Table of Contents
The overlapping of atomic orbitals distinguishes sigma and pi bonds from other types of covalent bonds. This same overlapping of atomic orbitals generates covalent bonds. In fact, the sigma bonds are made by the overlapping of atomic orbitals head-to-head, whereas pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals.
Sigma (σ) Bond
Such a type of covalent bond is formed by the head-on positive (same phase) overlap of atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis. Because of the direct overlapping of the orbitals involved, sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds. The electrons involved in a bond are often referred to as electrons. Each and every single bond are, in general, a sigma bond. They could be formed by combining the atomic orbitals listed below.
(1) S-S Overlapping: One’s orbital from each participating atom is overlapping head-on along the internuclear axis in this type of overlapping. It must be half-filled before overlapping with another s orbital. One such overlapping occurs in H2 molecules, where each hydrogen atom has a half-filled s orbital.
(2) S-P Overlapping: Along the internuclear axis, one half-filled s orbital overlaps with one half-filled p orbital, forming a covalent bond. Ammonia exhibits this type of overlapping. Here, the overlap of the 2px, 2py, and 2pz orbitals of the nitrogen atom and the 1s orbitals of the three hydrogen atoms forms three sigma bond in an NH3 molecule.
(3) P-P overlapping: One half-filled p orbital from each participating atom overlaps head-on along the internuclear axis in this condition. One Cl2 molecule has a p-p overlap of two chlorine atoms’ 3pz orbitals. It’s indeed important to note that head-to-head overlapping of two p orbitals results in a sigma bond, whereas lateral overlap results in pi bonds.
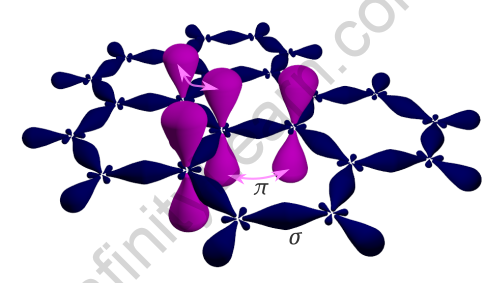
Pi (π) Bond
Pi bonds have been created by the sideways positive (same phase) overlap of atomic orbitals parallel to the internuclear axis. The axes of the atomic orbitals are parallel to each other during bond formation, while the overlapping is perpendicular to the internuclear axis.
Because of the significantly lower degree of overlapping, pi bonds are generally weaker than sigma bond. A typical double bond is made up of one sigma bond and one pi bond, whereas a typical triple bond is made up of two bonds and one bond. It really is important to note that a sigma-pi bond combination is always stronger than a single sigma bond.
Importance of the topic Sigma & Pi Bonds in JEE Exam
The topic sigma and pi bonds is an important part of the JEE syllabus for chemistry. Students need to understand the concept around this topic during their IIT JEE Preparation.
Related Topic: Difference Between Sigma and Pi Bond
FAQs
How many Pi bonds are there in double and triple bonds?
Two pi bonds and one sigma bond make up a triple bond. Similarly, one double bond is made up of one sigma bond and one pi bond. Sigma bond has always been formed by single bond.
How many Sigma and Pi bonds are there in a Benzene molecule?
The benzene ring has been made up of six carbon-carbon single bonds that are all sigma bonds. Also, there are six carbon-hydrogen sigma bond. As a result, a benzene molecule has a total of 12 sigma bonds. The aromatic is distinguished by alternating double bonds between carbon atoms. As a result, a benzene molecule has a total of three pi bonds.







