Table of Contents
The flower is a reproductive part of unfolding seed shops. It’s principally made of 4 concentric rings of structures similar to sepals, pistils, petals, and stamens. A fruit is a grown ovary containing seeds. And seeds are completely developed ovules that are able of producing a new factory. Seeds and fruits are formed by fertilization. In angiosperms, the formation of two structures is seen as a result of double fertilization – a diploid zygote and a triploid primary endosperm cell.
The zygote is ripened into an embryo, whereas, the endosperm cell gives birth to endosperm. It provides aliment to the growing embryo. The function of the flower is to ensure pollination. Flowers also give protection for the ovule and developing embryo inside a container. The function of the fruit is seed disbandment. They also cover the developing seed.
Overview
The seeds and fruits are the results of fertilization or sexual reduplication in shops. The ovary in angiosperms develops into the fruit whereas the ovules come from the seeds enclosed within the fruit. Seeds are planted both in gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Fruits contribute to a significant proportion of the world’s agrarian products, and some fruits have gained huge profitable, artistic, and emblematic meanings. Seeds develop in the angiosperms and gymnosperms groups of shops. Still, these two groups of shops will produce two types of seeds known as “ enclosed seeds” and “ naked seeds” independently. Fruit plays a vital part in seed disbandment by attracting creatures.
Seed plays a vital part in the reduplication of gymnosperm and angiosperm shops. In addition, seeds are important for the food of the embryo they’re also vital in spreading to a new position and guarding factory or dormancy during unfavorable conditions. Fruit doesn’t represent reduplication units. Seed Principally are used for reduplication, and it’s the product of the sexual reduplication of the plants.
Flower
There are all feathers of flower shapes, sizes, colors, and arrangements; still, there are many features that are central to all flowers anyhow of their form. A flower starts as an embryonic primordium that develops into a cub and it’s positioned on a technical branch at the end of a stalk called the peduncle.
The container is a small pad-such as a blown area on the very top of the peduncle. This serves as the platform for the flower corridor. Curls, which are three or further factory corridors, are attached to the container. The sepals are the remotest spiral and are generally green. Occasionally they’re confused with leaves. They’re generally three to five in number and are inclusively appertained to as the calyx.
The alternate spiral of the flower corridor are the petals and are inclusively appertained to as the corolla. The corolla is generally extra-showy to attract pollinators. In wind-pollinated shops, the corolla may be missing to maximize pollen exposure to the womanish flower corridor.
Just as the sepals in the calyx, the petals in the corolla may be fused or done as separate individual units. Nestled inside the two external curls are the sexual organs of the flower. The stamens number the manly structures semi-rigid hair with a sac called the anther swinging from the tip. Pollen grains develop in the anthers. Utmost anthers have gashes or pores on the sides to accommodate pollen release.
The womanish organs are inclusively appertained to as the pistil and include a‘ wharf pad at the top called the smirch, a slender stalk-suchlike style that leads down to the blown base called the ovary. The ovary is what will develop/ grow into a fruit.
Fruits
One of the numerous healthy effects available in the world moment is fruits. They’re substantially sweet to taste, are filled with nutrients and some of them are like tomatoes are also eaten as vegetables. The fruit is astronomically divided into the pericarp which is the colorful covering layers of the fruit and the seed or seeds which are present inside it. The pericarp of fruit can be further divided into
- Exocarp – It’s the remotest subcaste that’s formed from the external subcaste of the epidermis
- Mesocarp – Is the alternate or the middle subcaste which is frequently juicy and varies inconsistency in different fruits
- Endocarp – It’s the inmost subcaste and also is different in different kinds of fruits
Development of a Fruit
As mentioned before, formerly pollination and fertilization do, the zygote is formed and the ovary begins to separate into the fruit. The external wall of the ovary begins to separate into the pericarp whereas the seed develops within the fruit itself.
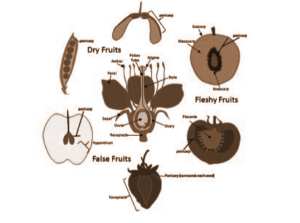
Types of Fruits
These fruits are formed by a single pistil only. They’re further divided into Fleshy and Dry fruits grounded on the nature of their pericarp and its layers.
