Table of Contents
Before delving into the differences between concave and convex mirrors, it’s essential to start with the basics: understanding what a mirror is.
What is a Mirror?
In the simplest terms, a mirror is an object with a smooth, highly reflective surface. The most common mirrors are designed with a thin layer of aluminum or silver backing a piece of glass, providing the reflective property. Mirrors, whether concave or convex, play an essential role in our daily lives, from personal grooming to safety on roads.
Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirror
When discussing mirrors in optics, it’s important to understand the distinctions between two main types: plane mirrors and spherical mirrors. Each type has unique characteristics and applications based on its shape and the way it reflects light.
Plane Mirrors
A plane mirror is the most common type of mirror that we encounter in daily life. It has a flat reflective surface. The reflections produced by plane mirrors are characterized by a few key properties:
- Image Characteristics: The image formed by a plane mirror is always virtual, upright, and of the same size as the object. The image also appears to be the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
- Applications: Plane mirrors are widely used in households for personal grooming, in art for creating symmetrical designs, and in optical instruments like periscopes.
- No Distortion: Because the reflective surface is flat, there’s no distortion of the image. The image is a mirror image, with left and right reversed.
Spherical Mirrors
Spherical mirrors, on the other hand, have curved reflective surfaces. They are parts of a sphere and come in two main types: concave and convex mirrors.
- Concave Mirrors: These mirrors have a reflective surface that curves inward. They can produce real images, which can be projected onto a screen, or virtual images, depending on the object’s distance from the mirror. Concave mirrors are used when magnification is needed, such as in telescopes, vehicle headlights, and shaving mirrors.
- Convex Mirrors: Convex mirrors have a reflective surface that curves outward. They always form a virtual, diminished, and upright image. Because they offer a wider field of view, they are commonly used in vehicle rear-view mirrors and security systems.
In the world of optics, mirrors play a fascinating role in reflecting light and forming images. While they appear simple, there’s more to them than meets the eye. Understanding the difference between concave and convex mirrors is crucial for comprehending how they work and their diverse applications.
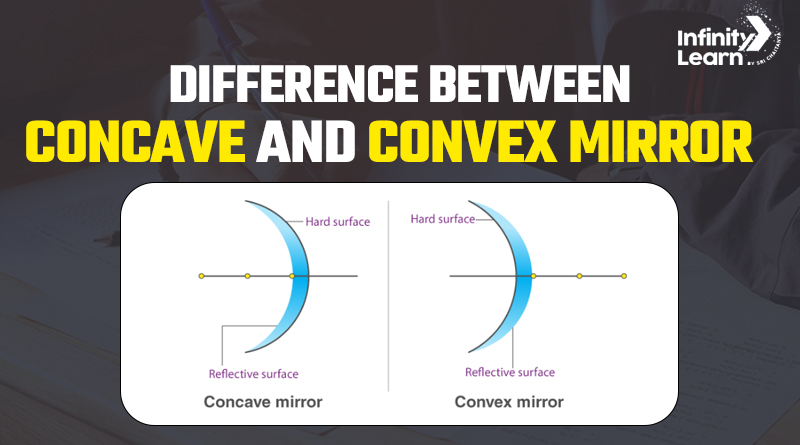
What is a Concave Mirror?
A concave mirror, also known as a converging mirror, is a curved mirror that bulges inwards like the inside of a spoon. It resembles the shape of a sphere cut in half, with the reflecting surface being the inner curve. This inward curvature is the key characteristic that sets it apart from other types of mirrors.
Uses of Concave Mirrors
Concave mirrors have a wide range of applications due to their unique property of converging light rays. Here are some prominent examples:
- Telescopes: Reflecting telescopes utilize large concave mirrors to gather and focus light from distant objects, allowing us to observe celestial bodies in detail.
- Microscopy: Concave mirrors are often employed in microscopes to magnify small objects by converging light rays onto them, making their structures visible.
- Shaving mirrors: The magnified reflection provided by a concave mirror can be helpful for shaving and applying makeup.
- Dental mirrors: Dentists use small concave mirrors to examine teeth and perform intricate procedures in the oral cavity.
- Solar concentrators: Large concave mirrors can be used to concentrate solar energy for various purposes, including generating electricity and heating water.
Characteristics of Concave Mirrors
- Converging nature: Concave mirrors converge parallel light rays to a single point called the focal point.
- Image formation: Depending on the object’s position, concave mirrors can form real, inverted, and enlarged images; real, inverted, and smaller images; or virtual and erect images.
- Focal length: The distance between the mirror’s center and the focal point is known as the focal length.
