Table of Contents
Concentration is a concept that is frequently used in chemistry and related fields. It is a measure of how much of one substance is mixed with another substance. This can refer to any type of chemical mixture, but it is most commonly used in the context of solutions, where it refers to the amount of solute dissolved in a solvent. To concentrate a solution, either more solute or less solvent must be added (for instance, by selective evaporation). To dilute a solution, one must either add more solvent or reduce the amount of solute. A concentration exists at which no more solute will dissolve in a solution. We can say that the solution is said to be saturated at this point. In case, you add more solute to a saturated solution, it will not dissolve. Instead, phase separation will occur, resulting in either coexisting or suspended phases. The point of saturation is determined by a number of factors, including ambient temperature and the precise chemical nature of the solvent and solute. Concentration can be expressed qualitatively (‘informally’) as well as quantitatively (‘numerically’).
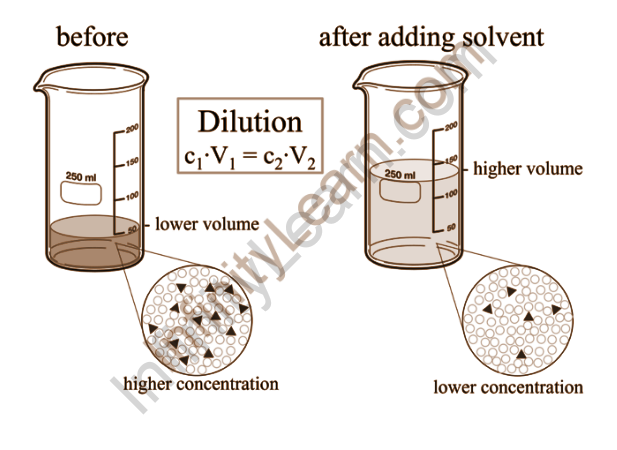
Overview
Concentration in chemistry relates to the quantity of a substance in a defined space. It is also defined as the ratio of solute in a solution to either solvent or total solution. Concentration is typically expressed as mass per unit volume and the solute concentration can be expressed in moles or units of volume. Concentration per unit mass may be used instead of volume. While concentration is typically applied to chemical solutions, it can be calculated for any mixture. Concentrations are frequently referred to as levels, reflecting the mental schema of levels on a graph’s vertical axis, which can be high or low.
Frequently, concentration is described qualitatively in informal, non-technical language, using adjectives such as “dilute” for solutions of relatively low concentration and “concentrated” for solutions of relatively high concentration. To concentrate a solution, either more solute (for example, alcohol) or less solvent must be added (for example, water). To dilute a solution, one must either add more solvent or reduce the amount of solute. Unless two substances are miscible, a concentration exists at which no more solute will dissolve in a solution and the solution is saturated at this point. If more solute is added to a saturated solution, it will not dissolve unless supersaturation occurs under certain conditions. Rather, phase separation will take place, resulting in coexisting phases that are either completely separated or mixed as a suspension. The point of saturation is determined by a number of factors, including ambient temperature and the precise chemical nature of the solvent and solute.
Concentration
Concentration in chemistry is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. There are four types of mathematical descriptions: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration. The concentration can refer to any type of chemical mixture, but it is most commonly used to describe solutes and solvents in solutions. Normal concentration and osmotic concentration are two types of molar (amount) concentration.
Concentration of solution
There are two components in an aqueous solution: solute and solvent. These are the two fundamental solution concentration terms that you must understand. We must always keep track of the amount of solute in the solution. In chemistry, the concentration of a solution is defined as the amount of solute in a solvent. When a solution contains more solute, it is referred to as a concentrated solution. When the solution contains more solvent, it is referred to as a dilute solution.
Dilute and concentrated solutions
Concentrated and dilute are two generic terms for each other. Concentrated refers to chemical solutions that contain a high concentration of a large amount of solute. A solution is said to be saturated when it has been concentrated to the point where no more solute will dissolve in the solvent. When compared to the amount of solvent, diluted solutions contain a small amount of solute.
More solute particles must be added to a solution to concentrate it, or some solvent must be removed. A solution can be concentrated by evaporating or boiling off the solvent if the solvent is non-volatile.
Dilutions are created by diluting a more concentrated solution with a solvent. Preparing a relatively concentrated solution, known as a stock solution, and using it to prepare more dilute solutions is common practice. Because it can be difficult to obtain an accurate measurement of a tiny amount of solute, this practise yields greater precision than simply mixing up a dilute solution. To make extremely dilute solutions, serial dilutions are used. To make a dilution, add stock solution to a volumetric flask and dilute with solvent to the mark.
Expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids
The mass percentage of a component in a given solution is the component’s mass per 100g of solution. If WA denotes the mass of component A, WB denotes the mass of component B in a solution. Then,
Mass Percentage of A in solution is,
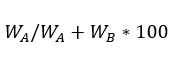
Volume percentage: it is used in case of a liquid dissolved in another liquid. The volume percentage is determined by the volume of the solute divided by the volume of the solution in 100 parts by volume.
Volume Percentage of A in solution is,
![]()
The strength of a solution is described as the quantity of solute present in one liter of solution in grams.
Strength= Mass of Solution in g/ Volume in solution in Liters
The number of moles of solute dissolved per liter of solution is characterized as a solution’s molarity.
Molarity = No of Moles of Solution / Volume of solution in Liters
Consider ‘a’ as the weight of the solute (in gms) present in the VCC volume of the solution.
Molarity is,
The information about the concentration of a solution from various chemistry-related articles is available here. In general, the solution’s concentration indicates how much solute has been dissolved in the solvent. Students who want to flourish in chemistry need to be well known about concentration to get deep knowledge about it to do well on their exams. Concentrated and dilute solutions and expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids are provided here to assist students in effectively understanding the respective topic. Continue to visit our website for additional chemistry help.
FAQ’s
What is the concentration of the solution?
The solution's concentration indicates how much solute has been dissolved in the solvent.
Does solution concentration change when solution volume changes?
When it comes to molarity, the answer is yes. Although if we take concentration by mass into account, it will still change unless the substance has an undefined density. Because the mass of a substance changes with its volume, so does its concentration. However, if both the solute and the solvent increase or decrease in volume/mass/moles in an equal ratio, the concentration and molarity remain constant.
What are the types of concentration?
There are four types of mathematical descriptions: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration.





