Table of Contents
Microbodies are single membrane organelles present in kingdom Plantae, Animalia, and protozoa. They are cytoplasmic organelle that are in globular shape. They are materials for metabolic activity. We can find them more frequently in liver and kidney cells. Microbodies are further classified into different types. Microbodies are known as subcellular respiratory organelle in eukaryotic organisms.
Learned about the microbodies, where they are located, their function of them, classification of microbes in detail. All are discussed in this article which is more important to read for any biology-related competitive exam. Brief about microbodies are Microbodies are single membrane organelles present in kingdom Plantae, Animalia, and protozoa. They are cytoplasmic organelle which is in globular shape. They are materials for metabolic activity. We can find them more frequently in liver and kidney cells. Microbodies are further classified into different types. Microbodies are known as subcellular respiratory organelle in eukaryotic organisms. This is all that we learn in this article, which is one of the main topics because its basic level chapters are necessary to learn.
Structure of microbodies
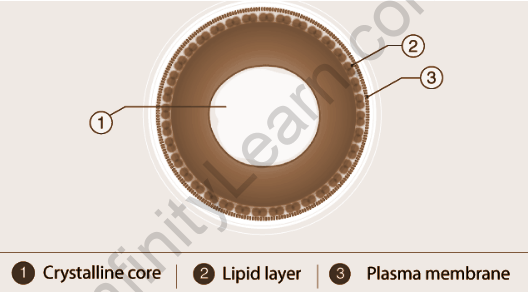
Microbodies are present in the cytoplasm of the cell by which they are known as cytosomes. They are in a very small size which is approximately 0.2 to 1.5 μm. They are enclosed with a single membrane. The matrix present in them is having proteins and enzymes. They don’t have DNA material specifically. They are usually in vesicles or spherical in shape. The membrane is made up of phospholipids and they are only visible under an electronic microscope.
Microbodies were first discovered and named by rhodium in 1954.
Functions of microbodies
Some of the functions of microbodies are:
- Have a crucial role in various biochemical reactions.
- Involved in detoxification of peroxides and in photorespiration in plants.
- Enzymes which are present in microbodies are helpful in facilitating various essential reactions like a breakdown of fats, alcohol, and amino acids.
Classification of microbodies
Different microbodies perform different functions in the living organism.
Some important types of microbodies are glyoxysomes, peroxisomes, glycosomes, and woronin bodies. Let’s study about them in detail:
- Peroxisomes: These are present in eukaryotic cells. They take part in the oxidative process. Also, they participate in lipid metabolism and catabolism of D-amino acids, polyamines, and bile acids. Peroxides are produced in this process by converting water by various enzymes like peroxidase and catalase. In plants, photorespiration occurs here. It performs beta-oxidation to break fatty acids.
- Glyoxysomes: These are specialized peroxisomes. Their main function is to convert fatty acids to carbohydrates. They are mainly found in plants and fungi. Glyoxysomes are widespread in the germinating seeds in their fat-storing tissues. They synthesize sugar by the process of gluconeogenesis.
- Glycosomes: Glycosome contains glycolytic enzymes and a dense proteinaceous matrix. some scientists believed that it evolved from peroxisomes. It contains both proximal and glycolysis enzymes.
- Woronin bodies: Woronin bodies are double membrane, dense core microbodies. It was found by scientist Stefanovich Voronin in Ascomycota. The main function of woronin bodies is to plug septal pores post hyphal wounding. It reduces the loss of cytoplasm from the site of injury. The size of the worn body may vary from 100 nm to more than 1 μm.
Importance of this chapter in NEET:
As in this chapter, we will learn about the cell organelles which is basic and we should know about all the cell organelles as it is a basic unit of the living body. From this chapter, you can expect ten to fifteen based on the function and membrane, and morphology also. As it has full information regarding organelles we just need to memorize and then get good marks. Don’t neglect this chapter as it is important for scoring high marks. We should study this chapter as it tells the cell organelle where the cell is the basic unit of life. Do not neglect this area which brings you to score easily.
Also read Important Topic Of Biology: Cell Cycle.
FAQs
Write about microbodies.
Microbodies are single membrane organelles in the kingdom Plantae, Animalia, and protozoa. They are cytoplasmic organelles that are globular in shape. They are materials for metabolic activity. We can find them more frequently in liver and kidney cells. Microbodies are further classified into different types. Microbodies are known as subcellular respiratory organelles in eukaryotic organisms.
What is the structure of microbodies?
Microbodies are present in the cell's cytoplasm, known as cytosomes. They are very small in size, which is approximately 0.2 to 1.5 μm. They are enclosed with a single membrane. The matrix present in them has proteins and enzymes. They don't have DNA material specifically. They are usually in vesicles or spherical in shape. The membrane is made up of phospholipids, and they are only visible under an electronic microscope. Microbodies were first discovered and named by rhodium in 1954.
Write about woronin bodies?
Woronin bodies are double membrane, dense core microbodies. It was found by scientist Stefanovich worn in Ascomycota. The main function of woronin bodies is to plug septal pores post-hyphal wounding. It reduces the loss of cytoplasm from the site of injury. The size of the worn body may vary from 100 nm to more than 1 μm.
Question: Write about types of micro bodies.
Answer: Different microbodies perform different functions in the living organism.
Some important microbodies are glyoxysomes, peroxisomes, glycosomes, and woronin bodies. Let’s study them in detail:
- Peroxisomes: These are present in eukaryotic cells. They take part in the oxidative process. Also, they participate in lipid metabolism and catabolism of D-amino acids, polyamines, and bile acids. Peroxides are produced by converting water with various enzymes like peroxidase and catalase. In plants, photorespiration occurs here. It performs beta-oxidation to break fatty acids.
- Glyoxysomes: These are specialized peroxisomes. Their main function is to convert fatty acids to carbohydrates. They are mainly found in plants and fungi. Glyoxysomes are widespread in the germinating seeds in their fat-storing tissues. They synthesize sugar through the process of gluconeogenesis.
- Glycosomes: Glycosome contains glycolytic enzymes and a dense proteinaceous matrix. some scientists believed that it evolved from peroxisomes. It contains both proximal and glycolysis enzymes.
- Woronin bodies: Woronin bodies are double membrane, dense core microbodies. It was found by scientist Stefanovich worn in Ascomycota. The main function of woronin bodies is to plug septal pores post-hyphal wounding. It reduces the loss of cytoplasm from the site of injury. The size of the worn body may vary from 100 nm to more than 1 μm.







