Table of Contents
Polymer, any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, known as macromolecules, which are multiples of simpler chemical units known as monomers. Polymers make up many of the materials found in living organisms, such as proteins, cellulose, and nucleic acids. Furthermore, they serve as the foundation for minerals such as diamond, quartz, and feldspar, as well as man-made materials such as concrete, glass, paper, plastics, and rubbers. A polymer is made up of an unknown number of monomer units. When the number of monomers is extremely high, the compound is referred to as a high polymer. Polymers are not limited to monomers that have the same chemical composition, molecular weight, or structure. Some natural polymers are made up of only one type of monomer. Most natural and synthetic polymers, on the other hand, are composed of two or more different types of monomers; these polymers are referred to as copolymers.
The biotic world in which humans live is made up of smaller subunits known as natural polymers. They are distinguished from synthetic polymers by the fact that they are composed of organic molecules or atoms. In the presence of natural polymers, the living component of the Earth’s ecosystem functions. They are the fundamental building blocks upon which all living interactions are based in all five biological kingdoms of the standard taxonomy. Their abundance in the natural world can be explained by the critical role they play in nature. Natural polymers that are important include cellulose, chiton, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Overview
Polymer is made up of two words: poly, which means many, and “mer”, which means unit. Polymers are large units made up of repeating units called monomers. Monomers, on the other hand, are simple molecules that polymerize. Polymerization is a chemical reaction that occurs when two or more molecules react and join to form polymers, which form a long chain of repeating units known as polymers. Monomers can combine in two ways: directly or indirectly. They join together and form long chains in direct combination, and they join together and release a water molecule in indirect combination.
A polymer is created by chemically joining small molecules or substances into a single giant molecule. Monomer refers to the small molecules that are used in the synthesis of a polymer. Natural Polymers are organic substances that can be found in nature. These polymers are created through either addition polymerization or condensation polymerization. Polymers can be found all over the place in nature. Our bodies, too, are made up of many natural polymers such as nucleic acids, proteins, and so on. Cellulose is another natural polymer that is an important structural component of plants. The majority of natural polymers are formed from condensation polymers, and as a by-product of this formation from monomers, water is obtained. Some natural polymers include DNA and RNA; these polymers play critical roles in all living organisms’ life processes. This messenger RNA is responsible for the formation of peptides, proteins, and enzymes in living organisms. Enzymes found within living organisms aid in the reactions, and peptides are structural components of hair, skin, and rhino horns. Other natural polymers include polysaccharides, also known as sugar polymers, and polypeptides, which are found in keratin, silk, and hair. Natural rubber is a natural polymer composed of hydrogen and carbon.
Polymers derived from living organisms like plants and animals. They are found in living things and help to keep metabolic processes running in plants and animals. Natural polymers are used in both kingdoms for bodybuilding and maintenance. They are ubiquitous and can be found anywhere. For example, cellulose, rubber, and so on.
Natural polymers examples
There are numerous examples of natural polymers found in nature. A brief description of a few of them is provided below-
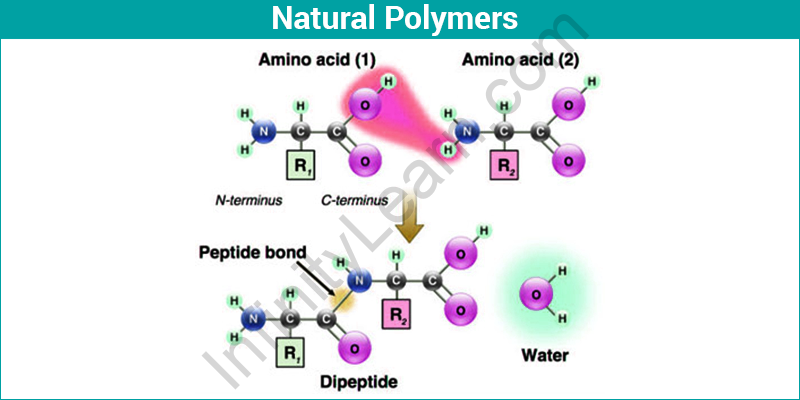
Proteins and Polypeptides- Proteins are the most basic type of natural polymer found in nearly all living organisms. Proteins are said to be the most versatile substances in nature. They can also function as catalysts. Some proteins are referred to as enzymes. These enzymes are in charge of various chemical reactions that occur in our bodies, and they occur a million times faster without these enzymes. Haemoglobin, a type of protein found in our blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the human body.
