Table of Contents
Introduction:
Chemical reactions: A complex is formed when one or even more compounds, termed reactants, are transformed into one or more distinct substances, called products. Chemical elements or molecules are illustrations of substances. The basic atoms of the reactants are rearranged in a chemical reaction, resulting in the formation of various substances as products. Chemical reactions are a crucial principle of technology, civilization, and even humanity. Chemical reactions proliferate in Earth’s geology, its atmosphere, and seas, and a plethora of sophisticated processes take place in all-natural systems. Many activities involving chemical reactions that have been understood and practiced for thousands of years include burning fuels, smelting iron, creating glass and earthenware, beer brewing, and making cheese and wine.
A brief outline
When chemical bonds between molecules are established or broken, chemical reactions occur. The reactants are indeed the components like that into a chemical reaction, and the products are the ones that happen out from the technique. Though a chemical reaction is not necessarily a “one-way street,” an arrow is drawn between the reactants and products to denote the direction of the reaction. The best illustration of physical and chemical transformation is a burning candle. Light a candle and put it on the table. We see why the candle converts to wax as time passes on. The candle will go out if you cover it with a jar.
The blazing of the candle is a chemical change, whereas the turning of the candle to wax is a physical difference in the demonstration. A physical change predominantly causes a shift in the state of a substance, whereas a chemical reaction usually results in the formation of a new substance in which energy is either released or absorbed. In conclusion, we can extrapolate those chemical changes are followed by physical modifications.
Fundamental Concepts-When two or more substances combine to generate a new product, it is called a chemical reaction (s). Reactants are molecules that tend to form new compounds, whilst products are recently created compounds. Chemical reactions are important in a variety of sectors, customs, and even our daily lives. They are constantly recurring in our circumstances, such as rust of iron, pottery, and wine fermenting, to cite a few. A chemical change must occur in a chemical reaction, which is commonly observed with physical changes such as precipitate, heat production, color change, and so on.
Important concepts
Chemical Equation
Because there are so many chemical reactions all around us, a nomenclature was created to make expressing a chemical process in the manner of a chemical equation easier. A chemical equation is an empirical statement that represents the production of a product from reactants while also indicating the conditions under which the reaction was carried out.
The reactants are on the left, with one-headed or double arrows connecting them to the products generated on the right. Consider a reaction.
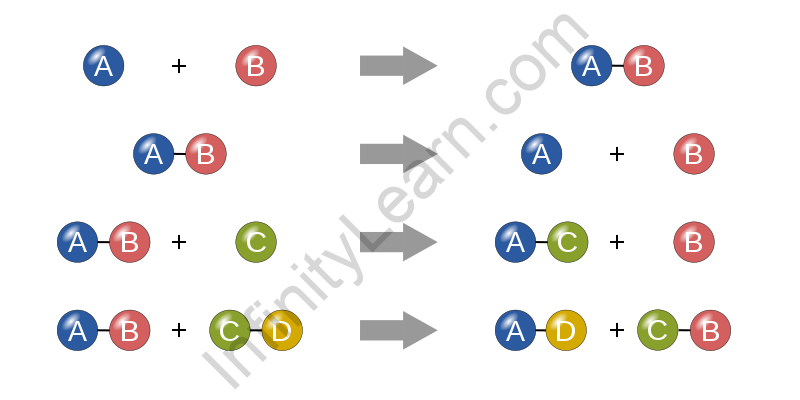
A + B → C + D
A and B appear to be the reactants, while C and D appear to be the process’s products. Chemical formulas are used to identify reactants in a chemical equation. To ensure the law of conservation of mass, a chemical equation must be balanced, which implies that the number of atoms on both sides must always be equal. The equation is calculated in this way.
Chemical Reactions Types:
- Combustion Reaction
The Combustion Reaction is the first step in the combustion process. A combustion reaction occurs when a combustible substance is combined with an oxidant to produce an oxidized product. An oxidizer is a chemical that allows fuel to burn, most often oxygen.
- Reaction of Decomposition
A decomposition reaction occurs when a single component is broken down into several compounds. Certain modifications in energy in the environment, such as heat, light, or electricity, must be made to break the bonds of the molecule.
- Neutralization Reaction
The interaction between an acid with a base that produces salt and water is known as a neutralization reaction. The combination of OH– ions and H+ ions from the water molecule.
- The Redox Process
A Reduction Oxidation is one in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. Consider the case of a redox reaction involving Zinc and Hydrogen in an electrochemical cell.
- Double-Displacement Reaction or Precipitation
It’s a displacing reaction in which two compounds engage and their anions and cations swap positions, resulting in the formation of two new products.
- Reaction of Synthesis
A synthesis reaction is among the most fundamental forms of reaction, in which several simple molecules mix under certain physical conditions to produce a complex product.
Examples of chemical change:
- In the presence of moisture and oxygen, iron rusts.
- Wood is burned.
- The curdling of milk
- Caramel is created by boiling sugar.
- Cookies and cakes are baked.
- Cooking any type of food
- The reaction of acid and base
- The process of food digestion
- Getting an egg to boil
- Fruit maturation
- Food spoilage
- Fermentation
- A matchstick is lit.
- Explosions of fireworks
- Photosynthesis
- Decomposition of waste
- Popcorn making
- Cheese is made from milk.
- Paper is being burned.
- Candles being lit
Chemical reaction examples
- water + carbon dioxide + light —> glucose and oxygen (photosynthesis)
- sodium + chloride —> sodium chloride (table salt)
- food —> proteins and carbohydrates (digestion process)
- zinc + hydrochloric acid —> zinc chloride and hydrogen gas
- zinc + silver nitrate —> zinc nitrate and silver metal
- iron sulfide + hydrogen chloride —> iron chloride and hydrogen sulfide (poisonous gas)
- lead nitrate + potassium iodide —> lead iodide and potassium nitrate (saltpeter)
- lime + carbon dioxide —> calcium carbonate (used to strengthen masonry)
Significance of chemical reactions in NEET exam
Students must have a conceptual comprehension of the complete subject in order to master the NEET exam. Though all of the chapters are absolutely vital, and you should never leave any section of your syllabus out, there are a few that you should pay special attention to. Because the NEET exam is such a significant milestone in every student’s life, choosing the ideal study material for the preparation is vital. Our goal is to instill confidence in our students. As a result, we created the Physics solutions in just such a way that they address every question that a student might have. Our solutions are available in pdf format, which students can access at any time and from any location.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Morphology
FAQs:
What is the distinction between a chemical reaction as well as a chemical equation?
A chemical reaction occurs when the bonds between reactant molecules are broken and new bonds are established between product molecules, resulting in the formation of new material. A chemical equation is a mathematical expression that depicts the formation of a product from reactants.
What are the different types of chemical reactions?
Different types of chemical reactions are Product of combustion, Degradation reaction, Neutralization response, Redox reaction, Precipitation or Double-Displacement reaction, and Synthesizing reaction, based on the products created.
What is the chemical reaction of combustion?
A combustion reaction occurs when a substance combines with oxygen gas, producing energy in the form of heat and light in the process.







