Table of Contents
Fragmentation most generally means the process of disintegration. All multicellular organisms can not reproduce by this method because the random increase in the number of cells, organization into tissue and then organs is not practical. Examples of organisms reproduced by fragmentation are:- Sea anemones, Sedum, bulbs, Tolmiea menziesii, corms, etc. Sponges and coral colonies also reproduce or naturally possess fragmentation. Fragmentation is a very common type of vegetative reproduction in plants.
Definition:
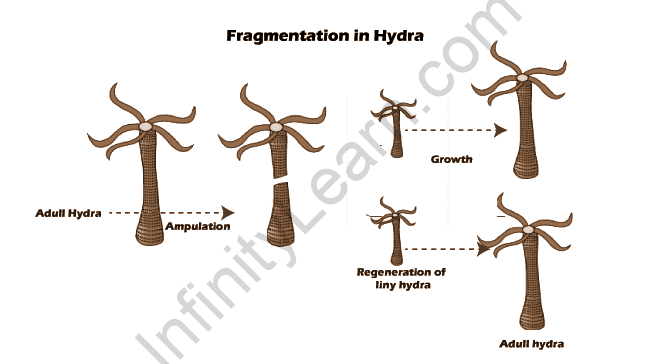
In a multicellular filamentous organism, the body breaks into fragments. Each filament grows into new individuals. This whole process is known as fragmentation.
Fragmentation in multicellular or colonial organisms is a form of asexual reproduction or cloning, where an organism is split into fragments. Each of these fragments develops into mature, fully grown individuals that are clones of the original organism. The organism may develop specific organs or zones to shed or be easily broken off. If the splitting occurs without the prior preparation of the organism, both fragments must be able to regenerate the complete organism for it to function as reproduction. Fragmentation as a method of reproduction is seen in organisms such as filamentous cyanobacteria, molds, lichens, sponges, acoel flatworms, some annelid worms, and sea stars.
Concept:
The breaking up of a body of a simple multicellular organism into two or more pieces on maturing, each of which grows to form a completely new organism is called fragmentation. The two main areas where fragmentation plays a very vital role in biological cells are apoptosis and DNA cloning. In DNA cloning part of the genes are transferred from the main body to fragments whereas, in apoptosis, the decay of dead cells occurs.
Examples:
Spirogyra(a green filamentous algae plant found in ponds, lakes, etc), sea anemones (marine animal). The filament simply breaks into two or more fragments on maturation and each fragment grows into a new spirogyra. All multicellular organisms can not reproduce by this method because the random increase in the number of cells, organization into tissue and then organs is not practical.
Fragmentation in various organisms:
Molds, yeasts, and mushrooms, all of which are part of the Fungi kingdom, produce tiny filaments called hyphae. These hyphae obtain food and nutrients from the body of other organisms to grow and fertilize. Then a piece of hyphae breaks off and grows into a new individual and the cycle continues. Many lichens produce specialized structures that can easily break away and disperse. These structures contain both hyphae of the mycobiont and the algae (phycobiont). Larger fragments of the thallus may break away when the lichen dries or due to mechanical disturbances. Fragmentation most generally means the process of fragmenting—breaking into pieces or being divided into parts. It can also refer to the state or result of being broken up or having been divided.
In Plants:
Fragmentation is a very common type of vegetative reproduction in plants. Many trees, shrubs, nonwoody perennials, and ferns form clonal colonies by producing new rooted shoots by rhizomes or stolons, which increases the diameter of the colony. If a rooted shoot becomes detached from the colony, then fragmentation has occurred. There are several other mechanisms of natural fragmentation in plants.
- Production of specialized reproductive structures: A few plants produce adventitious plantlets on their leaves, which drop off and form independent plants, e.g. Tolmiea menziesii and Kalanchoe daigremontiana. Others produce organs like bulbils and turions.
- Easily lost parts that have high potential to grow into a complete plant: Some woody plants like the willow naturally shed twigs. This is termed “Cladoptosis”. The lost twigs may form roots in a suitable environment to establish a new plant. River currents often tear off branch fragments from certain cottonwood species growing on riverbanks. Fragments reaching suitable environments can root and establish new plants. Some cacti and other plants have jointed stems. When a stem segment, called a pad, falls off, it can root and form a new plant. Leaves of some plants readily root when they fall off, e.g. Sedum and Echeveria.
- Fragmentation is observed in nonvascular plants as well, for example, in liverworts and mosses. Small pieces of moss “stems” or “leaves” are often scattered by the wind, water, or animals. If a moss fragment reaches a suitable environment, it can establish a new plant. They also produce “gemmae”, for example in the splash-cups of Marchantia polymorpha, that are easily broken off and distributed.
- People use fragmentation to artificially propagate many plants via division, layering, cuttings, grafting, micropropagation, and storage organs, such as bulbs, corms, tubers, and rhizomes.
In Animals:
Sponges and coral colonies naturally fragment and reproduce. Many species of annelids, flatworms, Montipora, Acropora, Pocillopora, Euphyllia, and Caulastrea reproduce by this method. When the splitting occurs due to specific developmental changes, the terms orchiectomy, laparotomy, and budding are used. In ‘architomy’ the animal splits at a particular point and the two fragments regenerate the missing organs and tissues. The splitting is not preceded by the development of the tissues to be lost. Prior to splitting, the animal may develop furrows at the zone of splitting.
Also read: Coronary Artery Disease
FAQs
Q. In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by?
- Regeneration
- Fragmentation
- Budding
- Binary Fission
Ans: Correct Answer is B.
In a multicellular filamentous organism, the body breaks into fragments. Each filament grows into new individuals. This whole process is known as fragmentation. And spirogyra shows this function so spirogyra reproduces by fragmentation.
What is the difference between fragmentation and regeneration?
Fragmentation is a method of asexual reproduction where an organism reproduces by the process of splitting into fragments and each fragment grows into an individual organism. Regeneration, on the other hand, happens when an organism regrows certain parts or limbs which is lost due to predation.
Q. Which of these organisms do not reproduce by means of fragmentation?
- Molds,
- Flatworms,
- Bacteria
Ans: Correct answer is C.
Because Asexual reproduction in bacteria is by binary fission. It is the main mode of their propagation. Binary fission leads to the formation of identical copies of a cell without any genetic recombination.