- Multiple uses: The versatility of concave mirrors makes them invaluable in various scientific, medical, and technological fields.
| Check all the Physics Difference Between Articles | |
| Difference Between Mass and Weight | Difference Between Speed and Velocity |
| Difference Between AC And DC | Difference Between Distance and Displacement |
| Difference Between Real and Virtual Images | |
What is a Convex Mirror?
In contrast to a concave mirror, a convex mirror, also known as a diverging mirror, bulges outwards like the back of a spoon. Imagine a sphere cut in half, with the reflecting surface being the outer curve. This outward curvature defines its distinct nature and functionality.
Uses of Convex Mirrors
Convex mirrors offer a wider field of view compared to flat mirrors, making them beneficial for various applications:
- Rearview mirrors: Convex mirrors are used in vehicles as rearview mirrors to provide a wider field of view behind the driver, enhancing safety and visibility.
- Security mirrors: Convex mirrors are used in shops and stores to provide a broader view of the surrounding area, aiding in security and surveillance.
- Blind spot mirrors: These small convex mirrors are attached to the side mirrors of vehicles to eliminate blind spots, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Traffic junctions: Convex mirrors placed at junctions with limited visibility help drivers navigate safely by providing a wider view of oncoming traffic.
- Decorative purposes: Convex mirrors can be used as decorative elements in architecture and interior design to create a sense of depth and spaciousness.
Characteristics of Convex Mirrors
- Diverging nature: Convex mirrors diverge parallel light rays away from a single point.
- Image formation: Convex mirrors always produce virtual, upright, and diminished images of the object.
- Field of view: They offer a wider field of view compared to flat mirrors, making them ideal for surveillance and observation purposes.
- Safety applications: Their ability to provide a broader perspective enhances safety in various contexts, such as driving and security.
What is concave and convex mirror? While concave mirrors have a reflective surface that curves inward, convex mirrors have a surface that bulges outward. Each type has distinct characteristics and uses.
Difference between Concave and Convex Mirror
Here’s a detailed comparison of concave and convex mirrors:
| Feature | Concave Mirror | Convex Mirror |
| Definition | A mirror with a reflective surface that curves inward, resembling the interior of a sphere. | A mirror with a reflective surface that curves outward, similar to the exterior of a sphere. |
| Shape | Curves inward like the inside of a spoon. | Bulges outward like the back of a spoon. |
| Type of Mirror | Converging mirror. | Diverging mirror. |
| Image Formation | Can form real or virtual images; the nature varies with the object’s distance from the mirror. | Always forms virtual, erect, and diminished images regardless of the object’s position. |
| Focal Point | Converges parallel light rays to a single focal point in front of the mirror. | Diverges light rays such that they appear to be coming from a focal point behind the mirror. |
| Applications | – Telescopes and microscopes for magnification.
– Shaving and makeup mirrors for enlarged views. – Dental mirrors for oral examinations. – Solar concentrators for energy focus. – Vehicle headlights for focused illumination. |
– Rearview mirrors in vehicles for a wider field of view.
– Security mirrors in stores and public places. – Blind spot mirrors for vehicles. <br>- Traffic mirrors at junctions for broader visibility. – Decorative purposes in architecture and interior design. |
| Characteristics | – Forms both real and virtual images.
– Real images can be larger or smaller than the object. – Virtual images are erect and larger. |
– Only forms virtual images.
– Images are always erect and smaller than the object. |
| Use in Safety | Limited use in safety due to the specific focus and magnification properties. | Widely used for safety due to the broad field of view, especially in vehicles and public spaces. |
FAQs on Difference Between Concave and Convex Mirror
What is the difference between concave, convex, and plane mirrors?
Concave mirror: Bulges inwards, converges light rays, forms real or virtual images depending on object position. Convex mirror: Bulges outwards, diverges light rays, always forms virtual and erect images. Plane mirror: Flat surface, reflects light rays at the same angle, forms virtual and upright images the same size as the object.
What are 10 examples of convex mirrors?
Rearview mirrors in cars and motorcycles Security mirrors in shops and stores Blind spot mirrors on vehicles Traffic junction mirrors Decorative mirrors in homes and interiors Spoons and other curved reflective surfaces Curved glass windows in some buildings Dental mirrors used for oral examinations Astronomical telescopes (secondary mirror) Makeup mirrors for wide-angle viewing
What are the uses of concave and convex mirrors?
Concave mirrors: Telescopes, microscopes, shaving mirrors, dental mirrors, solar concentrators, searchlights, projectors. Convex mirrors: Rearview mirrors, security mirrors, blind spot mirrors, traffic junction mirrors, decorative purposes, widening field of view in tight spaces, automobile headlights.









