Table of Contents
Covalent Bond: Elements having very excessive ionization energies are incapable of shifting electrons and elements having very low electron affinity cannot take up electrons. The atoms of such factors tend to share their electrons with the atoms of different factors or with different atoms of identical detail in a way that both the atoms acquire octet configuration of their respective valence shell and consequently attain stability. Such association via sharing of electron pairs amongst one of a kind or same types is known as Covalent Bond.
Covalent Bond can be Achieved in Ways:
- Sharing of electrons among atoms of the identical kind E.G. Formation of H2, Cl2, O2, and many others.
- Sharing of electrons between atoms of different kinds E.G. Formation of CH4, H2O, NH3, and so on.
Covalent Bonding(or)Bond in Carbon Atom
- As consistent with the electronic configuration of Carbon, it needs to benefit or lose 4 electrons to emerge as stable, which appears not possible as:
- Carbon can not gain four electrons to become C4-, because it may be hard for six protons to keep 10 electrons and so the atom turns risky.
- Carbon can’t lose 4 electrons to emerge as C4+ because it would require a big quantity of power to put off out four electrons and additionally the C4+ could have only 2 electrons held by using proton, so one can once more become unstable
- Carbon can not gain or donate electrons, so to complete its nearest noble gas configuration, it stocks electrons to shape a covalent bond.
Properties of Covalent Bond
If the everyday valence of an atom isn’t happy by way of sharing a single electron pair between atoms, the atoms may additionally proportion multiple electron pairs among them. Some of the homes of covalent bonds are:
- Covalent bonding does not bring about the formation of new electrons. The bond handiest pairs them.
- They are very powerful chemical bonds that exist among atoms.
- A covalent bond usually includes the power of about ~80 kilocalories in step with mole (kcal/mol).
- Covalent bonds rarely smash spontaneously after it’s far fashioned.
- Covalent bonds are directional wherein the atoms that are bonded show off particular orientations relative to one another.
- Most compounds having covalent bonds show off notably low melting points and boiling factors.
- Compounds with covalent bonds generally have lower enthalpies of vaporization and fusion.
- Compounds formed by covalent bonding don’t conduct strength because of the lack of free electrons.
- Covalent compounds are not soluble in water.
What is the Octet Rule?
All atoms except noble gases have less than 8 electrons in their valence shell. In other phrases, the valence shells of these atoms do no longer have strong configurations. Therefore, they integrate with different atoms to acquire strong electronic configurations.
Therefore,
“The tendency of atoms of various elements to attain strong configuration of eight electrons of their valence shells is the purpose of Chemical aggregate”
and
“The principle of reaching the most of eight electrons within the valence shell of atoms is referred to as octet rule.”
Lewis brought simple symbols to indicate the electrons present within the outer shell of an atom known as the valence electrons. These symbols are called Electron Dot Symbols and the structure of the compound is known as Lewis Dot Structure.
Conditions for writing the Lewis dot systems for covalent bonds
Sharing of an electron pair among the atoms affects the formation of covalent bonds.
During bond formation, every bond consists of two electrons which might be contributed by each one of the combining atoms.
By the mutual sharing of electrons, every atom attains an octet configuration in its valence shell.
Electron dot structures of covalent molecules are written with appreciation to the octet rule. According to this rule, all the atoms inside the molecule will have eight electrons of their valence shell beside the Hydrogen atom. Hydrogen will have only electrons because the simplest two electrons complete their first shell to reap helium configuration.
Thus the factors of organization 17 along with Cl would percentage one electron to acquire stable octet; the factors of institution 16 including O and S could proportion electrons; the elements of institution 15 might proportion 3 electrons and so forth.
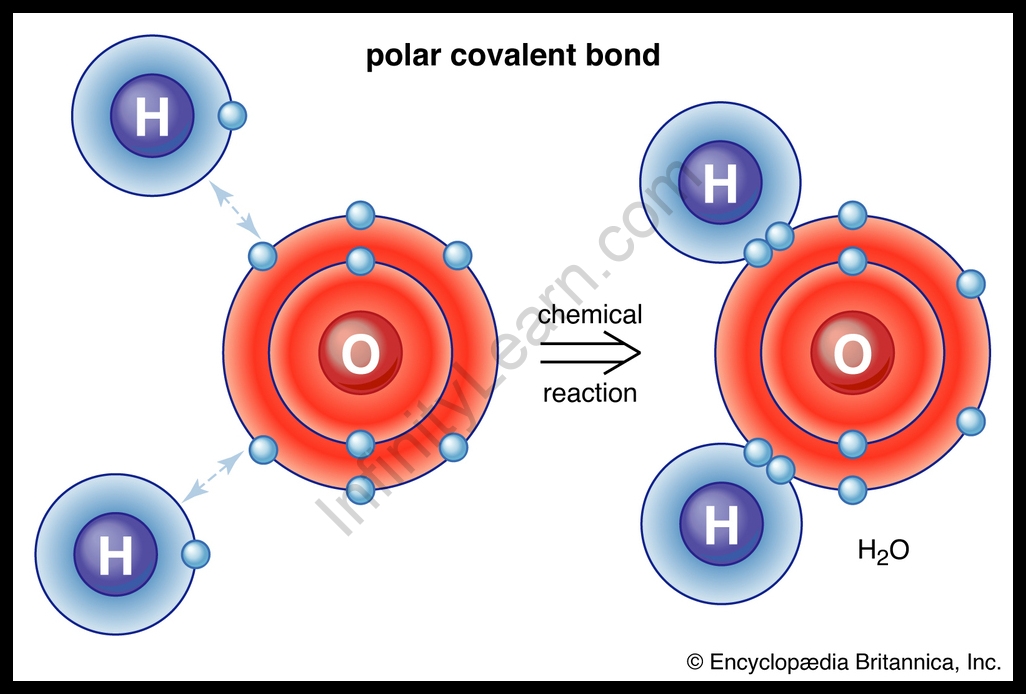
For Example, the oxygen atom which has six electrons in its valence shell completes its octet using sharing its electrons with two hydrogen atoms to shape a water molecule.
