Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Muscular Tissue
- Types of Muscular Tissue
- Striated Muscles
- Smooth Muscles
- Cardiac Muscles
- Summary
- Did You Know?
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we learned about connective tissues. In this segment, we will study Muscular tissues.
What is Muscular tissue?
Muscular tissues are the tissues in animals that help in movement and locomotion. Movement is the result of the function of the muscular tissue performed with contraction and relaxation actions in muscles.
The cells of the muscular tissue are elongated and contain contractile proteins, such as Actin and Myosin.
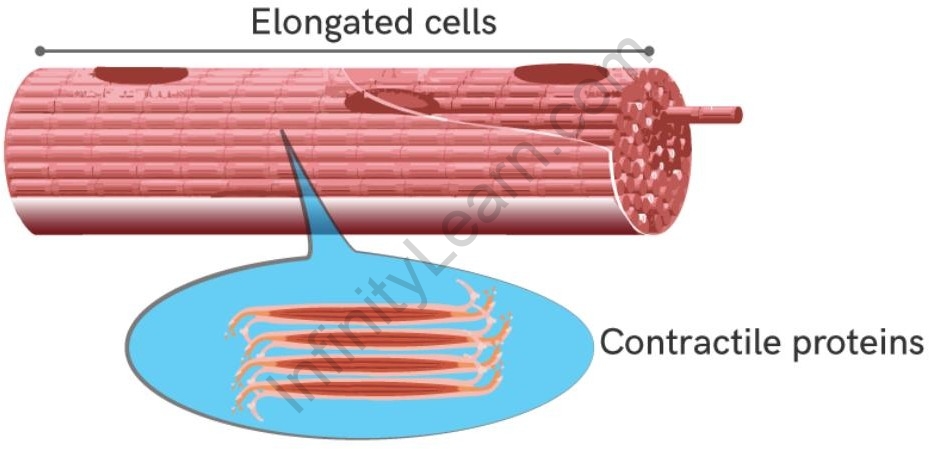
Cells of muscular tissue
What are the types of muscular tissue?
There are three major types of muscular tissues:
Striated muscles
These muscle tissues have striations in the form of alternate light and dark bands. Hence, they are known as striated muscle tissues.
They have a typical cylindrical structure due to the wrapping of the long muscle fibres together. These are usually unbranched and multi-nucleate in nature.
Striated muscles are attached to the bones.

They help in the movement of our hands and legs as well as with the locomotion. Since these muscles are involved in actions that are carried out according to our will, they are also called Voluntary muscles.
Smooth muscles
These muscles do not have any striation and are therefore known as smooth muscles or unstriated muscles.
These muscle tissues have long, spindle-shaped, uninucleate cells.
Smooth muscles are present in the stomach, bronchi, uterus, and iris of eyes.They perform important movements within our body, for example, the movement in the stomach, intestines, and lungs. These activities are not under our control and hence these muscles are known as involuntary muscles.
Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscle is a type of involuntary muscle tissue found in the walls of the heart. It is composed of individual cells joined together by intercalated discs, which are specialized junctions that help the heart contract and relax.
Cardiac muscle is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, and it is also the only muscle type that can contract without being stimulated by the nervous system.
Summary
Muscular tissue is a type of tissue found in animals. It is composed of cells called muscle fibers that are specialized for contraction, allowing movement of the body and organs. Muscular tissue is divided into three main types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movements of the body, such as running and lifting; cardiac muscles are responsible for the rhythmical contractions of the heart; and smooth muscles are found in the walls of organs, controlling involuntary movements such as digestion. Muscular tissue requires a constant supply of energy and oxygen to function properly and is able to regenerate itself when damaged.
Did you know?
Muscular tissue is a type of tissue found in animals that is made up of cells called muscle fibers.
These fibers are specialized for contraction, which allows them to move parts of the body.
Muscular tissue is also responsible for providing the body with stability and posture.
It also helps to generate heat and provide energy for activities such as walking, running, and lifting.






