Table of Contents
Electrolysis has been defined as the process of breaking down ionic compounds into their constituent elements by passing a direct electric current through the compound in a fluid state. The cathode reduces cations, while the anode oxidises anions. The core elements required for conducting electrolysis are an electrolyte, electrodes, and some form of external power source. A partition, such as an ion-exchange membrane or a salt bridge, may also be used, but this is optional. These were all primarily used to prevent the products from diffusing near the opposing electrode.
Electrolysis has been typically performed in a vessel known as an ‘electrolytic cell,’ which contains two electrodes (cathode and anode) connected to a direct current source and an electrolyte, which is said to be an ionic compound in decomposition, either molten or dissolved in a suitable solvent. Electrodes composed of metal, graphite, and semiconductor materials are commonly used. Even so, the selection of an appropriate electrode is based on the chemical reactivity of the electrode and electrolyte, as well as the manufacturing cost.
Electrolytic Process
The swap of ions and atoms caused by the addition or removal of electrons from the external circuit is referred to as electrolysis. As current starts flowing, cations move to the cathode, accept electrons from the cathode (supplied by the supply source battery), and discharge into the neutral atom. Once the neutral atom is solid, it is deposited on the cathode; if it is gas, it moves upwards. Throughout this reduction process, the cation is reduced at the cathode.
Simultaneously, anions surrender their extra electrons to the anode and are oxidised to neutral atoms at the anode. Electrons launched by anions travel across the electrical circuit and complete the circuit by reaching the cathode. Electrolysis tends to involve a simultaneous oxidation and reduction reaction at the anode and cathode.
Cell Potential or Voltage
The least potential required for electrolysis is determined by the ability of individual ions to absorb or release electrons. It’s also recognised as decomposition potential or decomposition voltage, and it is the minimum voltage (difference in electrode potential) that allows electrolysis to occur between the anode and cathode of an electrolytic cell.
The voltage during which electrolysis is thermodynamically preferred is calculated using the Nernst equation as the difference of the electrode potentials. The application of extra voltage, or overpotential, could really increase the rate of reaction and is frequently required above the thermodynamic value. A potential equivalent to or slightly greater than that is applied externally in electrolysis.
(FAQs) Frequently Ask Questions For Electrolysis
What is the use of electrolysis?
A number of metals and nonmetals are produced using electrolysis in the industry (e.g., aluminium, magnesium, chlorine, and fluorine). Electrolysis has been frequently used to coat one metal with another. Electroplating is really the process of coating one metal with another using an electric current.
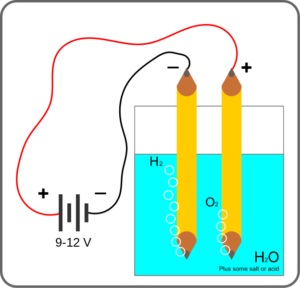
What is electrolysis in water?
Water electrolysis would be the use of electricity to decompose water into oxygen and hydrogen gas through a process known as electrolysis. The whole hydrogen gas can be used as hydrogen fuel or mixed with oxygen to produce oxyhydrogen gas, which is used in welding and other applications.







