Table of Contents
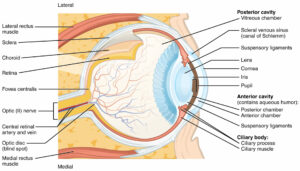
The ciliary body is a circular structure in the eye connected to the iris and located directly behind it. It produces a liquid with water inside the eye. It connects with the muscles that make the eye lens focus on nearby objects. This tissue ring is one of the three components that make up the uvea of the eye – the middle layer of the colored eye. The other two parts are the iris (colored part of the eye) and choroid (the part of the eye that enlarges the retina). These two parts are connected together by the ciliary body.
What is the ciliary body?
Structurally, the ciliary body is a ring of tissue around the iris and connects it to the choroid. It cannot be seen by looking at the eye because it is located behind the iris and sclera, which is the white part of the eye.
Structures contained within the ciliary body include:
- Ciliary muscle affects the shape of the lens inside the eye. The contraction of the muscles makes the lens more convex, allowing the eye to focus on nearby objects. The cilliary muscle is attached to the lens by a series of very thin strands arranged in radially shaped ciliary zonules (also called zonular fibers or Zinn zonules), which hold the lens in place inside the eye.
- Ciliary processes are about 70 layers in the body consisting of cells involved in producing aqueous humor in the eye that regulates eye pressure.
Functions of the ciliary body
There are three main functions: the living space, holding the lens in place, and producing fluid.
- Seating refers to the ability to automatically increase its concentration so that the eye can see objects in greater detail. This action relies on the ciliary muscle.
- It holds the lens of the eye behind the pupil using tiny filaments called zonules or Zinn zonules.
- The production of fluid occurs in the ciliary body. Liquid fluid (or aqueous humor) is a clear liquid in the eye that provides nutrition and helps the eye maintain its shape and healthy pressure levels.
Each of these functions is important for the health of the eye – in fact, conditions such as ocular hypertension and glaucoma can occur when too much fluid is produced by the ciliary body.
Ciliary body and glaucoma
The aqueous humor – which is constantly produced by the ciliary body – draws through a path called the trabecular meshwork at an angle where the iris and cornea meet.
There must be a balance between how much aqueous jokes are produced and how much light to maintain in order to maintain a healthy amount of pressure in the eye. This is known as intraocular pressure (IOP).
Ocular hypertension is a term used to describe a higher IOP than normal. This high pressure can lead to glaucoma – a term used to describe a set of related eye conditions that cause optic nerve damage and can lead to blindness if left untreated.
How does glaucoma treatment affect the ciliary body?
Typically, the first treatment used for glaucoma is eye drops, which are designed to help control eye strain by reducing the production of fluid by the ciliary body and/or increasing its output from the eye.
Some of the most common types of glaucoma treatments that affects:
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as Azopt (brinzolamide) and Trusopt (dorzolamide).
- Beta-blockers such as Betoptic (betaxolol) and Timoptic (timolol).
- Alpha-adrenergic agonists such as Alphagan P (brimonidine) and Iopidine (apraclonidine).
Ciliary body and presbyopia
Presbyopia is a common, age-related loss of eyes focused on nearby objects. It usually occurs sometime after 40 years.
Presbyopia occurs because
- the lens of the eye thickens over time and loses its natural flexibility
- or the ciliary muscles lose their flexibility
Fortunately, presbyopia can be treated with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or vision surgery. For some, reading over the counter is a simple presbyopia solution.
When to see an eye doctor?
Problems related are with serious eye conditions such as glaucoma. Because there are no early warning signs of the disease, a thorough eye examination by an optometrist or ophthalmologist is the only way to prevent vision loss in glaucoma. If you have experienced symptoms of presbyopia, consult an eye specialist for an eye examination and discuss the best treatment option in the future.
The ciliary body is not the only part of the visual system that needs to be taken care of. Stay up to date with the latest eye tests to ensure complete eye and vision health, and do not hesitate to contact your optometrist for any additional vision problems you may have.
FAQs
How do ciliary muscles help in the living space?
Reaching the ciliary muscles makes the lens round and increases the ability to concentrate. When loosened, the zonular fibers are enlarged to make the lens flat, which can accentuate an object far away from the retina. This is known as the accommodation reflex.
What is a ciliary muscle's function?
One function of the ciliary body is to control the lens of the eye. The ciliary body's smooth muscles contract and relax to focus on near or far away objects. Muscle contractions are partly responsible for the round shape of the eye's lenses since fine ligaments directly attach the lens to the ciliary body.







