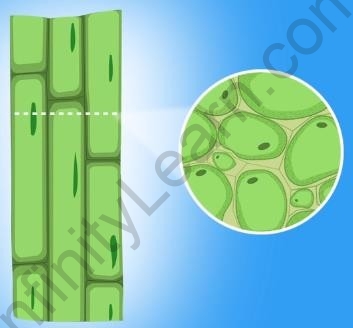
Collenchyma
Characteristics of collenchyma:
-
- Thick walls
- Elongated shape
- Little intercellular space
- Living cells
Sclerenchyma tissues
Sclerenchyma tissue is the toughest of the three simple permanent tissues. This tissue provides stiffness to the plant structure. Sclerenchyma is found in the plant body in the leaf veins, stem, around vascular bundles, in the tough coverings of nuts and seeds.
For example, the outer husk of coconuts is hard due to the presence of the sclerenchyma tissue.
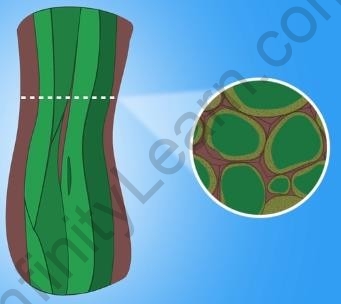
Sclerenchyma





