Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Connective Tissues
- Connective Tissue Types
- Bones and Cartilage
- Areolar Tissue
- Adipose Tissue
- Blood
- Summary
- Did You Know?
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we learned about the types of epithelial tissues. In this segment, we will learn about Connective tissue.
What are Connective tissues?
The connective tissue is a type of tissue that helps to connect the various parts of our body. It is made up of two major components: cells and the matrix.

Components of connective tissue
What are the types of connective tissues?
Cells in the connective tissues are loosely embedded in the matrix. This matrix can either be jelly-like, fluidic, dense, or rigid; and this depends on the location and the respective function of the connective tissues. Let us now look at types of connective tissues.
- Bones and Cartilage
- Bones
The bones in humans contain cells that are embedded in a hard matrix. The rigid nature of the matrix is due to the deposition of calcium and phosphorus, which make the bones strong and non-flexible.
A major function of bones includes anchoring the muscles and various organs within.
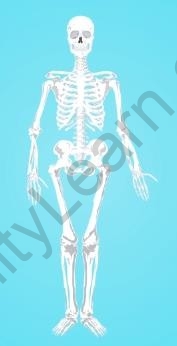
Bones in the human body
-
- Ligaments
Another type of connective tissue, called the ligament, joins different bones together. This tissue has a little matrix, which makes it elastic and strong.
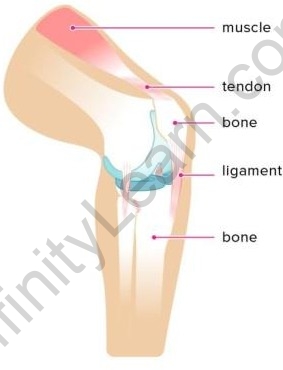
Ligament
-
- Tendons
The movement of bones is brought about by the muscles connected by the tendons. These tendons are fibrous in nature and although they have strength, there is limited flexibility.
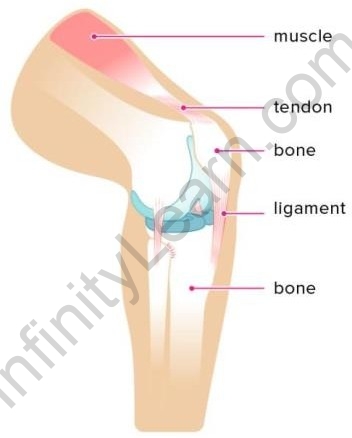
Tendons
-
- Cartilage
Cartilage is a bone-like tissue that is also a connecting tissue type. It has a matrix that is not as rigid as that of the bones. The matrix is made up of sugars and proteins, along with widely spaced cells. Thus, it has flexibility along with a proper shape.
The nose tips and the ears in a human body are flexible due to the presence of cartilage.
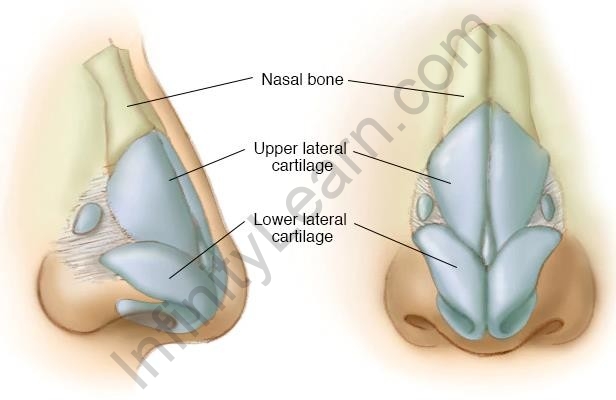
Cartilage
An extremely important function of cartilage is to smoothen the surfaces of bones at the joints. In a human body, cartilage is also present in the respiratory tract; that is, in the trachea and larynx.

