Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Lighting a Torch Bulb with 1 Electric Cell
- Summary
- Did You Know?
- What’s Next?
In the last segment, we learned about the electric cell and torch bulb. In this segment, we will learn how a bulb glows with the help of an electric cell.
Lighting a torch bulb with 1 electric cell
For this experiment, we need an electric cell, a light bulb, two insulated copper wires, and electrical tape. All the necessary precautions have to be taken, such as wearing insulated hand gloves and leather footwear.

Copper wires
The insulated part from either end of all the wires is to be removed so that the copper metal is visible. With the help of the electrical tape, one end of the copper wire is attached to one of the terminals of the cell. The other end is joined to the terminal of the bulb using the tape.

Copper wire connecting cell and bulb
Now another copper wire is joined to the other terminal of the cell using electrical tape. When the free end of this wire is joined to the second terminal of the bulb, it glows.
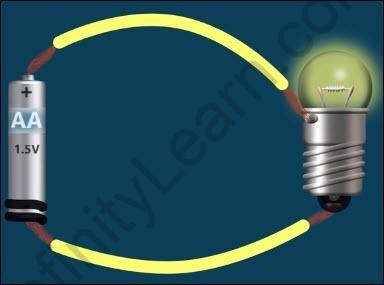
Bulb glows
Why does the bulb glow?
The bulb glows because of the negatively charged particles (electrons) moving through the wire. The electrons move from the negative terminal of the cell to its positive terminal. This movement of electrons is referred to as ‘Electric current.’
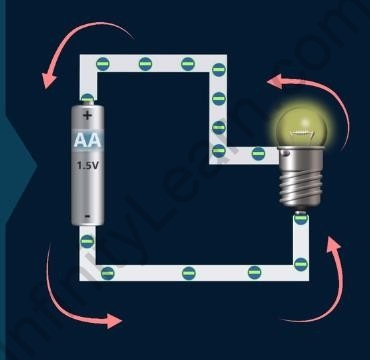
Movement of electrons
However, by convention, the direction of electric current is taken to be from positive to
negative, that is from the cell’s positive terminal to its negative terminal.







