Table of Contents
Introduction
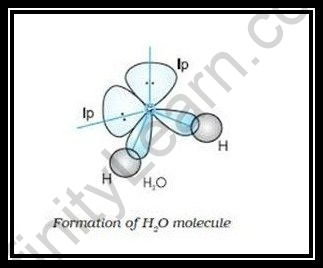
Just the middle molecule goes through the hybridization interaction, as per the common guideline of hybridization. We focus on the oxygen iota during the making of a water particle. The oxygen iota is sp3 hybridized during H2O hybridization.
- Name of the Molecule: Water
- Sub-atomic Formula: H2 O
- Hybridization Type: sp3
- Bond Angle: 104.5o
- Math: Angular or V-formed
The focal iota, which is hybridized, is oxygen. In the development of the water atom, there are three 2p orbitals and one 2s orbital. They are consolidated to create the sp3 cross breed orbitals.
Moreover, every hydrogen particle structures covalent associations with two crossover orbitals and two mixture orbitals are involved by solitary sets during the interaction.
Calculation of Hybridization
The sp3 particle is oxygen that has been hybridized to frame H2O
atoms. Solitary pairings prepare two half and half orbitals, while the other two are occupied with hydrogen iota holding.
Since solitary sets don’t add to a particle’s calculation, H2O has a rakish shape.
The repugnance of (solitary pair-solitary pair) is more prominent than that of (solitary pair-bond pair) or (bond pair-bond pair). Accordingly, the point shaped by H-O-H is 104.5°, which is not exactly the ideal tetrahedral point of 109°28′.
The steric number of the focal particle (O) is 2+2 since H2O atoms have two solitary sets and two bond sets, Nonetheless, it has the exemption of the odd electron species and stereo-chemically latent solitary sets, where
steric no. = solitary sets + bond sets.
FAQs
Q: What is Meant by the sp3 Hybridization of Water?
Ans: The valence orbitals of a particle included by a tetrahedral plan of solitary combines and holding sets having a bunch of four sp3 mixture orbitals are named as the hybridization of H2O. The mixtures are a result of the mixing of one (s) orbital and each of the three (p) orbitals that produce four comparative sp3 mixture orbitals. Allude to the underneath picture to see well the instrument of sp3 hybridization in water. In the event that you notice, you will find that every one of these crossover orbitals is pointing in an alternate corner of a tetrahedron.
Q: Are There Any Criteria to Observe a Particular Type of Hybridization?
Ans: Indeed. Adhering to are the arrangement of guidelines that are guessed to layout to get the kind of hybridization in a compound or a particle.
- Work out the absolute number of solitary sets of electrons
- Compute the number of valence electrons.
- Compute the quantity of octet or duplex
- Assess the absolute number of utilized orbital = Number of duplex or octet + Number of solitary sets of electrons
If there should be an occurrence of no solitary pair of electrons, then, at that point, the H2O hybridization and calculation of orbitals and particles will be unique.
Q: What are the circumstances to notice a particular sort of Hybridization?
Ans: Coming up next are a bunch of decisions that have been proposed to decide the kind of hybridization in a synthetic or a particle.
- Work out the complete number of electron solitary sets.
- Decide the number of valence electrons there are.
- Compute the number of octets or duplexes in an organization.
- Number of duplex or octet + Number of solitary sets of electrons = complete number of used orbitals
- Without a trace of a solitary pair of electrons, the H2O hybridization and orbital and sub-atomic math will be changed.
Q: What is H2O?
Ans: Water ( H2O) is an inorganic synthetic compound that is straightforward, dull, scentless, and basically dismal.
It is the fundamental part of the Earth’s hydrosphere and the liquids of all known living things (where it goes about as dissolvable).
However it needs calories and natural supplements, it is fundamental for all realized living things. As expressed by its compound recipe, H2O, every one of its particles has one oxygen and two hydrogen molecules associated with covalent bonds.
Q: What are the physical and substance properties of H2O?
Ans: For sure, water in nature generally contains disintegrated synthetic compounds, requiring extra cycles to make artificially unadulterated water. In typical earthbound circumstances, water is the main normal substance that exists as a strong, fluid, and gas.
- Water is one of a kind among fluids in that it loses thickness as it freezes.
- At a tension of one air (atm), ice melts or water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit),
- while the water bubbles or fume gathers at 100 degrees Celsius (212 degrees Fahrenheit).
- In spite of the fact that people have specific sensors that can identify the presence of water in their mouths, and frogs are accepted to have the option to smell it, unadulterated water is ordinarily viewed as bland and scentless.
- Unadulterated water seems blue because of light ingestion in the 600-800 nm district.
- A particle of water in the fluid or strong state can make up to four hydrogen bonds with encompassing atoms because of its extremity.
- The electrical conductivity of unadulterated water increments when a limited quantity of ionic substance, like normal salt, is broken down.
Q: What impact does H2O have on life including anabolism and catabolism?
Ans: Water has an assortment of organic characteristics that are fundamental for the spread of life. It achieves this by permitting natural synthetic compounds to respond in manners that permit replication to happen. All known types of life require the presence of water.
- Water is essential for some metabolic cycles in the body, as well as a dissolvable in which a large number of the body’s solutes break down. Anabolism and catabolism are the two parts of digestion.
- Water is taken from atoms during anabolism to develop bigger particles. Water is utilized in catabolism to break bonds and structure more modest particles (e.g., glucose, unsaturated fats, and amino acids to be utilized for powers for energy use or different purposes).
- These metabolic exercises would not be able to be done without the presence of water.
Q: What does the compound holding of water propose?
Ans: Water (H2O) is a straightforward triatomic bowed particle with C2V sub-atomic balance and a 104.5° bond point between the middle oxygen and hydrogen molecules.
Despite the fact that it is one of the least difficult triatomic compounds, its synthetic holding plan is muddled since a few of its holding boundaries, for example, bond point, ionization energy, and electronic state energy can’t be clarified by a solitary brought together holding model.
There are various works of art and progressed holding models which are used to satisfactorily clarify synthetic holding. They are to be specific:
The basic Lewis and VSEPR structure
- Valence bond hypothesis
- Sub-atomic orbital hypothesis
- Isovalent hybridization
- Twisted’s standard