- True Fruits-True fruits are those that are formed solely from the ovary with ovules inside it. No other flower corridor form a part of this type of fruit.
- False Fruits-False fruits are formed from the grown ovary along with some other flower corridor like the base or container, the perianth.
Fruits with seeds
Fleshy Fruits
Fleshy fruits, as the name mentions, have a fleshy and juicy pericarp. They’re further of numerous different types
- Drupe-In this type of fleshy simple fruit, the exocarp is thin, the mesocarp is thick and juicy while the endocarp is stony. Exemplifications of similar fruits are mango, pearl, and coconut.
- Berry-In this type of fleshy fruit, the endocarp is absent and the seeds are scattered in the mesocarp. Exemplifications are grapes, bananas, tomatoes.
- Pome-This is a false fruit as the thalamus forms a part of the fruit. Exemplifications of this type of fruit are apples, pears.
Dry fruits
Sot fruits don’t have juicy or thick pericarps and are of two types.
Dehiscent dry fruits
These fruits burst on their own to release the seeds. They’re of numerous types
- Follicle – These fruits are formed from a single carpel and dehisce along one fissure or periphery only. Ex Calotropis
- Legume – These fruits are formed from a single carpel and dehisce along both sutures. Ex legumes, sap
- Capsule – Is formed from multiple carpels. It has numerous pores or chambers in it and it dehisces by unyoking into numerous corridors to release seeds. Example Lady’s Finger
- Siliqua – It’s formed by two carpels and dehisces from the base overhead with the seeds attached to the base itself.
Indehiscent dry fruits
These fruits don’t dehisce or burst to release the seeds. They’re of numerous types.
Achene Is single-seeded and the seed fleece is separate from the fruit fleece or pericarp.
- Caryopsis This is analogous to the achene except that the seed fleece and the fruit fleece are united or fused. Example Maize
- Nut One- planted fruit with a stony pericarp. It may contain a cocoon on its wall as well. Example Oak, Chestnut
- Cypsela Is formed from a carpellary inferior pistil. It’s also one- planted. Illustration Sunflower
- Aggregate Fruits: These fruits are developed from a total or cluster of multiple separate pistils that are borne on a single flower. This total or group of fruits that are developed from a single flower are known as an etaerio. Illustration Jeer.
- Multiple Fruits: When an entire inflorescence develops into a single fruit, it’s called multiple fruits. Illustration Pineapple, figs, mulberry, jackfruit.
Seeds
Once fertilization occurs, the mature ovule begins to separate into a seed. A seed contains numerous corridors, videlicet
- Seed Fleece – is formed from the integuments of the ovule. The seed fleece contains a hilum which is a scar that represents the spot where the ovule was attached to the ovarian wall. The seed fleece is present each over the seed except for a small severance called the micropyle which the where the new factory will germinate on chancing a favorable terrain.
- The cotyledons – Monocots contain a single cotyledon whereas the dicots contain two cotyledons. The two cotyledons act as accessories and help in the immersion of food from the endosperm.
- Endosperm – It’s a triploid towel that’s formed by the emulsion of one of the manly capitals (haploid) and the vegetative capitals (diploid).
Also read: Root, Stem, and Leaves
FAQs
Which part of the flower grows into fruit and seeds?
Ovary grows into fruit and seeds.
What are the two essential parts of a flower needed in seed formation?
Stamen (male part) and the pistil (female part) are needed in the seed formation.
What is common between fruits and seeds?
Creatures that eat fruit help to spread the seeds further down. The plants that grow from seed will have the same type of flower and fruit which was produced by the plant. Flowers produce seeds before they die.
Which type of relationship is seen between seeds and flowers?
A plant has one reason to grow – to reproduce and make further shops like it. Flowers are the reproductive corridor of utmost shops. For a seed to develop, pollen has to move from a manly to the womanish corridor of flowers and grow down to the ovary.







