Table of Contents
An occupational respiratory disorder can be described as any lung ailment that a person acquires when exposed to certain chemicals, toxins, or dust for a long time. Occupational exposure is the main cause of almost all respiratory disorders. The contribution of the work environment to the development and in enhancing the disease is still not recognized and is certainly under-reported. People are not aware of the severity of the disease. Government, media, and educated individuals should step ahead to make people aware of these diseases, and proper measures should be taken to avoid these disorders before it’s too late.
Definition:
Occupational respiratory disorders are often seen in developed countries as they have more industries producing dust and hazardous gases. Materials that are breathed in the workplace can cause major chronic lung diseases. Because of the difference in the genetic constitution and metabolism, particular occupational agents may cause different host susceptibility. Smoking cigarettes have a different impact on other people. Asthma has become the most common chronic occupational lung disease in developed countries, such as Pneumoconiosis from silica or coal dust. Detecting a workplace-related cause of the occupational disorder is important to prevent and cure it.
A brief outline of the topic:
Work-related lung diseases are lung conditions that are exacerbated by specific work environments. They are caused by long-term inhalation of certain irritants into the lungs. These lung diseases may have long-term consequences, even after exposure.
These lung problems are caused by particles in the air that come from various sources. Among the sources are factories, smokestacks, exhaust, fires, mining, construction, and agriculture. The smaller the particles, the greater the damage to the lungs. Smaller particles can be easily inhaled and penetrate deep into the lungs. Instead of being coughed out, they are absorbed into the body.
Causes Of Occupational respiratory disorder
- Dust: originating from coal, asbestos(asbestosis, lung cancer), silica(silicosis), wood, cotton, talc, pesticides, drug powders, and fiberglass can affect the lungs. Some cereal grains, coffee particles, and food flavorings can also damage the lungs.
- Fumes or smoke: from metals that arise after heating and cooling it repeatedly and quickly, tobacco, burning materials which result in the suspension of fine particles in the air. Workplaces involve welding, smelting, furnace work, pottery making, and plastics manufacturing.
- Spray: from paints, lacquers, pesticides, acids, hair spray, oils, and turpentine.
- BCME (Bis(chloromethyl) ether): It can cause lung disorders like cancer.
- Inorganic Elements: Beryllium, cadmium, chromium.
- Exhaust arising from diesel.
Symptoms of Occupational Respiratory Disorders
When some of the pollutants accumulate in the body beyond their normal concentration or are inhaled for long durations, they start to develop major symptoms, which are:
- Coughing
- Dry, sore, and scratchy throat
- Fever
- Running nose
- Shortness of breath
- Chest Tightness or congestion
- Chest Pain
- Alteration in breathing patterns
- Body ache
- Muscle ache
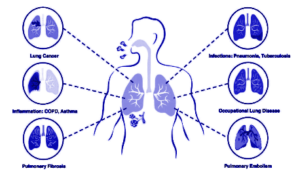
Classification of Occupational respiratory disorders :
There is a complete list of disorders that can be acquired at workplaces. Some of them are quoted below-
-
Occupational Asthma: Occupational asthma can be caused due to a variety of causes, some of which are sensitization to a specific agent, which leads to an allergic reaction. Using latex gloves, workers in Isocyanate synthesizing industries are on the verge of having occupational asthma. Allergic agents stimulate mast cells that release histamines. Histamines are responsible for causing allergic reactions, inflammation, and constriction of respiratory pathways. Asthma is characterized by a ‘Wheezing sound’ and difficulty in breathing.
-
COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease): results in emphysema. Workplaces like mining, construction, and manufacturing industries (rubber, leather, textiles, plastic) have a higher risk of causing COPD. These workplaces have air surrounded by high amounts of silica and coal dust. When workers inhale, they develop symptoms like congestion, suffocation, and difficulty breathing.
-
Lung Cancer: aluminum, beryllium, cadmium, coke, coal gasification, arsenic, asbestos, bis-chloromethyl ether, metals, dust, ionizing radiation, and fibers are the factors that can lead to the proliferation of lung tissues and eventually lung cancer.
-
Mesothelioma: It can be defined as cancer of the mesothelium of the lungs that usually occurs when a person is exposed to asbestos and starts developing symptoms of asbestosis, which on a long-term basis, leads to mesothelioma.
-
Allergic alveolitis or Farmer’s lung: when organic dust is inhaled, it causes inflammation of alveoli in the lungs as the dust particles act as allergic agents.
-
Smoke inhalation: carbon monoxide (CO) and cyanide are the major gaseous constituents of smoke that obstruct respiratory pathways.CO has a higher affinity to bind with hemoglobin than oxygen. As a result, it prevents oxygen from hemoglobin and effectively affects the transport of oxygen into the body. Cyanide affects the activity of ‘cytochrome oxidase, which is responsible for the proper utilization of oxygen.
-
Pneumoconiosis (Coal worker’s Pneumoconiosis, also known as black lung disease): When dust mainly constitutes silica, asbestos, and coal dust and accumulates in the lungs in high amounts, it severely affects respiratory health.
Diagnosis of Occupational Respiratory Disorders
For diagnosing occupational lung disorders, various tests and techniques are applied to analyze the type and severity of the disease based on symptoms arising in the affected individual’s body.
In the initial stages of diagnosis, usually, a chest X-ray or CT Scan is performed, after that further tests that can be performed are-
Biopsy or autopsy of tissue, cells, and fluids from the lungs (microscopic examination technique).
Biochemical and cellular studies of lung fluids
- Measurement of respiratory or gas exchange functions
- Examination of airway or bronchial activity
Pulmonary function tests
The tests are usually performed with special machines into which the person must breathe. Help measure the lungs’ ability to move air in and out of the lungs effectively.
Factors that determine Treatment of Occupational Disorders
The following factors are responsible which deciding the treatment or medication of occupational respiratory disorders-
- Age and overall health.
- Medical history.
- Type and extent of lung disease
- Tolerance for specific medications, therapies, or procedures.
- Expectations for the course of the disease.
Prevention of Occupational Respiratory Disorders
Occupational disorders can be prevented by taking the following measures
- Smoking must be avoided.
- Minimal exposure to Pollutants- indoor as well as outdoor.
- Use protective masks while working in areas having bad air quality.
- Prevent Infection.
- Regular Check-ups.
- Exercise- Running, Brisk walking, Cardio exercises, Meditation, Inhalation, and exhalation exercises.
- Healthy and balanced diet.
- Proper sleep.
- Reduce stress.
Also, read Body Fluids and Circulation.
FAQs
What is occupational respiratory disorder?
An occupational respiratory disorder can be described as any lung ailment that a person acquires when exposed to certain chemicals, toxins, or dust for a long time.
What are the major constituents that cause Occupational disorders?
Silica, Asbestos, Dust, Pollen grains, BCME, Polyaromatic hydrocarbons, Nanoparticles, Beryllium, Chromium, Cadmium, Coal dust, Smoke, etc.
What are the methods of diagnosing occupational disorders?
Biopsy or autopsy, Biochemical and cellular studies of lung fluids, Measurement of respiratory or gas exchange functions, Examination of airway or bronchial activity, etc.
Question: List five occupational respiratory disorders.
Answer:
- Occupational asthma
- Pneumoconiosis
- COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- Mesothelioma
- Lung cancer