Carbohydrates are macromolecules that are found in all living organisms. They are made up of monomers known as monosaccharides. Carbohydrate molecules are classified as di, tri, tetra, or polysaccharide-based on the number of monosaccharide units present. Carbohydrates act as fuels and provide a lot of energy.
Proteins, also known as polypeptides, are polypeptides made up of individual amino acids. The macromolecular structure is formed by combining these amino acids with the help of peptide linkages. Enzymes are the most well-known proteins that aid in the catalysis of all biological reactions.
Cellulose– Cellulose is one of the most abundant organic compounds on the planet, and cotton is the purest form of natural cellulose. The main component of paper made from tree wood and the supporting materials in leaves and plants is cellulose. It, too, is a polymer derived from glucose monomers, like amylose.
Names of natural polymers
Natural polymers are polymers found in living systems and are made up of organic or inorganic subunits. These occur naturally and play a role in an organism’s vital functioning. Natural polymers have monosaccharides, amino acids, or nucleotides as subunits. Cellulose and starch, for example, are polysaccharides that are basically polymers of sugars; proteins are polymers of amino acids and other compounds. Natural polymers found in the body perform functions such as providing structural integrity to the cell, transmitting genetic information across generations, serving as a source of energy, and contributing to various metabolic activities of the biological system.
Natural and synthetic polymers
Natural polymers are those that are derived from natural sources. They are primarily derived from plants, animals, and humans. For example, DNA, RNA, glucose, and so on. Natural foods are composed of naturally occurring polymers such as carbohydrates, proteins, and so on. Polymers are also used in the packaging of food, such as plastic containers, packets, one-time use cutlery, and so on. Organic polymers are important in living things because they provide basic structural materials and participate in vital life processes. Polymers, for example, make up the solid parts of all plants. Among these are cellulose, lignin, and various resins. Cellulose is a polysaccharide, which is a polymer made up of sugar molecules. Lignin is made up of a complex three-dimensional network of polymers. Wood resins are polymers of isoprene, a simple hydrocarbon. Rubber is another well-known isoprene polymer .
As a byproduct of certain chemical reactions, synthetic polymers are created in the laboratory. These macromolecules do not exist naturally and must be synthesised. A synthetic polymer is long-chain polyethylene, which is formed by adding ethylene subunits to a growing long chain. Everyday thermolabile plastic is a polymer of vinyl chloride known as polyvinyl chloride. Aside from these two types of polymers, there is a third type of polymer known as semi-synthetic polymers, which are derived from naturally occurring cellulose. The name semi-synthetic polymer comes from the fact that the polymer’s origin is natural but it is ultimately manufactured in a laboratory.
FAQs
What are the most important natural polymer sources?
Natural polymers, as the name implies, are primarily found in natural sources. They are abundant in the bodies of plants and animals. They are not man-made, as opposed to synthetic or semi-synthetic polymers. They are organic molecules that make up the ecosystem's biotic component. Because of their vital functions, they help to sustain natural life on the planet. They are responsible for the cell and organ systems of living beings.
What are some of the important functions of natural polymers in the human body?
The naturally occurring polymers in the human body are carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy production and aid in the production of energy for sustaining life and other activities such as locomotion. Proteins, which exist in the human body as amino acids, are another important organic polymer. Amino acids come in a variety of forms and serve a variety of functions. The most crucial of all is the process of DNA multiplication and replication. Nucleic acids are the primary components of human DNA and RNA, and they determine our genetic make-up.