Types of Covalent Bonds
Depending upon the number of shared electron pairs, the covalent bond can be labelled into:
- Single Covalent Bond
- Double Covalent Bond
- Triple Covalent Bond
Single Bonds
A single bond is shaped when most effectively one pair of electrons is shared between the two participating atoms. It is represented through one sprint (-). Although this form of covalent bond has a smaller density and is weaker than a double and triple bond, it’s miles the most stable.
For Example, the HCL molecule has one Hydrogen atom with one valence electron and one Chlorine atom with seven valence electrons. In this example, a single bond is formed between hydrogen and chlorine by way of sharing one electron.
Double Bonds
A double bond is formed while two pairs of electrons are shared among the 2 participating atoms. It is represented with the aid of two dashes (=). Double covalent bonds are much more potent than a single bond, but they’re less solid.
Example: A carbon dioxide molecule has one carbon atom with six valence electrons and two oxygen atoms with 4 valence electrons.
To the whole its octet, carbon stocks two of its valence electrons with one oxygen atom and two with every other oxygen atom. Each oxygen atom shares its electrons with carbon and consequently, there are two double bonds in CO2.
Oxygen-Molecule: In the formation of the oxygen molecule, each oxygen atom has six electrons of its valence shell. Each atom calls for more electrons to complete its octet. Accordingly, the iotas share two electrons each to frame the oxygen particle. Since electron pairs are shared there’s a double bond among the two oxygen atoms.
Ethylene Molecule: In ethylene, each carbon atom shares its valence electron with two hydrogen atoms and the last electrons with the other carbon atom. So there is a twofold connection between the carbon iotas
Triple Bond
A triple bond is fashioned while 3 pairs of electrons are shared among the two taking part atoms. Triple covalent bonds are represented through 3 dashes (≡) and are the least stable varieties of covalent bonds.
For Example:
In the formation of a nitrogen molecule, each nitrogen atom having five valence electrons gives 3 electrons to form 3 electron pairs for sharing. Thus, a triple bond is shaped among the two nitrogen atoms.
Polar Covalent Bond
This form of covalent bond exists wherein the unequal sharing of electrons occurs because of the distinction in the electronegativity of combining atoms. More electronegative atoms may have a stronger pull for electrons. The electronegative distinction among the atoms is more than 0 and less than 2.0. As a result, the shared pair of electrons might be closer to that atom.
For example, molecules form hydrogen bonding as a result of an unbalanced electrostatic capacity. For this situation, the hydrogen particle is associated with electronegative fluorine, hydrogen, or oxygen.
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
This form of covalent bond is formed on every occasion there’s the same percentage of electrons among atoms. The electronegativity difference among atoms is zero. It takes place wherever the combining atoms have similar electron affinity (diatomic factors).
For example, Nonpolar Covalent Bond is determined in gasoline molecules like Hydrogen fuel, Nitrogen fuel, etc.
Polarization of Covalent Bonds
It is determined that within the sigma bonds among special atoms, the electron cloud is usually toward the greater electronegative of the two atoms taking part inside the sigma bond. Due to this, there may be an everlasting dipole that arises in the bond, and the covalent bond is stated to be polarized.
Also read: Ionic Equilibrium lonization and Dissociation
FAQs
What is a covalent bond with an instance?
The electronegativity difference between two atoms is 0. It occurs in any place the combining atoms have comparable electron affinity (diatomic elements). For example, Nonpolar Covalent Bond is discovered in fuel molecules like Hydrogen gasoline, Nitrogen gas, and so on.
How do you become aware of a covalent bond?
There is a pair of exceptional approaches to determine if a bond is ionic or covalent. By definition, an ionic bond is between a steel and a nonmetal, and a covalent bond is between 2 nonmetals. So you generally just have a look at the periodic table and decide whether or not your compound is manufactured from a metal/nonmetal or is just 2 nonmetals.







