Table of Contents
Definition:
Chemical integration and integration is a process that occurs primarily in our endocrine glands. This gland secretes many hormones that control the function of various parts of the human body. In animals, vertebrates have a highly developed and complex endocrine system. These glands are not present in plants, but they release other hormones that control their function.
What are the endocrine glands?
The human endocrine glands are a combination of a complex network of glands responsible for producing several timely hormones in the human body that help regulate the function of tissues and cells in the body. Note, some of the endocrine glands are directly related to the ovary in women and testicles in men. The hormones produced by these glands are divided into two categories, namely, lipid-soluble hormones and water-soluble hormones.
Chemical Nature of Hormone: – Animal hormones can be divided into 6 categories.
- Amino acid sources: – The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are derived from the adrenal medulla and thyroxine from the thyroid gland are found in amino acids.
- Short-acting peptides: – The hormones Oxytocin and vasopressin from the posterior part of the pituitary gland are short-acting amino acid peptides 9. The melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) from the middle part of the pituitary gland is also a short peptide of 13 amino acids.
- Long peptides: – The hormone insulin from the pancreas, adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary gland, calcitonin from the thyroid gland are peptides longer than 30 amino acids, parathormone in the parathyroid gland contains 84 amino acids.
- Proteins: – Gonadotropic, thyrotropic, and somatotropic hormones from the anterior pituitary gland are proteins with a high molecular weight.
- Steroids (Soluble Fats): – Hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone from the adrenal cortex, testosterone from the testes cells of the testes, estrogen and progesterone from the Graaffian follicles of the ovary and the ovary -placenta are examples of steroid hormones. These hormones contain cholesterol and bile salts.
- Fatty acid derivative: – Prostaglandin
The list of endocrine glands in the human body is as follows: –
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid glands
- Pituitary gland
- Adrenal glands
- Predators
- Gonads
- Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Thymus
The Functions of the Various Glands Located in the Human Body
Components and function of the human endocrine system
As we learned above, there are various components of an endocrine system. Therefore, let us briefly consider the role and functions of these body parts separately.
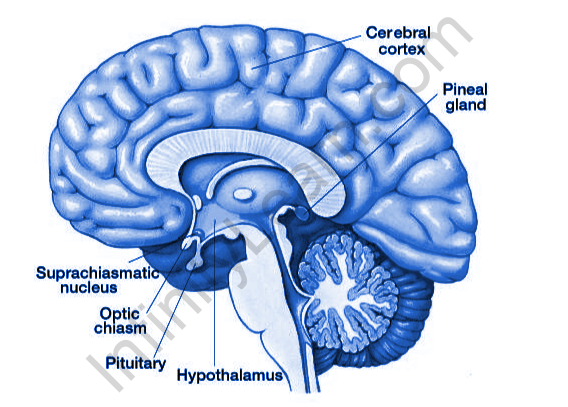
- Hypothalamus: This gland is also part of the nervous system, which contains neurosecretory cells. It is associated with both the endocrine and nervous systems. Gonadotropin and growth hormones are secreted by the Hypothalamus.
- Pituitary Gland: This gland is also known as the main gland in the human body. The size of the pituitary gland is similar to that of a pea, and it is found beneath the brain. Some glands are controlled by this gland. Other major hormones are released by the thyroid gland, are FSH and LH.
- Pineal Gland: This gland is found in the brain. Melatonin is released by the thyroid which regulates the immune system, sleep clock, etc., in the human body.
- Parathyroid Gland: It is a butterfly-like gland. This gland releases parathormone that helps our body maintain a level of phosphorus and calcium in the bones.
- Cerebral Cortex: The cerebellar cortex receives information from many parts of the body, as well as from many other areas of the brain. The cerebellum collects this information and sends signals back to the rest of the brain, thus enabling precise and precise movement.
- Suprachiasmatic Nucleus: The nucleus or suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) is a small area of the brain in the hypothalamus, located just above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for controlling the circadian rhythm. The neuronal functions and the hormone produced produce many different bodily functions in a 24-hour cycle.
The structures of various hormones are produced by the human body
- These hormones are produced by the endocrine glands and enter the bloodstream directly.
- These hormones are short-lived and have no antigens.
- Proinsulin Hormones produced by the pituitary gland are made up of ineffective mechanisms.
- Hormones regulate different metabolic and physiological functions.
- Low concentration is required.
- These hormones also work faster.
A combination of chemical and control models and endocrine glands. Our body produces a lot of hormones every day. The endocrine system is one of the most important systems of the human body as all human growth such as flexibility, reproduction, body growth, etc depends on this.
Chemical integration and integration is a process that occurs primarily in our endocrine glands. This gland secretes many hormones that control the function of various parts of the human body.
The production of the human body contains various glands such as the thyroid gland, Parathyroid gland, Pituitary gland, Adrenal glands, Pancreas, Gonads, Pineal gland which produce various hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, adrenocorticotropic hormones, testosterone, adrenaline, and cortisol. These hormones are essential for the various functions of the human body.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Thyroid
FAQs
What is Thyroid?
The thyroid in the human body is a system of glands and organs where these are located in front of the neck wrapped around the trachea. It helps to regulate and regulate all the functions of the human body and metabolism.
What is the role of the pancreas in the human body?
The pancreas is a stomach organ surrounded by the spleen, liver, and small intestines and located behind the abdomen. It is an important part of the digestive system that regulates blood sugar levels. Digestive enzymes are produced by the pancreas in the duodenum. These enzymes help digest sugar, proteins, and lipids. Pomegranates contain the islands of Langerhans, which produce hormones such as insulin and glucagon in the bloodstream.
What are the gonads in the human body?
The male and female reproductive organs are called gonads. It is part of the endocrine system and the main reproductive system. The male gonads, like the testes, produce male sex hormones, while the female gonads, like the ovary, produce female sex hormones.